Abstract
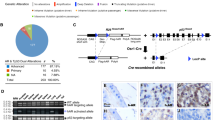
Prostate cancer (CaP) is the most common cancer in adult men in North America. Since there is no naturally occurring prostate cancer in the mouse, preclinical studies stipulate for the establishment of a genetically manipulated mouse CaP model with features close to the human situation. In view of the limitations of transgenic technique-derived CaP models, herein we report the first application of knockin technology to establish a new mouse adenocarcinoma prostate model (PSP-KIMAP) by targeting of SV40 Tag to a prostate tissue-specific gene, PSP94 (prostate secretory protein of 94 amino acids). In order to demonstrate its novelty, we compared KIMAP to a PSP94 gene-directed transgenic mouse adenocarcinoma of the prostate (PSP-TGMAP) model. The CaP development of the PSP-KIMAP mice started almost immediately after puberty at 10 weeks of age from mouse prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (mPIN) with microinvasion to well-differentiated CaP, and demonstrated a close-to-human kinetics of prolonged tumor growth and a predominance of well and moderately differentiated tumors. The invasive nature of KIMAP model was demonstrated by multitissue metastases (lymph node, lung and liver etc) and also by immunohistochemical study of multiple invasive prostate tumor markers. PSP-KIMAP model is responsive to androgen deprivation (castration). The knockin technology in our KIMAP model demonstrates highly predictive CaP development procedures and many advantageous features, which the traditional transgenic technique-derived CaP models could not reach for both basic and clinical studies. These features include the high stability of both phenotype and genotype, highly synchronous prostate cancer development, high and precise prostate tissue targeting and with no founder line variation. The differences between the two CaP models were attributed to the introduction of a single endogenous knockin mutation, resulting in a CaP model self-regulated and controlled by a prostate gene promoter/enhancer of PSP94.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PSP94:
-
β-microseminoprotein, prostate secretory protein of 94 amino acids
- CaP:
-
prostate cancer
- GE:
-
genetically engineered
- ES cell:
-
embryonic stem cell
- PSP-TGMAP:
-
PSP94-transgenic mouse adenocarcinoma of the prostate
- PSP-KIMAP:
-
PSP94-knockin mouse adenocarcinoma of the prostate
- DLP:
-
dorsolateral prostate
- VP:
-
ventral prostate
- AP/CG:
-
anterior lobe, or coagulation gland
- mPIN:
-
mouse prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- SV40 Tag:
-
simian virus T antigen
- AR:
-
androgen receptor
- NE:
-
neuroendocrine
- NPT:
-
nonprostate targeting
- RT–PCR:
-
reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemistry
- H&E:
-
hematoxylin and eosin staining
- PCNA:
-
proliferating cell nuclear antigen
References
Abate-Shen C and Shen MM . (2002). Trends Genet., 18, S1–S5.
Abrahamsson P-A, Lilja H, Falkmer S and Wadstrom LB . (1988). Prostate, 12, 39–46.
Cleutjens KB, van der Korput HA, Ehren-van Eekelen CC, Sikes RA, Fasciana C, Chung LW and Trapman J . (1997). Mol. Endocrinol., 11, 1256–1265.
Deshmukh N and Foster CS . (1998) Foster CS, Bostwick DG (eds). Pathology of the Prostate Cancer. WB Saunders: Philadelphia, pp. 191–227.
Di Cristofano A, De Acetis M, Koff A, Cordon-Cardo C and Pandolfi PP . (2001). Nat. Genet., 27, 222–224.
DiGiovanni J, Kiguchi K, Frijhoff A, Wilker E, Bol DK, Beltran L, Moats S, Ramirez A, Jorcano J and Conti C . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 3455–3460.
Dube JY, Frenette G, Paquin R, Chapdelaine P, Tremblay J, Tremblay RR, Lazure C, Seidah N and Chretien M . (1987). J. Androl., 8, 182–189.
Fernlund P, Granberg L and Larson I . (1996). Arch Biochem. Biophys., 334, 73–82.
Fong GH, Klingensmith J, Wood CR, Rossant J and Breitman ML . (1995). Nature, 376, 66–70.
Gabril MY, Onita T, Ji PG, Sakai H, Chan FL, Koropatnick J, Chin JL, Moussa M and Xuan JW . (2002). Gene Therapy, 9, 1589–1599.
Garabedian EM, Humphrey PA and Gordon JI . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 62, 227–237.
Gingrich JR, Barrios RJ, Morton RA, Boyce BF, DeMayo FJ, Finegold MJ, Angelopoulou R, Rosen JM and Greenberg NM . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 4096–4102.
Greenberg NM, Demayo F, Finegold MJ, Medina D, Tilley WD, Aspinall JO, Cunha GR, Donjacour AA, Matusik RJ and Rosen JM . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 3439–3443.
Green JE, Greenberg NM, Ashendel CL, Barrett JC, Boone C, Getzenberg RH, Henkin J, Matusik RJ, Janus TJ and Scher HI . (1998). Prostate, 36, 59–63.
Hara M and Kimura H . (1989). J. Lab. Clin. Med, 113, 541–548.
Huss WJ, Maddison LA and Greenberg NM . (2001). Semin. Cancer Biol, 11, 245–260.
