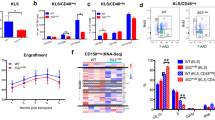
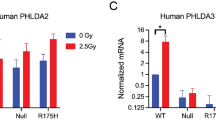
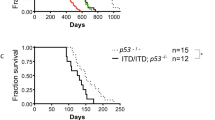
Abstract
Murine radiation-induced acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is characterized by loss of one copy of chromosome 2. Previously, we positioned the critical haematopoietic-specific transcription factor PU.1 within a minimally deleted region. We now report a high frequency (>65%) of missense mutation at codon 235 in the DNA-binding Ets domain of PU.1 in murine AML. Earlier studies, outside the context of malignancy, determined that conversion of arginine 235 (R235) to any other amino-acid residue leads to ablation of DNA-binding function and loss of expression of downstream targets. We show that mutation of R235 does not lead to protein loss, and occurs specifically in those AMLs showing loss of one copy of PU.1 (P=0.001, Fisher's exact test). PU.1 mutations were not found in the coding region, UTRs or promoter of human therapy-related AMLs. Potentially regulatory elements upstream of PU.1 were located but no mutations found. In conclusion, we have identified the cause of murine radiation-induced AML and have shown that loss of one copy of PU.1, as a consequence of flanking radiation-sensitive fragile domains on chromosome 2, and subsequent R235 conversion are highly specific to this mouse model. Such a mechanism does not operate, or is extremely rare, in human AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson KL, Smith KA, Perkin H, Hermanson G, Anderson CG, Jolly DJ, Maki RA and Torbett BE . (1999). Blood, 94, 2310–2318.
Bouffler SD, Meijne EIM, Morris DJ and Papworth D . (1997). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 72, 181–189.
Breckon G, Papworth D and Cox R . (1991). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 3, 367–375.
Chen HM, Zhang P, Voso MT, Hohaus S, Gonzalez DA, Glass CK, Zhang DE and Tenen DG . (1995). Blood, 85, 2918–2928.
Clark DJ, Meijne EI, Bouffler SD, Huiskamp R, Skidmore CJ, Cox R and Silver ARJ . (1996). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 4, 238–246.
Dohner K, Tobis K, Bischof T, Hein S, Schlenk RF, Frohling S and Dohner H . (2003). Blood, 102, 3850.
Donaldson LW, Petersen JM, Graves BJ and McIntosh LP . (1994). Biochemistry, 33, 13509–13516.
Finnon R, Moody J, Meijne E, Haines J, Clark D, Edwards A, Cox R and Silver A . (2002). Mol. Carcinogen., 34, 64–71.
Galson DL, Hensold JO, Bishop TR, Schalling M, D'Andrea AD, Jones C, Auron PE and Housman DE . (1993). Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 2929–2941.
Hohaus S, Petrovick MS, Voso MT, Sun Z, Zhang DE and Tenen DG . (1995). Mol. Cell. Biol., 15, 5830–5845.
Hromas R, Orazi A, Neiman RS, Maki R, Van Beveran C, Moore J and Klemsz M . (1993). Blood, 82, 2998–3004.
Jia X, Lee LK, Light J, Palmer AG and Assa-Munt N . (1999). J. Mol. Biol., 292, 1083–1093.
Klemsz MJ, McKercher SR, Celada A, Van Beveren C and Maki RA . (1990). Cell, 61, 113–124.
Kodandapani R, Pio F, Ni CZ, Piccialli G, Klemsz M, McKercher S, Maki RA and Ely KR . (1996). Nature, 380, 456–460.
Lamandin C, Sagot C, Roumier C, Lepelley P, De Botton S, Cosson A, Fenaux P and Preudhomme C . (2002). Blood, 100, 4680–4681.
Leone G, Mele L, Pulsoni A, Equitani F and Pagano L . (1999). Haematologica, 84, 937–945.
Ley TJ, Minx PJ, Walter MJ, Ries RE, Sun H, McLellan M, DiPersio JF, Link DC, Tomasson MH, Graubert TA, McLeod H, Khoury H, Watson M, Shannon W, Trinkaus K, Heath S, Vardiman JW, Caligiuri MA, Bloomfield CD, Milbrandt JD, Mardis ER and Wilson RK . (2003). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 100, 14275–14280.
