Abstract
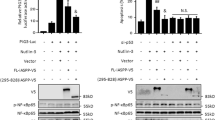
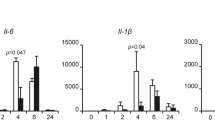
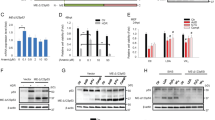
Both genotoxic and oncogenic stress activates the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and p53 proteins; however, the p53 activity is antagonized by NF-κB signaling. Dmp1 is a Myb-like transcription factor that activates the Arf-p53 pathway. The Dmp1 promoter was activated by a classical NF-κB activator tumor necrosis factor α, but repressed by treatment of cells with non-classical NF-κB activators, anthracyclins and UV-C. p65 and other subsets of NF-κB proteins were bound to the Dmp1 promoter following anthracyclin/UV-C treatment of rodent fibroblasts. This resulted in the downregulation of Dmp1 mRNA and protein. Repression of the Dmp1 transcription by anthracyclins depended on the unique NF-κB site on the promoter. Downregulation of p65 significantly attenuated the repression of the Dmp1 promoter by anthracyclins/UV-C. The amount of Dmp1 bound to the Arf promoter decreased significantly upon anthracyclin treatment; this, in turn, downregulated the Arf levels. Repression of the Arf promoter by p65 or anthracyclins depended on Dmp1, which was significantly attenuated in Dmp1−/− cells. Both Dmp1−/−and Arf−/−cells showed resistance to anthracyclin-induced cell death compared to wild-type cells; non-immortalized p65-knockdown cells were much more sensitive. Thus, the Dmp1-Arf pathway is repressed by p65 in response to genotoxic stress, which implicates a novel mechanism of p53 inactivation by NF-κB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB . (2004). Initiating cellular stress responses. Cell 118: 9–17.
Campbell JK, Rocha S, Perkins ND . (2004). Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-κB. Mol Cell 13: 853–865.
DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA . (2005). Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams & Willkins: Hagerstown, MD, USA.
Gallagher S, Kefford RF, Rizos H . (2005). Enforced expression of p14ARF induces p53-dependent cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis. Cell Cycle 4: 465–472.
Gapuzan ME, Schmah O, Pollock AD, Hoffmann A, Gilmore TD . (2005). Immortalized fibroblasts from NF-kappaB RelA knockout mice show phenotypic heterogeneity and maintain increased sensitivity to tumor necrosis factor alpha after transformation by v-Ras. Oncogene 24: 6574–6583.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2004). Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev 18: 2195–2224.
Huang DB, Vu D, Ghosh G . (2005). NF-kappaB RelB forms an intertwined homodimer. Structure 13: 1365–1373.
Inoue K, Mallakin A, Frazier DP . (2007). Dmp1 and tumor suppression (review). Oncogene Epub ahead of print Jan 22.
Inoue K, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ . (1999). Induction of ARF tumor suppressor gene expression and cell cycle arrest by transcription factor DMP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 3993–3998.
Inoue K, Wen R, Rehg JE, Adachi M, Cleveland JL, Roussel MF et al. (2000). Disruption of the ARF transcriptional activator DMP1 facilitates cell immortalization, Ras transformation and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 14: 1797–1809.
Inoue K, Zindy F, Randle DH, Rehg JE, Sherr CJ . (2001). Dmp1 is haplo-insufficient for tumor suppression and modifies the frequencies of Arf and p53 mutations in Myc-induced lymphomas. Genes Dev 15: 2934–2939.
Karin M . (2006). Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441: 431–436.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li Z-W . (2002). NF-κB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 301–310.
Kurz EU, Douglas P, Lees-Miller SP . (2004). Doxorubicin activates ATM-dependent phosphorylation of multiple downstream targets in part through the generation of reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem 279: 53272–53281.
Lowe S, Sherr CJ . (2003). Tumor suppression by Ink4a-Arf: Progress and puzzles. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 77–83.
Mallakin A, Taneja P, Matise LA, Willingham MC, Inoue K . (2006). Expression of Dmp1 in specific differentiated, nonproliferating cells and its repression by E2Fs. Oncogene 25: 7703–7713.
Perkins ND . (2004). NF-κB: tumor promoter or suppressor? Trends Cell Biol 14: 64–69.
Rocha S, Martin AM, Meek DW, Perkins ND . (2003). p53 represses cyclin D1 transcription through down regulation of Bcl-3 and inducing increased association of the p52 NF-kappaB subunit with histone deacetylase 1. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4713–4727.
Ruas M, Peters G . (1998). The p16INK4a/CDKN2A tumor suppressor and its relatives. Biochem Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1378: F115–F177.
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, Vousden KH . (2000). Role of NF-κB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 404: 892–897.
Saccani S, Pantano S, Natoli G . (2003). Modulation of NF-κB activity by exchange of dimers. Mol Cell 11: 1563–1574.
Sherr CJ . (2001). The INK4a/ARF network in tumor suppression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 731–737.
Sherr CJ . (2006). Divorcing ARF and p53: an unsettled case. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 663–673.
Sreeramaneni R, Chaudhry A, McMahon M, Sherr CJ, Inoue K . (2005). Ras-Raf-Arf signaling critically depends on Dmp1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 25: 220–232.
Tergaonkar V, Pando M, Vafa O, Wahl G, Verma I . (2002). p53 stabilization is decreased upon NFκB activation: a role for NFκB in acquisition of resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 1: 493–503.
Watts TH . (2005). TNF/TNFR family members in costimulation of T cell responses. Ann Rev Immunol 23: 23–68.
Webster GA, Perkins ND . (1999). Transcriptional cross talk between NF-κB and p53. Mol Cell Biol 19: 3485–3495.
Yoshimura A . (2006). Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development. Cancer Sci 97: 439–447.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr George Kulik and Ms Karen Klein for critical reading of the manuscript and Drs Neil Perkins, Alexander Hoffmann, Bruce Torbett and Mario Tschan for helpful discussions and sharing unpublished data. We are grateful to Drs Gioacchino Natoli, Andrew Thorburn, Michael Ostrowski, Charles Sherr and Martine Roussel for plasmid DNAs. We also thank Ramesh Sreeramaneni and Scott Barton for technical assistance. This work was supported by NIH/NCI 5R01CA106314 (K Inoue) and by a Wake Forest University Comprehensive Cancer Center ‘Push’ grant (Center grant CA12197-31) to K Inoue.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taneja, P., Mallakin, A., Matise, L. et al. Repression of Dmp1 and Arf transcription by anthracyclins: critical roles of the NF-κB subunit p65. Oncogene 26, 7457–7466 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210568
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210568