Abstract
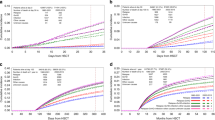
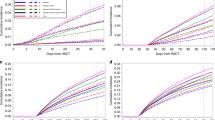
Infectious complications remain a major problem contributing to significant mortality after hematopoietic allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Few studies have previously analyzed mortality due to late infections. Forty-four patients dying from an infectious complication were identified from a cohort of 688 consecutive patients surviving more than 6 months without relapse. A control group of 162 patients was selected using the year of HSCT as the matching criterion. Out of 44 patients, 30 (68%) died from pneumonia, 7/44 (16%) from sepsis, 5/44 (11%) from central nervous system infection and 2/44 (4.5%) from disseminated varicella. The cumulative incidences of different types of infection were 1.6% for viral, 1.5% for bacterial and 1.3% for fungal infections and 0.15% for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. The majority (66%) of the lethal infections occurred within 18 months after HSCT. Acute GVHD (relative risk (RR): 7.19, P<0.0001), chronic GVHD (RR: 6.49, P<0.001), CMV infection (RR: 4.69, P=0.001), mismatched or unrelated donor (RR: 3.86, P=0.004) and TBI (RR: 2.65, P=0.047) were independent risk factors of dying from a late infection. In conclusion, infections occurring later than 6 months after HSCT are important contributors to late non-relapse mortality after HSCT. CMV infection or acute GVHD markedly increase the risk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Frassoni F, Rocha V, Niederwieser D, Reusser P et al. Cause of death after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in early leukaemias: an EBMT analysis of lethal infectious complications and changes over calendar time. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 757–769.
Socie G, Stone JV, Wingard JR, Weisdorf D, Henslee-Downey PJ, Bredeson C et al. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Late Effects Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 14–21.
Junghanss C, Marr KA . Infectious risks and outcomes after stem cell transplantation: are nonmyeloablative transplants changing the picture? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2002; 15: 347–353.
Thomas ED . Bone marrow transplantation: a review. Semin Hematol 1999; 36 (Suppl 7): 95–103.
Leather HL, Wingard JR . Infections following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2001; 15: 483–520.
Engels EA, Ellis CA, Supran SE, Schmid CH, Barza M, Schenkein DP et al. Early infection in bone marrow transplantation: quantitative study of clinical factors that affect risk. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 256–266.
Ringden O, Ruutu T, Remberger M, Nikoskelainen J, Volin L, Vindelov L et al. A randomized trial comparing busulfan with total body irradiation as conditioning in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with leukemia: a report from the Nordic Bone Marrow Transplantation Group. Blood 1994; 83: 2723–2730.
Le Blanc K, Remberger M, Uzunel M, Mattsson J, Barkholt L, Ringden O . A comparison of nonmyeloablative and reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2004; 78: 1014–1020.
Svenberg P, Remberger M, Svennilson J, Mattsson J, Leblanc K, Gustafsson B et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for nonmalignant disorders using matched unrelated donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 877–882.
Ringden O, Backman L, Lonnqvist B, Heimdahl A, Lindholm A, Bolme P et al. A randomized trial comparing use of cyclosporin and methotrexate for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in bone marrow transplant recipients with haematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 1986; 1: 41–51.
Ringden O, Pihlstedt P, Markling L, Aschan J, Baryd I, Ljungman P et al. Prevention of graft-versus-host disease with T cell depletion or cyclosporin and methotrexate. A randomized trial in adult leukemic marrow recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 1991; 7: 221–226.
Thomas E, Storb R, Clift RA, Fefer A, Johnson FL, Neiman PE et al. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975; 292: 832–843.
Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA, Fefer A, Johnson L, Neiman PE et al. Bone-marrow transplantation (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975; 292: 895–902.
Remberger M, Kumlien G, Aschan J, Barkholt L, Hentschke P, Ljungman P et al. Risk factors for moderate-to-severe chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 674–682.
Sullivan KM, Witherspoon RP, Storb R, Weiden P, Flournoy N, Dahlberg S . Prednisone and azathioprine compared with prednisone and placebo for treatment of chronic graft-v-host disease: prognostic influence of prolonged thrombocytopenia after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Blood 1988; 72: 546–554.
Hymes SR, Morison WL, Farmer ER, Walters LL, Tutschka PJ, Santos GW . Methoxsalen and ultraviolet A radiation in treatment of chronic cutaneous graft-versus-host reaction. J Am Acad Dermatol 1985; 12 (Part 1): 30–37.
Vogelsang GB, Farmer ER, Hess AD, Altamonte V, Beschorner WE, Jabs DA et al. Thalidomide for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med 1992; 326: 1055–1058.
Besnier DP, Chabannes D, Mahe B, Mussini JM, Baranger TA, Muller JY et al. Treatment of graft-versus-host disease by extracorporeal photochemotherapy: a pilot study. Transplantation 1997; 64: 49–54.
