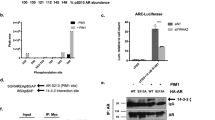
Abstract
Regulation of nuclear receptor activity is the focus of numerous ongoing studies to develop novel therapies for the treatment of hormone-related cancer. Although cyclin D1 functions to control the activity of several nuclear receptors, the region(s) of the protein responsible for such transcriptional comodulation remain poorly defined. Herein, we map the region of cyclin D1 required for binding and repression of the androgen receptor (AR) to a central, exclusively α-helical domain. Deletion of this domain disrupted AR binding and corepressor activity. Further investigations showed that this domain is sufficient for AR interaction and possesses the ability to bind histone deacetylase 3. Strikingly, overexpression of this repressor region attenuates cell cycle progression in prostatic adenocarcinoma cells. The requirement of this domain for nuclear receptor repression was conserved with respect to thyroid hormone receptor beta-1, whereas cyclin D1 activation of the estrogen receptor occurred independently of the central region. Together, these data identify a minimal repression module within cyclin D1 and demonstrate that the coactivator and corepressor functions of cyclin D1 are distinct. In addition, our data suggest that properties of the cyclin D1 central domain could be exploited to develop novel prostate cancer therapeutics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczak R, Porollo A and Meller J . (2004). Proteins, 4, 753–767.
Arnold A, Kim HG, Gaz RD, Eddy RL, Fukushima Y, Byers MG, Shows TB and Kronenberg HM . (1989). J. Clin. Invest., 83, 2034–2040.
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M and Bartek J . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 1027–1037.
Bienvenu F, Gascan H and Coqueret O . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 16840–16847.
Brown NR, Noble ME, Endicott JA, Garman EF, Wakatsuki S, Mitchell E, Rasmussen B, Hunt T and Johnson LN . (1995). Structure, 3, 1235–1247.
Burd CJ, Petre-Draviam C, Moghadam H, Wilson EM and Knudsen KE . Mol. Endocrinol. in revision.
Card GL, Knowles P, Laman H, Jones N and McDonald NQ . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 2877–2888.
Chen C and Okayama H . (1987). Mol. Cell. Biol., 7, 2745–2752.
Cleutjens KB, van der Korput HA, van Eekelen CC, van Rooij HC, Faber PW and Trapman J . (1997). Mol. Endocrinol., 11, 148–161.
Coqueret O . (2002). Gene, 299, 35–55.
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 3499–3511.
Diehl JA and Sherr CJ . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 7362–7374.
Diehl JA, Zindy F and Sherr CJ . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 957–972.
Drobnjak M, Osman I, Scher HI, Fazzari M and Cordon-Cardo C . (2000). Clin. Cancer Res., 6, 1891–1895.
Dyson N . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2245–2262.
Ewen ME and Lamb J . (2004). Trends Mol. Med., 10, 158–162.
Ganter B, Fu S and Lipsick JS . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 255–268.
Gaughan L, Logan IR, Cook S, Neal DE and Robson CN . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 25904–25913.
Gladden AB and Diehl JA . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 9754–9760.
Guan KL and Dixon JE . (1991). Anal. Biochem., 192, 262–267.
Gumbiner LM, Gumerlock PH, Mack PC, Chi SG, deVere White RW, Mohler JL, Pretlow TG and Tricoli JV . (1999). Prostate, 38, 40–45.
Hinds PW, Dowdy SF, Eaton EN, Arnold A and Weinberg RA . (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 709–713.
Inoue K and Sherr CJ . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 1590–1600.
Jeffrey PD, Russo AA, Polyak K, Gibbs E, Hurwitz J, Massague J and Pavletich NP . (1995). Nature, 376, 313–320.
Jeffrey PD, Tong L and Pavletich NP . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 3115–3125.
Kato J, Matsushime H, Hiebert SW, Ewen ME and Sherr CJ . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 331–342.
Khan OY and Nawaz Z . (2003). Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev., 6, 692–701.