Hyakutake H, Sakai H, Yogi Y, Tsuda R, Minami Y, Yushita Y, Kanetake H, Nakazono I and Saito Y . (1993). Prostate, 22, 347–355.
Imasato Y, Xuan JW, Sakai H, Izawa JI, Saito Y, Chin JL and Moussa M . (2000). J. Urol., 164, 1819–1824.
Imasato Y, Onita T, Moussa M, Sakai H, Chan FL, Koropatnick J, Chin JL and Xuan JW . (2001). Endocrinology, 142, 2138–2146.
Kas K, Finger E, Grall F, Gu X, Akbarali Y, Boltax J, Weiss A, Oettgen P, Kapeller R and Libermann TA . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2986–2998.
Kim MJ, Bhatia-Gaur R, Banach-Petrosky WA, Desai N, Wang Y, Hayward SW, Cunha GR, Cardiff RD, Shen MM and Abate-Shen C . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 2999–3004.
Lazure C, Villemure M, Gauthier D, Naude RJ and Mbikay M . (2001). Protein Sci., 10, 2207–2218.
Lokeshwar BL, Hurkadli KS, Sheth AR and Block NL . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 4855–4859.
Maroulakou IG, Anver M, Garrett L and Green JE . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 11236–11240.
Masumori N, Thomas TZ, Chaurand P, Case T, Paul M, Kasper S, Caprioli RM, Tsukamoto T, Shappell SB and Matusik RJ . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2239–2249.
Matsubara S, Wada Y, Gardner TA, Egawa M, Park MS, Hsieh CL, Zhau HE, Kao C, Kamidono S, Gillenwater JY and Chung LWK . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6012–6019.
Matusik RJ, Masumori N, Thomas T, Case T, Paul M, Kasper S and Shappell SB . (2001) Matuk M, Brown CW, Kumar TR (eds). Contemporary Endocrinology: Transgenics in Endocrinology. Human Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, pp. 401–425.
Miyamoto N, Yoshida M, Kuratani S, Matsuo I and Aizawa S . (1997). Development, 124, 1653–1664.
Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA and Davis CJE . (2002). Histological Typing of Prostate Tumours 2nd edn. World Health Organization, International Histological Classification of Tumours. Springer: Berlin.
Oettgen P, Kas K, Dube A, Gu X, Grall F, Thamrongsak U, Akbarali Y, Finger E, Boltax J, Endress G, Munger K, Kunsch C and Libermann TA . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 29439–29452.
Peng J, Zhang L, Drysdale L and Fong GH . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 8386–8391.
Perez-Stable C, Altman NH, Mehta PP, Deftos LJ and Roos BA . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 900–906.
Pham CT, MacIvor DM, Hug BA, Heusel JW and Ley TJ . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 13090–13095.
Podsypanina K, Ellenson LH, Nemes A, Gu J, Tamura M, Yamada KM, Cordon-Cardo C, Catoretti G, Fisher PE and Parsons R . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 1563–1568.
Schreiber-Agus N, Meng Y, Hoang T, Hou Jr H, Chen K, Greenberg R, Cordon-Cardo C, Lee HW and DePinho RA . (1998). Nature, 393, 483–487.
Shibata MA, Ward JM, Devor DE, Liu ML and Green JE . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 4894–4903.
Shukeir N, Arakelian A, Kadhim S, Garde S and Rabbani SA . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 2072–2078.
Spence AM, Scheppard PC, Davie JR, Matuo Y, Nishi N, McKeehan WL, Dodd JG and Matusik RJ . (1989). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 7843–7847.
Stege R, Grande M, Carlstrom K, Tribukait B and Pousette A . (2000). Clin. Cancer Res., 6, 160–165.
Thompson T . (1996). Urol Oncol., 2, 99–128.
Watabe T, Lin M, Ide H, Donjacour AA, Cunha GR, Witte ON and Reiter RE . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 401–406.
Wei C, Willis RA, Tilton BR, Looney RJ, Lord EM, Barth RK and Frelinger JG . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 6369–6374.
Xuan JW, Kwong J, Chan FL, Ricci M, Imasato Y, Sakai H, Fong GH, Panchal C and Chin JL . (1999). DNA Cell Biol, 18, 11–26.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (UOP-63722, MT-15390), The Kidney Foundation of Canada, The Prostate Cancer Research Foundation of Canada, and from Procyon Biopharma Inc. Montreal, Quebec, Canada. JWX is a recipient of CIHR University-Industry Scientist salary award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on Oncogene Website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, W., Gabril, M., Moussa, M. et al. Knockin of SV40 Tag oncogene in a mouse adenocarcinoma of the prostate model demonstrates advantageous features over the transgenic model. Oncogene 24, 1510–1524 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208229
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208229
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Oral administration of E-type prostanoid (EP) 1 receptor antagonist suppresses carcinogenesis and development of prostate cancer via upregulation of apoptosis in an animal model
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Biology and evolution of poorly differentiated neuroendocrine tumors
Nature Medicine (2017)
-
Modeling prostate cancer in mice: something old, something new, something premalignant, something metastatic
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2013)
-
Interferon-γ induces regression of epithelial cell carcinoma: critical roles of IRF-1 and ICSBP transcription factors
Oncogene (2006)