Ljungman P, Cordonnier C, de Bock R, Einsele H, Engelhard D, Grundy J et al. Immunisations after bone marrow transplantation: results of a European survey and recommendations from the infectious diseases working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 455–460.
Ljungman P, Aschan J, Lewensohn-Fuchs I, Carlens S, Larsson K, Lonnqvist B et al. Results of different strategies for reducing cytomegalovirus-associated mortality in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Transplantation 1998; 66: 1330–1334.
Ehrnst A, Barkholt L, Brattstrom C, Czajkowski J, Teodosiu O, Tollemar J et al. Detection of CMV-matrix pp65 antigen in leucocytes by immunofluorescence as a marker of CMV disease. J Med Virol 1993; 39: 118–124.
Ehrnst A, Barkholt L, Lewensohn-Fuchs I, Ljungman P, Teodosiu O, Staland A et al. CMV PCR monitoring in leucocytes of transplant patients. Clin Diagn Virol 1995; 3: 139–153.
Yun Z, Lewensohn-Fuchs I, Ljungman P, Ringholm L, Jonsson J, Albert J . A real-time TaqMan PCR for routine quantitation of cytomegalovirus DNA in crude leukocyte lysates from stem cell transplant patients. J Virol Methods 2003; 110: 73–79.
Ljungman P, Lore K, Aschan J, Klaesson S, Lewensohn-Fuchs I, Lonnqvist B et al. Use of a semi-quantitative PCR for cytomegalovirus DNA as a basis for pre-emptive antiviral therapy in allogeneic bone marrow transplant patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 583–587.
Reusser P, Einsele H, Lee J, Volin L, Rovira M, Engelhard D et al. Randomized multicenter trial of foscarnet versus ganciclovir for preemptive therapy of cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2002; 99: 1159–1164.
Ljungman P, Griffiths P, Paya C . Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 1094–1097.
Aschan J, Ringden O, Ljungman P, Lonnqvist B, Ohlman S . Foscarnet for treatment of cytomegalovirus infections in bone marrow transplant recipients. Scand J Infect Dis 1992; 24: 143–150.
Ljungman P, Engelhard D, Link H, Biron P, Brandt L, Brunet S et al. Treatment of interstitial pneumonitis due to cytomegalovirus with ganciclovir and intravenous immune globulin: experience of European Bone Marrow Transplant Group. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 14: 831–835.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A proportional hazards model for subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Williamson EC, Millar MR, Steward CG, Cornish JM, Foot AB, Oakhill A et al. Infections in adults undergoing unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 1999; 104: 560–568.
Maury S, Mary JY, Rabian C, Schwarzinger M, Toubert A, Scieux C et al. Prolonged immune deficiency following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: risk factors and complications in adult patients. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: 630–641.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L . Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002; 100: 4358–4366.
Grow WB, Moreb JS, Roque D, Manion K, Leather H, Reddy V et al. Late onset of invasive aspergillus infection in bone marrow transplant patients at a university hospital. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 15–19.
Boeckh M, Leisenring W, Riddell SR, Bowden RA, Huang ML, Myerson D et al. Late cytomegalovirus disease and mortality in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants: importance of viral load and T-cell immunity. Blood 2003; 101: 407–414.
Abrahamsen IW, Somme S, Heldal D, Egeland T, Kvale D, Tjonnfjord GE . Immune reconstitution after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: the impact of stem cell source and graft-versus-host disease. Haematologica 2005; 90: 86–93.
Socie G, Salooja N, Cohen A, Rovelli A, Carreras E, Locasciulli A et al. Nonmalignant late effects after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 101: 3373–3385.
Kalhs P, Panzer S, Kletter K, Minar E, Stain-Kos M, Walter R et al. Functional asplenia after bone marrow transplantation. A late complication related to extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease. Ann Intern Med 1988; 109: 461–464.
Ringden O, Paulin T, Lonnqvist B, Nilsson B . An analysis of factors predisposing to chronic graft-versus-host disease. Exp Hematol 1985; 13: 1062–1067.
Atkinson K, Horowitz MM, Gale RP, van Bekkum DW, Gluckman E, Good RA et al. Risk factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1990; 75: 2459–2464.
Carlens S, Ringden O, Remberger M, Lonnqvist B, Hagglund H, Klaesson S et al. Risk factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective single centre analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 755–761.
Claman HN . Corticosteroids and lymphoid cells. N Engl J Med 1972; 287: 388–397.
Small TN, Papadopoulos EB, Boulad F, Black P, Castro-Malaspina H, Childs BH et al. Comparison of immune reconstitution after unrelated and related T-cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation: effect of patient age and donor leukocyte infusions. Blood 1999; 93: 467–480.
Lehner PJ, Wilkinson GW . Cytomegalovirus: from evasion to suppression? Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 993–994.
