Abstract
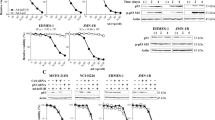
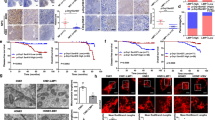
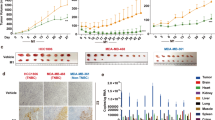
We have previously reported that the downregulation of MMP-2 by adenovirus-mediated delivery of MMP-2 siRNA (Ad-MMP-2) reduced spheroid invasion and angiogenesis in vitro, and, metastasis and tumor growth in vivo. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of Ad-MMP-2-mediated growth inhibition in vitro and in vivo. Ad-MMP-2 infection led to the induction of apoptosis as determined by TUNEL assay, Annexin-V staining and PARP-1 cleavage in a dose-dependent manner in A549 cells. Ad-MMP-2 decreased the content of the antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family proteins (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL) and increased the content of the pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family (Bax and Bcl-xS) as determined by immunoblotting analysis. Furthermore, Ad-MMP-2-mediated apoptosis was accompanied by increase in truncated Bid, release of cytochrome c and the activation of caspase-8, -9 and -3. Immunoblot analysis showed that Ad-MMP-2 infection caused upregulation of Fas/Fas-L and FADD, and Anti-Fas-L antibody reversed Ad-MMP-2-induced apoptosis. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-3, an endogenous inhibitor of MMP-2, which cleaves Fas-L and activates the Fas/Fas-L inducing apoptotic pathway, was increased in Ad-MMP-2-treated cells. Adenovirus-mediated expression of MMP-2 siRNA in human lung xenografts in vivo resulted in increased immunostaining of Fas, Fas-L, cleaved Bid and TIMP-3. This is the first report, to our knowledge, showing that MMP-2 inhibition upregulates TIMP-3 levels, which in turn, promotes apoptosis in lung cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahonen M, la-Aho R, Baker AH, George SJ, Grenman R, Saarialho-Kere U et al. (2002). Antitumor activity and bystander effect of adenovirally delivered tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3. Mol Ther 5: 705–715.
Baker AH, Edwards DR, Murphy G . (2002). Metalloproteinase inhibitors: biological actions and therapeutic opportunities. J Cell Sci 115: 3719–3727.
Baker AH, George SJ, Zaltsman AB, Murphy G, Newby AC . (1999). Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptotic cell death of cancer cell lines by overexpression of TIMP-3. Br J Cancer 79: 1347–1355.
Baker AH, Zaltsman AB, George SJ, Newby AC . (1998). Divergent effects of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, -2 or -3 overexpression on rat vascular smooth muscle cell invasion, proliferation, and death in vitro. TIMP-3 promotes apoptosis. J Clin Invest 101: 1478–1487.
Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WG, Bodden MK, Windsor LJ, Birkedal-Hansen B, DeCarlo A et al. (1993). Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 4: 197–250.
Bond M, Murphy G, Bennett MR, Amour A, Knauper V, Newby AC et al. (2000). Localization of the death domain of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 to the N terminus. Metalloproteinase inhibition is associated with proapoptotic activity. J Biol Chem 275: 41358–41363.
Bond M, Murphy G, Bennett MR, Newby AC, Baker AH . (2002). Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 induces a Fas-associated death domain-dependent type II apoptotic pathway. J Biol Chem 277: 13787–13795.
Bramhall SR, Hallissey MT, Whiting J, Scholefield J, Tierney G, Stuart RC et al. (2002). Marimastat as maintenance therapy for patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomised trial. Br J Cancer 86: 1864–1870.
Brew K, Dinakarpandian D, Nagase H . (2000). Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: evolution, structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1477: 267–283.
Brown PD, Giavazzi R . (1995). Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition: a review of anti-tumour activity. Ann Oncol 6: 967–974.
Cawston TE . (1995). Proteinases and inhibitors. Br Med Bull 51: 385–401.
Chetty C, Bhoopathi P, Joseph P, Chittivelu S, Rao JS, Lakka SS . (2006). Adenovirus-mediated siRNA against MMP-2 suppresses tumor growth and lung metastasis in mice. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 2289–2299.
Chinnaiyan AM, O'Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM. (1995). FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81: 505–512.
Drynda A, Quax PH, Neumann M, van der Laan WH, Pap G, Drynda S et al. (2005). Gene transfer of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 reverses the inhibitory effects of TNF-alpha on Fas-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol 174: 6524–6531.
