Abstract
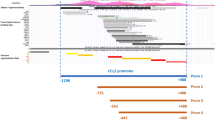
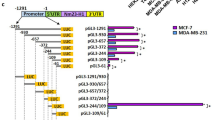
The protooncogene c-met encodes the tyrosine kinase receptor for the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF). While overexpression of c-met is documented in many types of tumors, the mechanism of c-met regulation remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate Daxx as a repressor of c-met transcription. The expression of c-met is elevated in Daxx knockout mouse cells and is reversed by Daxx reconstitution. C-met promoter analysis of Daxx−/− cells reveled changes in chromatin acetylation, but not in DNA methylation. Daxx binds to the mouse c-met promoter and Daxx-binding region is sufficient for transcription repression, while HDAC2 is associated with c-met promoter mostly in Daxx+/+ cells, pointing to Daxx-dependent HDAC2 recruitment as a potential mechanism of c-met repression. HGF-induced cell mobility and invasion confirmed augmented activity of c-Met/HGF pathway in Daxx−/− cells. Finally, inverse correlation between Daxx and c-Met in cancer cell lines and in metastatic breast cancer specimens suggests potential function of Daxx as a c-met repressor during cancer progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baylin SB, Ohm JE . (2006). Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer—a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer 6: 107–116.
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF . (2003). Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 915–925.
Boon EM, van der Neut R, van de Wetering M, Clevers H, Pals ST . (2002). Wnt signaling regulates expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase met in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 62: 5126–5128.
Epstein JA, Shapiro DN, Cheng J, Lam PY, Maas RL . (1996). Pax3 modulates expression of the c-Met receptor during limb muscle development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4213–4218.
Gambarotta G, Boccaccio C, Giordano S, Ando M, Stella MC, Comoglio PM . (1996). Ets up-regulates MET transcription. Oncogene 13: 1911–1917.
Gibbons RJ, McDowell TL, Raman S, O'Rourke DM, Garrick D, Ayyub H et al. (2000). Mutations in ATRX, encoding a SWI/SNF-like protein, cause diverse changes in the pattern of DNA methylation. Nat Genet 24: 368–371.
Hollenbach AD, McPherson CJ, Mientjes EJ, Iyengar R, Grosveld G . (2002). Daxx and histone deacetylase II associate with chromatin through an interaction with core histones and the chromatin-associated protein Dek. J Cell Sci 115: 3319–3330.
Hollenbach AD, Sublett JE, McPherson CJ, Grosveld G . (1999). The Pax3-FKHR oncoprotein is unresponsive to the Pax3-associated repressor hDaxx. EMBO J 18: 3702–3711.
Ishov AM, Vladimirova OV, Maul GG . (2004). Heterochromatin and ND10 are cell-cycle regulated and phosphorylation-dependent alternate nuclear sites of the transcription repressor Daxx and SWI/SNF protein ATRX. J Cell Sci 117: 3807–3820.
Kim EJ, Park JS, Um SJ . (2003). Identification of Daxx interacting with p73, one of the p53 family, and its regulation of p53 activity by competitive interaction with PML. Nucleic Acids Res 31: 5356–5367.
Leroy C, Deheuninck J, Reveneau S, Foveau B, Ji Z, Villenet C et al. (2006). HGF/SF regulates expression of apoptotic genes in MCF-10A human mammary epithelial cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 1090: 188–202.
Li H, Leo C, Zhu J, Wu X, O'Neil J, Park EJ et al. (2000a). Sequestration and inhibition of Daxx-mediated transcriptional repression by PML. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1784–1796.
Li R, Pei H, Watson DK, Papas TS . (2000b). EAP1/Daxx interacts with ETS1 and represses transcriptional activation of ETS1 target genes. Oncogene 19: 745–753.
Lindsay CR, Scholz A, Morozov VM, Ishov AM . (2007). Daxx shortens mitotic arrest caused by paclitaxel. Cell Cycle 6: 1200–1204.
Maulik G, Shrikhande A, Kijima T, Ma PC, Morrison PT, Salgia R . (2002). Role of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13: 41–59.
Michaelson JS, Bader D, Kuo F, Kozak C, Leder P . (1999). Loss of Daxx, a promiscuously interacting protein, results in extensive apoptosis in early mouse development. Genes Dev 13: 1918–1923.
Michaelson JS, Leder P . (2003). RNAi reveals anti-apoptotic and transcriptionally repressive activities of DAXX. J Cell Sci 116: 345–352.
Morotti A, Mila S, Accornero P, Tagliabue E, Ponzetto C . (2002). K252a inhibits the oncogenic properties of Met, the HGF receptor. Oncogene 21: 4885–4893.
