Abstract
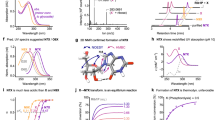
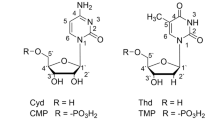
THOUGH the manner in which the four nucleotides of ribonucleic acid are combined in the intact molecule is not completely settled, the data obtained from analyses of the chemical degradation products are most compatible with phosphoryl-group attachments through the C2 and C3 positions of the ribose group1. The exclusion of C5 phosphoryl linkages rests principally upon the failure to isolate 5′ nucleotides or the acid-stable ribose-5-phosphate from acid hydrolysates of ribonucleic acid. However, Gulland and Jackson2, hydrolysing yeast ribonucleic acid with a snake venom containing a phosphodiesterase and a specific 5′ nucleotidase, found 35 per cent of the total phosphate liberated as inorganic phosphate, suggesting that a large number of the phosphoryl groups were attached to the ribose C5 position. Recently, Schmidt3, utilizing periodate titrations of ribonuclease-hydrolysed yeast ribonucleic acid, concluded that some nucleotide groups had been linked to positions other than ribose C2 or C3 in the original ribonucleic acid. The experiments described below indicate that intact 5′ nucleotides can be isolated from enzymatically hydrolysed calf liver ribonucleic acid.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levene, P. A., and Bass, L. W., “Nucleic Acids” (Chemical Catalog Co., 1931). Gulland, J. M., J. Chem. Soc., 1722 (1938). Tipson, R. S., “Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry”, 1, 193 (Academic Press, Inc., 1945).
Gulland, J. M., and Jackson, E. M., J. Chem. Soc., 1492 (1938).
Schmidt, G., Cubiles, R., and Thannhauser, S. J. (in the press).
Volkin, E., and Carter, C. E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. (in the press).
Klein, Willibald, Z. physiol. Chem., 218, 164 (1933).
Cohn, W. E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 72, 1471 and 2811 (1950).
Carter, C. E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 72, 1466 (1950).
Kalckar, H. M., J. Biol. Chem., 167, 461 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COHN, W., VOLKIN, E. Nucleoside-5′-Phosphates from Ribonucleic Acid. Nature 167, 483–484 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/167483a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/167483a0
This article is cited by
-
Quantitative profiling of pseudouridylation landscape in the human transcriptome
Nature Chemical Biology (2023)
-
Coordination of RNA modifications in the brain and beyond
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Semi-quantitative detection of pseudouridine modifications and type I/II hypermodifications in human mRNAs using direct long-read sequencing
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Mapping the m1A, m5C, m6A and m7G methylation atlas in zebrafish brain under hypoxic conditions by MeRIP-seq
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Detection of m6A from direct RNA sequencing using a multiple instance learning framework
Nature Methods (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.