Summary:
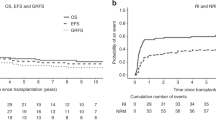
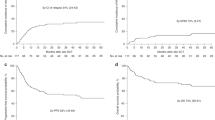
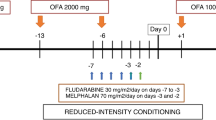
The possible advantage of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is a graft-versus-lymphoma effect. We explored the feasibility and efficacy of allo-HSCT with reduced-intensity (RI) regimens in advanced malignant lymphoma (ML). A total of 20 patients with indolent (n=9) or aggressive lymphoma (n=11) received allo-HSCT with an RI regimen (RIST). The preparative regimen consisted of a combination of purine analog and alkylating agent with or without antithymocyte globulin. A total of 11 patients had chemorefractory disease, seven had chemosensitive relapsed disease and two had residual disease. All of the patients received G-CSF-mobilized blood stem cells from HLA-matched siblings. Of the 20 patients, 19 achieved engraftment with acceptable regimen-related toxicities. Seven patients developed grade II–IV acute GVHD and 15 developed chronic GVHD. Of the 15 patients with evaluable disease, 12 achieved a complete response. One died of invasive fusariosis, four subsequently died of GVHD complicated with fungal infection and one died of progressive disease. With a median follow-up of 358 days, the Kaplan–Meier estimates for 1-year overall and progression-free survival were both 70%. The high response rate with low relapse observed in this study suggests that RIST may be an effective alternative curative treatment for patients with advanced ML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Besien KW, de Lima M, Giralt SA et al. Management of lymphoma recurrence after allogeneic transplantation: the relevance of graft-versus-lymphoma effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 977–982.
Verdonck LF, Dekker AW, Lokhorst HM et al. Allogeneic versus autologous bone marrow transplantation for refractory and recurrent low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood 1997; 90: 4201–4205.
van Besien K, Sobocinski KA, Rowlings PA et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for low-grade lymphoma. Blood 1998; 92: 1832–1836.
Khouri IF, Lee MS, Romaguera J et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation for mantle-cell lymphoma: molecular remissions and evidence of graft-versus-malignancy. Ann Oncol 1999; 10: 1293–1299.
Ratanatharathorn V, Uberti J, Karanes C et al. Prospective comparative trial of autologous versus allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood 1994; 84: 1050–1055.
Jones RJ, Ambinder RF, Piantadosi S, Santos GW . Evidence of a graft-versus-lymphoma effect associated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1991; 77: 649–653.
Chopra R, Goldstone AH, Pearce R et al. Autologous versus allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a case-controlled analysis of the European Bone Marrow Transplant Group Registry data. J Clin Oncol 1992; 10: 1690–1695.
Verdonck LF . Allogeneic versus autologous bone marrow transplantation for refractory and recurrent low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: updated results of the Utrecht experience. Leuk Lymphoma 1999; 34: 129–136.
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik Y et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
Khouri IF, Keating M, Korbling M et al. Transplant-lite: induction of graft-versus-malignancy using fludarabine-based nonablative chemotherapy and allogeneic blood progenitor-cell transplantation as treatment for lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2817–2824.
Sykes M, Preffer F, McAfee S et al. Mixed lymphohaemopoietic chimerism and graft-versus-lymphoma effects after non-myeloablative therapy and HLA-mismatched bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet 1999; 353: 1755–1759.
McSweeney PA, Niederwieser D, Shizuru JA et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with hematologic malignancies: replacing high-dose cytotoxic therapy with graft-versus-tumor effects. Blood 2001; 97: 3390–3400.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 631–637.
Nagler A, Slavin S, Varadi G et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation using a fludarabine-based low intensity conditioning regimen for malignant lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 1021–1028.
Khouri IF, Saliba RM, Giralt SA et al. Nonablative allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation as adoptive immunotherapy for indolent lymphoma: low incidence of toxicity, acute graft-versus-host disease, and treatment-related mortality. Blood 2001; 98: 3595–3599.
Saito T, Kanda Y, Kami M et al. Therapeutic potential of a reduced-intensity preparative regimen for allogeneic transplantation with cladribine, busulfan, and antithymocyte globulin against advanced/refractory acute leukemia/lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 1014–1020.
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IRAC Press: Lyons, 2001.
Bornhauser M, Thiede C, Schuler U et al. Dose-reduced conditioning for allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: durable engraftment without antithymocyte globulin. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 119–125.
Kanda Y, Mineishi S, Saito T et al. Long-term low-dose acyclovir against varicella-zoster virus reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 689–692.
Kanda Y, Mineishi S, Saito T et al. Pre-emptive therapy against cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease guided by CMV antigenemia assay after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single-center experience in Japan. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 437–444.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol 1991; 28: 250–259.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1244.
Dhedin N, Giraudier S, Gaulard P et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (excluding Burkitt and lymphoblastic lymphoma): a series of 73 patients from the SFGM database. Societ Francaise de Greffe de Moelle. Br J Haematol 1999; 107: 154–161.
Tsai T, Goodman S, Saez R et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in patients who relapse after autologous transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 859–863.
van Besien KW, Mehra RC, Giralt SA et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for poor-prognosis lymphoma: response, toxicity and survival depend on disease histology. Am J Med 1996; 100: 299–307.
Mossad SB, Avery RK, Longworth DL et al. Infectious complications within the first year after nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 491–495.
Nakai K, Kanda Y, Mineishi S et al. Suspected delayed immune recovery against cytomegalovirus after reduced-intensity stem cell transplantation using antithymocyte globulin. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 237–241.
Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, Storb R et al. Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as treatment of acute and chronic leukemia. Blood 1989; 73: 1720–1728.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Stem Cell Transplant Unit nursing staff for providing excellent patient care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanimoto, T., Kusumi, E., Hamaki, T. et al. High complete response rate after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in advanced malignant lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 32, 131–137 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704118
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704118
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advanced-Stage III/IV Follicular Lymphoma
Strahlentherapie und Onkologie (2010)
-
Reduced-intensity allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplantation induces durable responses in patients with chronic B-lymphoproliferative disorders
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2006)
-
The graft-versus-lymphoma effect: clinical review and future opportunities
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2005)