McKercher SR, Torbett BE, Anderson KL, Henkel GW, Vestal DJ, Baribault H, Klemsz M, Feeney AJ, Wu GE, Paige CJ and Maki RA . (1996). EMBO J., 15, 5647–5658.
Mckercher SR, Lombardo CR, Bobkov A, Jia X and Assa-Munt N . (2003). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 100, 511–516.
Mitelman F, Mertens F and Johansson B . (1997). Nat. Genet., 15, 417–474.
Mo Y, Vaessen B, Johnston K and Marmorstein R . (1998). Mol. Cell, 2, 201–212.
Moreau-Gachelin F, Ray D, Mattei MG, Tambourin P and Tavitian A . (1989). Oncogene, 4, 1449–1456.
Mueller BU, Pabst T, Osato M, Asou N, Johansen LM, Dayaram T, Behre G, Hiddemann W, Ito Y and Tenen TG . (2003). Blood, 102, 3851.
Mueller BU, Pabst T, Osato M, Asou N, Johansen LM, Minden MD, Behre G, Hiddemann W, Ito Y and Tenen DG . (2002). Blood, 100, 998–1007.
Nagulapalli S, Pongubala JMR and Atchinson ML . (1995). J. Immunol., 155, 4331–4337.
Pahl HL, Scheibe RJ, Zhang DE, Chen HM, Galson DL, Maki RA and Tenen DG . (1993). J. Biol. Chem., 268, 5014–5020.
Petrovick MS, Hiebert SW, Friedman AD, Hetherington CJ, Tenen DG and Dong-er Z . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 3915–3925.
Pham CT, MacIvor DM, Hug BA, Heusel JW and Ley TJ . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 13090–13095.
Pio F, Kodandapani R, Ni CZ, Shepard W, Klemsz M, McKercher SR, Maki RA and Ely KR . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23329–23337.
Rosenbauer F, Wagner K, Kutok JL, Iwasaki H, Le Beau MM, Okuno Y, Akashi K, Fiering S and Tenen DG . (2004). Nat. Genet., 36, 624–630.
Scott EW, Simon MC, Anastai J and Singh H . (1994). Science, 265, 1573–1577.
Seki M, Yoshida K, Nishimura M and Nemoto K . (1991). Radiat. Res., 127, 146–149.
Silver ARJ, Moody J, Dunford R, Clark D, Ganz S, Bulman R, Bouffler S, Finnon P, Meijne E, Huiskamp R and Cox R . (1999). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 24, 95–104.
Smith LT, Hohaus S, Gonzalez DA, Dziennis SE and Tenen DG . (1996). Blood, 88, 1234–1247.
Smith RE . (2003). Clin. Breast Cancer, 4, 273–279.
Tenen DG, Hromas R, Licht JD and Zhang D-E . (1997). Blood, 90, 489–519.
Vangala RK, Heiss-Neumann MS, Rangatia JS, Singh SM, Schoch C, Tenen DG, Hiddemann W and Behre G . (2003). Blood, 101, 270–277.
Vegesna V, Takeuchi S, Hofmann WK, Ikezoe T, Tavor S, Krug U, Fermin AC, Heaney A, Miller CW and Koeffler HP . (2002). Leukemia Res., 26, 451–457.
Yamamoto H, Kihara-Negishi F, Yamada T, Hashimoto Y and Oikawa T . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 1495–1501.
Zhang DE, Hetherington CJ, Chen HM and Tenen DG . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 373–381.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support by Cancer Research UK and EU under 4th and 5th framework programmes (contract numbers F14PLT-95-00089, FIGH-CT-1999-00006 and FIGH-CT-1999-00035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suraweera, N., Meijne, E., Moody, J. et al. Mutations of the PU.1 Ets domain are specifically associated with murine radiation-induced, but not human therapy-related, acute myeloid leukaemia. Oncogene 24, 3678–3683 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208422
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208422
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hyper-radiosensitivity affects low-dose acute myeloid leukemia incidence in a mathematical model
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (2022)
-
Modeling low-dose radiation-induced acute myeloid leukemia in male CBA/H mice
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (2021)
-
Low-dose radiation accelerates aging of the T-cell receptor repertoire in CBA/Ca mice
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2017)
-
Genome-scale definition of the transcriptional programme associated with compromised PU.1 activity in acute myeloid leukaemia
Leukemia (2016)
-
Radiation-induced myeloid leukemia in murine models
Human Genomics (2014)