Abstract
Objective: To investigate the accuracy of foot-to-foot impedance methodology for the prediction of total body water and whether leg length rather than stature should be used in the prediction of total body water.
Design: Cross-sectional study using volunteers from the community.
Setting: University laboratory.
Subjects: 57 subjects (29 male; 28 female) aged 19–56 y.
Interventions: Total body water was measured using a deuterium oxide dilution technique. Total body water was also predicted using foot-to-foot impedance apparatus (Tanita Inc, Tokyo, Japan, Model TBF 305).
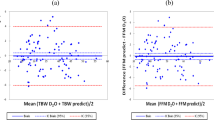
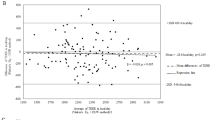
Results: Mean values for predicted and measured total body water differed by 0.7 l. However this bias was not constant across all individuals with a progressive underestimation of total body water by foot-to-foot impedance technology as the water content of the body increases. Also the use of leg length did not improve the accuracy of the prediction equation.
Conclusions: At the population level predictions of total body water obtained from foot-to-foot impedance technology compare well with measured total body water. However the significant correlation between the difference between predicted and measured total body water and the absolute value for total body water is a concern especially if the technology is used for body composition assessment during a weight loss program.
Sponsorship: RJH was in receipt of a Queensland University of Technology Vacation Scholarship.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, N., McClure, P., Hill, R. et al. Assessment of foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysis for the prediction of total body water. Eur J Clin Nutr 52, 856–859 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600661
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600661
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The impact of total body water on breath alcohol calculations
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift (2020)
-
The relationship of high sensitivity C-reactive protein to percent body fat mass, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and waist circumference in a Taiwanese population
BMC Public Health (2010)
-
Validation of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Adolescents Across Different Ethnic Groups
Obesity (2010)
-
A Novel Stable Isotope Approach for Determining the Impact of Thickening Agents on Water Absorption
Dysphagia (2010)
-
Development of height-weight based equation for assessment of body composition in Sri Lankan children
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2010)