Evans JD, Stark A, Johnson CD, Daniel F, Carmichael J, Buckels J et al. (2001). A phase II trial of marimastat in advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 85: 1865–1870.
Fata JE, Leco KJ, Voura EB, Yu HY, Waterhouse P, Murphy G et al. (2001). Accelerated apoptosis in the Timp-3-deficient mammary gland. J Clin Invest 108: 831–841.
Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP . (1997). Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol 74: 111–122.
Haro H, Crawford HC, Fingleton B, Shinomiya K, Spengler DM, Matrisian LM . (2000). Matrix metalloproteinase-7-dependent release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a model of herniated disc resorption. J Clin Invest 105: 143–150.
Hengartner MO . (2000). The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407: 770–776.
Kang SH, Choi HH, Kim SG, Jong HS, Kim NK, Kim SJ et al. (2000). Transcriptional inactivation of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 gene by dna hypermethylation of the 5'-CpG island in human gastric cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 86: 632–635.
Khong HT, Restifo NP . (2002). Natural selection of tumor variants in the generation of ‘tumor escape‘ phenotypes. Nat Immunol 3: 999–1005.
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES et al. (1997). Cytochrome-c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91: 479–489.
Li WQ, Zafarullah M. (1998). Oncostatin M up-regulates tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 gene expression in articular chondrocytes via de novo transcription, protein synthesis, and tyrosine kinase- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanisms. J Immunol. 161: 5000–5007.
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X . (1998). Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome-c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94: 481–490.
Medema JP, Toes RE, Scaffidi C, Zheng TS, Flavell RA, Melief CJ et al. (1997). Cleavage of FLICE (caspase-8) by granzyme B during cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 27: 3492–3498.
Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, Anderson KC . (2001). Induction of tumour cell apoptosis by matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: new tricks from a (not so) old drug. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 10: 1075–1084.
Nyormoi O, Mills L, Bar-Eli M . (2003). An MMP-2/MMP-9 inhibitor, 5a, enhances apoptosis induced by ligands of the TNF receptor superfamily in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 10: 558–569.
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ et al. (1998). Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J 17: 1675–1687.
Spurbeck WW, Ng CY, Strom TS, Vanin EF, Davidoff AM . (2002). Enforced expression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-3 affects functional capillary morphogenesis and inhibits tumor growth in a murine tumor model. Blood 100: 3361–3368.
Strand S, Vollmer P, van den AL, Gottfried D, Alla V, Heid H et al. (2004). Cleavage of CD95 by matrix metalloproteinase-7 induces apoptosis resistance in tumour cells. Oncogene 23: 3732–3736.
Tanaka M, Suda T, Takahashi T, Nagata S . (1995). Expression of the functional soluble form of human fas ligand in activated lymphocytes. EMBO J 14: 1129–1135.
Uramoto H, Osaki T, Inoue M, Taga S, Takenoyama M, Hanagiri T et al. (1999). Fas expression in non-small cell lung cancer: its prognostic effect in completely resected stage III patients. Eur J Cancer 35: 1462–1465.
Acknowledgements
We thank Noorjehan Ali for technical assistance, Shellee Abraham for manuscript preparation and Diana Meister and Sushma Jasti for review of this paper. This research was supported by National Cancer Institute Grant CA75557, CA92393, CA95058, CA116708 and NINDS NS47699, NS57529 and Caterpillar Inc., OSF Saint Francis Medical Center, Peoria, IL, USA (to JSR) and American Cancer Society Grant no.; 06-03 (SSL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetty, C., Bhoopathi, P., Lakka, S. et al. MMP-2 siRNA induced Fas/CD95-mediated extrinsic II apoptotic pathway in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Oncogene 26, 7675–7683 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210584
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210584
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vicenin-2: a potential radiosensitizer of non-small cell lung cancer cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2018)
-
MMI-166, a selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, promotes apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer
Medical Oncology (2015)
-
Metastasis review: from bench to bedside
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
Effects of RNAi-Mediated Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Gene Silencing on the Invasiveness and Adhesion of Esophageal Carcinoma Cells, KYSE150
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2012)
-
Trials, tribulations and speculation! Report from the 7th Biennial Hatter Cardiovascular Institute Workshop
Basic Research in Cardiology (2012)