Boeckh M, Nichols WG . Immunosuppressive effects of beta-herpesviruses. Herpes 2003; 10: 12–16.
Laursen AL, Mogensen SC, Andersen HM, Andersen PL, Ellermann-Eriksen S . The impact of CMV on the respiratory burst of macrophages in response to Pneumocystis carinii. Clin Exp Immunol 2001; 123: 239–246.
Kutza AS, Muhl E, Hackstein H, Kirchner H, Bein G . High incidence of active cytomegalovirus infection among septic patients. Clin Infect Dis 1998; 26: 1076–1082.
Tait RC, Burnett AK, Robertson AG, McNee S, Riyami BM, Carter R et al. Subclinical pulmonary function defects following autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: relationship to total body irradiation and graft-versus-host disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1991; 20: 1219–1227.
Kulkarni S, Powles R, Treleaven J, Riley U, Singhal S, Horton C et al. Chronic graft versus host disease is associated with long-term risk for pneumococcal infections in recipients of bone marrow transplants. Blood 2000; 95: 3683–3686.
Knecht H, Jost R, Gmur J, Burger J, Fehr J . Functional hyposplenia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is detected by epinephrine stimulation test and splenic ultrasonography. Eur J Haematol 1988; 41: 382–387.
Maris MB, Niederwieser D, Sandmaier BM, Storer B, Stuart M, Maloney D et al. HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2003; 102: 2021–2030.
Ljungman P, Engelhard D, de la Camara R, Einsele H, Locasciulli A, Martino R et al. Vaccination of stem cell transplant recipients: recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 737–746.
Stem Cell Trialists' Group. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem-cell compared with bone marrow transplantation in the management of hematologic malignancies: an individual patient data meta-analysis of nine randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 5074–5087.
Anderson D, DeFor T, Burns L, McGlave P, Miller J, Wagner J et al. A comparison of related donor peripheral blood and bone marrow transplants: importance of late-onset chronic graft-versus-host disease and infections. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2003; 9: 52–59.
Boeckh M, Kim HW, Flowers ME, Meyers JD, Bowden RA . Long-term acyclovir for prevention of varicella zoster virus disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation—a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Blood 2006; 107: 1800–1805.
Miller W, Flynn P, McCullough J, Balfour Jr HH, Goldman A, Haake R et al. Cytomegalovirus infection after bone marrow transplantation: an association with acute graft-v-host disease. Blood 1986; 67: 1162–1167.
Ljungman P, Perez-Bercoff L, Jonsson J, Avetisyan G, Sparrelid E, Aschan J et al. Risk factors for the development of cytomegalovirus disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2006; 91: 78–83.
Lonnqvist B, Ringden O, Wahren B, Gahrton G, Lundgren G . Cytomegalovirus infection associated with and preceding chronic graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 1984; 38: 465–468.
Soderberg C, Larsson S, Rozell BL, Sumitran-Karuppan S, Ljungman P, Moller E . Cytomegalovirus-induced CD13-specific autoimmunity—a possible cause of chronic graft-vs-host disease. Transplantation 1996; 61: 600–609.
CDC. Guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Recommendations of CDC, the Infectious Disease Society of America, and the American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2000; 49 (RR-10): 1–125.
Hammarström V, Pauksen K, Azinge J, Öberg G, Ljungman P . The influence of graft versus host reaction on the response to pneumococcal vaccination in bone marrow transplant patients. J Supportive Care Cancer 1993; 1: 195–199.
Pauksen K, Linde A, Hammarstrom V, Sjolin J, Carneskog J, Jonsson G et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as immunomodulating factor together with influenza vaccination in stem cell transplant patients. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 30: 342–348.
Ljungman P, Wilczek H, Gahrton G, Gustavsson A, Lundgren G, Lonnqvist B et al. Long-term acyclovir prophylaxis in bone marrow transplant recipients and lymphocyte proliferation responses to herpes virus antigens in vitro. Bone Marrow Transplant 1986; 1: 185–192.
Ullmann AJ, Lipton JH, Vesole DH, Chandrasekar P, Langston A, Tarantolo SR et al. Posaconazole or fluconazole for prophylaxis in severe graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 335–347.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from The Stockholm Cancer Fund and from The Cancer and Traffic Injury Fund, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjorklund, A., Aschan, J., Labopin, M. et al. Risk factors for fatal infectious complications developing late after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 40, 1055–1062 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705856
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705856
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CMV Infection Post Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in a Resource Limited Country
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2024)
-
Patterns of infection and infectious-related mortality in patients receiving post-transplant high dose cyclophosphamide as graft-versus-host-disease prophylaxis: impact of HLA donor matching
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
The incidence, mortality and timing of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia after hematopoietic cell transplantation: a CIBMTR analysis
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
Pulmonary complications in hematopoietic SCT: a prospective study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)