Summary:
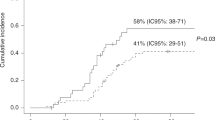
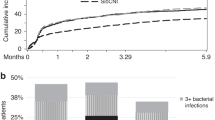
A total of 85 allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients with invasive aspergillosis treated with amphotericin B lipid complex (ABLC) were identified from the Collaborative Exchange of Antifungal Research (CLEAR) database. Of these patients, 78% (66/85) presented with pulmonary aspergillosis. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was present in 24 of 85 patients. The response rate to ABLC was 31% (26/85) overall and 21% (5/24) in patients with GVHD. The overall response rate to first-line ABLC treatment was 41% (11/27). Four of nine (44%) patients with GVHD responded to first-line treatment with ABLC, while only one of 13 (8%) responded to ABLC as second-line therapy. Five of 18 (28%) and four of 14 (29%) patients, respectively, responded to sequential or concurrent treatment with ABLC and itraconazole. None of seven patients responded who continued receiving itraconazole after the start of ABLC therapy. At the end of ABLC therapy, serum creatinine had doubled in 12% of patients (10/85), and 2% (2/85) had developed a requirement for dialysis. These data suggest that ABLC, especially when administered as first-line therapy, can result in clinical response even in the most immunocompromised patients, that is, HCT recipients with GVHD, with minimal effects on renal function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baddley JW, Stroud TP, Salzman D, Pappas PG . Invasive mold infections in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 1319–1324.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Crippa F et al. Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 909–917.
Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM . Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 358–366.
Wald A, Leisenring W, van Burik JA, Bowden RA . Epidemiology of Aspergillus infections in a large cohort of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Infect Dis 1997; 175: 1459–1466.
Gallis HA, Drew RH, Pickard WW . Amphotericin B: 30 years of clinical experience. Rev Infect Dis 1990; 12: 308–329.
Wingard JR, Kubilis P, Lee L et al. Clinical significance of nephrotoxicity in patients treated with amphotericin B for suspected or proven aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29: 1402–1407.
Harbarth S, Pestotnik SL, Lloyd JF et al. The epidemiology of nephrotoxicity associated with conventional amphotericin B therapy. Am J Med 2001; 111: 528–534.
Bates DW, Su L, Yu DT et al. Mortality and costs of acute renal failure associated with amphotericin B therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 686–693.
Gubbins PO, Penzak SR, Polston S et al. Characterizing and predicting amphotericin B-associated nephrotoxicity in bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell transplant recipients. Pharmacotherapy 2002; 22: 961–971.
Zager RA, O'Quigley J, Zager BK et al. Acute renal failure following bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective study of 272 patients. Am J Kidney Dis 1989; 13: 210–216.
Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 408–415.
Pappas PG . Amphotericin B lipid complex in the treatment of invasive fungal infections: results of the Collaborative Exchange of Antifungal Research (CLEAR), an industry-supported patient registry. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40 (Suppl. 6): S379–S383.
Alexander BD, Wingard JR . Study of renal safety in amphotericin B lipid complex-treated patients. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40 (Suppl 6): S414–S421.
Hooshmand-Rad R, Reed MD, Chu A et al. Retrospective study of the renal effects of Amphotericin B Lipid Complex when used at higher than recommended dosages and longer durations compared with lower dosages and shorter durations in patients with systemic fungal infections. Clin Ther 2004; 26: 1652–1662.
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH . Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976; 16: 31–41.
Bowden R, Chandrasekar P, White MH et al. A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion versus amphotericin B for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 35: 359–366.
Maertens J, Raad I, Petrikkos G et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 1563–1571.
Wingard JR . Efficacy of amphotericin B lipid complex injection (ABLC) in bone marrow transplant recipients with life-threatening systemic mycoses. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 343–347.
Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 7–14.
Wong-Beringer A, Jacobs RA, Guglielmo BJ . Lipid formulations of amphotericin B: clinical efficacy and toxicities. Clin Infect Dis 1998; 27: 603–618.
Luke RG, Boyle JA . Renal effects of amphotericin B lipid complex. Am J Kidney Dis 1998; 31: 780–785.
Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE . Toward more effective antifungal therapy: the prospects of combination therapy. Br J Haematol 2004; 126: 165–175.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gigi Xiang and Sherry Yu for expert statistical analysis support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, J., Chandrasekar, P. & Hooshmand-Rad, R. Effectiveness of amphotericin B lipid complex (ABLC) treatment in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients with invasive aspergillosis (IA). Bone Marrow Transplant 36, 873–877 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705143
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705143
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Real-Life Challenges to the Use of Antifungal Agents in Hematology Patients
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2017)
-
Treatment of invasive fungal infections in cancer patients—updated recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO)
Annals of Hematology (2014)
-
Caspofungin Use in Daily Clinical Practice for Treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis: Results of a Prospective Observational Registry
BMC Infectious Diseases (2010)
-
Aspergillosis in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: Risk factors, prophylaxis, and treatment
Current Infectious Disease Reports (2009)
-
Treatment of invasive fungal infections in cancer patients—Recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO)
Annals of Hematology (2009)