Muromoto R, Sugiyama K, Takachi A, Imoto S, Sato N, Yamamoto T et al. (2004). Physical and functional interactions between Daxx and DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein, DMAP1. J Immunol 172: 2985–2993.
Ohiro Y, Usheva A, Kobayashi S, Duffy SL, Nantz R, Gius D et al. (2003). Inhibition of stress-inducible kinase pathways by tumorigenic mutant p53. Mol Cell Biol 23: 322–334.
Olek A, Oswald J, Walter J . (1996). A modified and improved method for bisulphite based cytosine methylation analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 24: 5064–5066.
Pennacchietti S, Michieli P, Galluzzo M, Mazzone M, Giordano S, Comoglio PM . (2003). Hypoxia promotes invasive growth by transcriptional activation of the met protooncogene. Cancer Cell 3: 347–361.
Radaeva S, Jaruga B, Hong F, Kim WH, Fan S, Cai H et al. (2002). Interferon-alpha activates multiple STAT signals and down-regulates c-Met in primary human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 122: 1020–1034.
Rong S, Segal S, Anver M, Resau JH, Vande Woude GF . (1994). Invasiveness and metastasis of NIH 3T3 cells induced by Met-hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor autocrine stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 4731–4735.
Salomoni P, Khelifi AF . (2006). Daxx: death or survival protein? Trends Cell Biol 16: 97–104.
Seol DW, Chen Q, Smith ML, Zarnegar R . (1999). Regulation of the c-met proto-oncogene promoter by p53. J Biol Chem 274: 3565–3572.
Seol DW, Chen Q, Zarnegar R . (2000). Transcriptional activation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-met) gene by its ligand (hepatocyte growth factor) is mediated through AP-1. Oncogene 19: 1132–1137.
Seol DW, Zarnegar R . (1998). Structural and functional characterization of the mouse c-met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) promoter. Biochim Biophys Acta 1395: 252–258.
Shimoda K, Kamesaki K, Numata A, Aoki K, Matsuda T, Oritani K et al. (2002). Cutting edge: tyk2 is required for the induction and nuclear translocation of Daxx which regulates IFN-alpha-induced suppression of B lymphocyte formation. J Immunol 169: 4707–4711.
Takayama H, LaRochelle WJ, Sharp R, Otsuka T, Kriebel P, Anver M et al. (1997). Diverse tumorigenesis associated with aberrant development in mice overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 701–706.
Tang J, Wu S, Liu H, Stratt R, Barak OG, Shiekhattar R et al. (2004). A novel transcription regulatory complex containing death domain-associated protein and the ATR-X syndrome protein. J Biol Chem 279: 20369–20377.
Tzeng SL, Cheng YW, Li CH, Lin YS, Hsu HC, Kang JJ . (2006). Physiological and functional interactions between Tcf4 and Daxx in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281: 15405–15411.
Xue Y, Gibbons R, Yan Z, Yang D, McDowell TL, Sechi S et al. (2003). The ATRX syndrome protein forms a chromatin-remodeling complex with Daxx and localizes in promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 10635–10640.
Zhang X, Liu Y . (2003). Suppression of HGF receptor gene expression by oxidative stress is mediated through the interplay between Sp1 and Egr-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284: F1216–F1225.
Zhang X, Yang J, Li Y, Liu Y . (2005). Both Sp1 and Smad participate in mediating TGF-beta1-induced HGF receptor expression in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F16–F26.
Zhao LY, Colosimo AL, Liu Y, Wan Y, Liao D . (2003). Adenovirus E1B 55-kilodalton oncoprotein binds to Daxx and eliminates enhancement of p53-dependent transcription by Daxx. J Virol 77: 11809–11821.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Dr Martha Campbell-Thompson and Tracy Clarke, Molecular Pathology Core, Department of Pathology, Immunology and Laboratory Medicine, UF for help in ICH. This work was supported by FAMRI Clinical Innovation Award 32088, Florida James & Esther King Biomedical Research Program 05NIR-07 and ACS-IRG-01-188-01 for VMM and AMI and by NIH AI 41136 for OVV and GGM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, V., Massoll, N., Vladimirova, O. et al. Regulation of c-met expression by transcription repressor Daxx. Oncogene 27, 2177–2186 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210865
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210865
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A three layered histone epigenetics in breast cancer metastasis
Cell & Bioscience (2020)
-
Daxx inhibits hypoxia-induced lung cancer cell metastasis by suppressing the HIF-1α/HDAC1/Slug axis
Nature Communications (2016)
-
USP7 and Daxx regulate mitosis progression and taxane sensitivity by affecting stability of Aurora-A kinase
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)
-
Regulation of mitosis and taxane response by Daxx and Rassf1
Oncogene (2012)