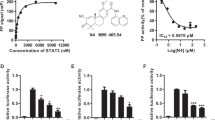
Abstract
Prostate cancer is the second highest cause of cancer-related deaths of men in the US. Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) proteins are a small family of latent cytoplasmic transcription factors that act downstream of Janus kinase (JAK) activation and mediate intracellular signaling from a wide variety of cytokines, growth factors, and hormones. Aberrant activation of STAT3 has been implicated in the progression of many human carcinomas, including prostate cancer. Previously, we have characterized a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor peptide, Tkip, that is a mimetic of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1). Similar to SOCS-1, Tkip binds to the autophosphorylation site of JAK2 and inhibits phosphorylation of STAT1α. In this study, we determined the inhibitory effects of Tkip on the human prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and LNCaP. Tkip inhibited cellular proliferation of both DU145 and LNCaP cells, with a slightly greater antiproliferative effect on DU145 cells. Cell cycle analysis using flow cytometry showed Tkip blockage of progression into the S phase of the cell cycle. Tkip also inhibited constitutive (DU145) and IL-6-induced (LNCaP) activation of STAT3, consistent with the fact that STAT3 activation is mediated by JAK2. Tkip also slightly reduced the levels of cyclin D1, an important regulator of cell cycle progression into S phase, in DU145 and LNCaP cancer cell lines. These data describe a potentially important therapeutic that targets both constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 activation in human prostate cancer cell lines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander WS and Hilton DJ . (2004). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 22, 503–529.
Barton BE, Karras JG, Murphy TF, Barton A and Huang HF . (2004). Mol. Cancer Ther., 3, 11–20.
Becker S, Corthals GL, Aebersold R, Groner B and Muller CW . (1998). FEBS Lett., 441, 141–147.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE . (1999). Cell, 98, 295–303.
Calo V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N and Russo A . (2003). J. Cell Physiol., 197, 157–168.
Chan KS, Carbajal S, Kiguchi K, Clifford J, Sano S and DiGiovanni J . (2004). Cancer Res., 64, 2382–2389.
Chen T, Wang LH and Farrar WL . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 2132–2135.
Chim CS, Fung TK, Cheung WC, Liang R and Kwong YL . (2004). Blood, 103, 4630–4635.
Chung TD, Yu JJ, Spiotto MT, Bartkowski M and Simons JW . (1999). Prostate, 38, 199–207.
Crawford ED . (2003). Urology, 62, 3–12.
Culig Z, Hobisch A, Cronauer MV, Radmayr C, Trapman J, Hittmair A, Bartsch G and Klocker H . (1994). Cancer Res., 54, 5474–5478.
De La Taille A, Vacherot F, Salomon L, Druel C, Gil Diez De Medina S, Abbou C, Buttyan R and Chopin D . (2001). Prostate Cancer Prostat. Dis., 4, 204–212.
Deutsch E, Maggiorella L, Eschwege P, Bourhis J, Soria JC and Abdulkarim B . (2004). Lancet Oncol., 5, 303–313.
Dhir R, Ni Z, Lou W, DeMiguel F, Grandis JR and Gao AC . (2002). Prostate, 51, 241–246.
Flowers LO, Johnson HM, Mujtaba MG, Ellis MR, Haider SM and Subramaniam PS . (2004). J. Immunol., 172, 7510–7518.
Giri D, Ozen M and Ittmann M . (2001). Am. J. Pathol., 159, 2159–2165.
Gregory CW, Fei X, Ponguta LA, He B, Bill HM, French FS and Wilson EM . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 7119–7130.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-Newen G and Schaper F . (2003). Biochem. J., 374, 1–20.
Hobeika AC, Etienne W, Cruz PE, Subramaniam PS and Johnson HM . (1998). Int. J. Cancer, 77, 138–145.
Hobisch A, Eder IE, Putz T, Horninger W, Bartsch G, Klocker H and Culig Z . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 4640–4645.
Kisseleva T, Bhattacharya S, Braunstein J and Schindler CW . (2002). Gene, 285, 1–24.
Larsen L and Ropke C . (2002). APMIS, 110, 833–844.
Lorenzo GD, Bianco R, Tortora G and Ciardiello F . (2003). Clin. Prostate Cancer, 2, 50–57.
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J, Ahmad N, Garcia R, Bowman T, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Cantor A, Muro-Cacho C, Livingston S, Karras J, Pow-Sang J and Jove R . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 6659–6666.
Nazareth LV and Weigel NL . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 19900–19907.
Okamoto M, Lee C and Oyasu R . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 141–146.
Petre-Draviam CE, Cook SL, Burd CJ, Marshall TW, Wetherill YB and Knudsen KE . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 4903–4913.
Ritchie CK, Andrews LR, Thomas KG, Tindall DJ and Fitzpatrick LA . (1997). Endocrinology, 138, 1145–1150.
Sadar MD . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 7777–7783.
Sgambato A, Camerini A, Faraglia B, Ardito R, Bianchino G, Spada D, Boninsegna A, Valentini V and Cittadini A . (2004). J. Cell Physiol., 201, 97–105.
Shi XB, Ma AH, Tepper CG, Xia L, Gregg JP, Gandour-Edwards R, Mack PC, Kung HJ and deVere White RW . (2004). Prostate, 60, 257–271.
Smith PC, Hobisch A, Lin DL, Culig Z and Keller ET . (2001). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 12, 33–40.
Stacey DW . (2003). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 15, 158–163.
Szente BE, Weiner IJ, Jablonsky MJ, Krishna NR, Torres BA and Johnson HM . (1996). J. Interferon Cytokine Res., 16, 813–817.
Thiam K, Loing E, Verwaerde C, Auriault C and Gras-Masse H . (1999). J. Med. Chem., 42, 3732–3736.
Ueda T, Bruchovsky N and Sadar M . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 7076–7085.
Xia L, Wang L, Chung AS, Ivanov SS, Ling MY, Dragoi AM, Platt A, Gilmer TM, Fu XY and Chin YE . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 30716–30723.
Yasukawa H, Misawa H, Sakamoto H, Masuhara M, Sasaki A, Wakioka T, Ohtsuka S, Imaizumi T, Matsuda T, Ihle JN and Yoshimura A . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1309–1320.
Yoshida T, Ogata H, Kamio M, Joo A, Shiraishi H, Tokunaga Y, Sata M, Nagai H and Yoshimura A . (2004). J. Exp. Med., 199, 1701–1707.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant AI56152 (to HMJ) from the National Institutes of Health and by the UNCF-Merck Graduate Science Research Dissertation Fellowship (to LOF). This manuscript is Florida Experiment Station Journal Series No. R-10648.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flowers, L., Subramaniam, P. & Johnson, H. A SOCS-1 peptide mimetic inhibits both constitutive and IL-6 induced activation of STAT3 in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 24, 2114–2120 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208437
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208437
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tissue levels of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3) in mycosis fungoides
Archives of Dermatological Research (2022)
-
Expression of SOCS1 and the downstream targets of its putative tumor suppressor functions in prostate cancer
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
SOCS1 inhibits migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells, attenuates tumor growth and modulates the tumor stroma
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2017)
-
MicroRNA-155 Deficiency Promotes Nephrin Acetylation and Attenuates Renal Damage in Hyperglycemia-Induced Nephropathy
Inflammation (2015)
-
Potent antitumor activity of oncolytic adenovirus-mediated SOCS1 for hepatocellular carcinoma
Gene Therapy (2013)