Kim KK, Chamberlin HM, Morgan DO and Kim SH . (1996). Nat. Struct. Biol., 3, 849–855.
Knudsen KE, Cavenee WK and Arden KC . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 2297–2301.
Lamb J, Ramaswamy S, Ford HL, Contreras B, Martinez RV, Kittrell FS, Zahnow CA, Patterson N, Golub TR and Ewen ME . (2003). Cell, 114, 323–334.
Lin HM, Zhao L and Cheng SY . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 28733–28741.
Maddison LA, Huss WJ, Barrios RM and Greenberg NM . (2004). Prostate, 58, 335–344.
Martinez ED and Danielsen M . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 29719–29729.
Marvada P, Dmitrieva NI, East-Palmer J and Yen PM . (2004). Mol. Biol. Cell., 4, 1895–1903.
McMahon C, Suthiphongchai T, DiRenzo J and Ewen ME . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 5382–5387.
Mittnacht S . (1998). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 21–27.
Morgan DO . (1995). Nature, 374, 131–134.
Motokura T, Bloom T, Kim HG, Juppner H, Ruderman JV, Kronenberg HM and Arnold A . (1991). Nature, 350, 512–515.
Neuman E, Ladha MH, Lin N, Upton TM, Miller SJ, DiRenzo J, Pestell RG, Hinds PW, Dowdy SF, Brown M and Ewen ME . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 5338–5347.
Petre CE, Wetherill YB, Danielsen M and Knudsen KE . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 2207–2215.
Petre-Draviam CE, Cook SL, Burd CJ, Marshall TW, Wetherill YB and Knudsen KE . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 4903–4913.
Porollo A, Adamczak R and Meller J . (2004). Bioinformatics. April 8 [Epub ahead of print].
Pratt WB and Toft DO . (1997). Endocr. Rev., 18, 306–360.
Ratineau C, Petry MW, Mutoh H and Leiter AB . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 8847–8853.
Reutens AT, Fu M, Wang C, Albanese C, McPhaul MJ, Sun Z, Balk SP, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ and Pestell RG . (2001). Mol. Endocrinol., 15, 797–811.
Rosenberg CL, Kim HG, Shows TB, Kronenberg HM and Arnold A . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 449–453.
Sayle RA and Milner-White EJ . (1995). Trends Biochem. Sci., 20, 374.
Schulze-Gahmen U and Kim SH . (2002). Nat. Struct. Biol., 9, 177–181.
Shao Z and Robbins PD . (1995). Oncogene, 10, 221–228.
Solomon DA, Wang Y, Fox SR, Lambeck TC, Giesting S, Lan Z, Senderowicz AM and Knudsen ES . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 30339–30347.
Summers MASG . (1987). Tex. Agric. Exp. Sta. Bull., 1555.
Wang C, Pattabiraman N, Zhou JN, Fu M, Sakamaki T, Albanese C, Li Z, Wu K, Hulit J, Neumeister P, Novikoff PM, Brownlee M, Scherer PE, Jones JG, Whitney KD, Donehower LA, Harris EL, Rohan T, Johns DC and Pestell RG . (2003). Mol. Cell. Biol., 23, 6159–6173.
Zukerberg LR, Benedict WF, Arnold A, Dyson N, Harlow E and Harris NL . (1996). Blood, 88, 268–276.
Zwijsen RM, Buckle RS, Hijmans EM, Loomans CJ and Bernards R . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 3488–3498.
Zwijsen RM, Wientjens E, Klompmaker R, van der Sman J, Bernards R and Michalides RJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 405–415.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr G Babcock and S Schwemberger for aid in acquiring flow cytometry data. We thank Dr E Knudsen and the Knudsen Laboratories for their technical assistance and critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by RO1 CA099996 and the Center for Environmental Genetics (Center Grant NIH/NIEHS P30-ES06096) (to KEK), NIH CA93237 (to JAD), the University of Cincinnati Distinguished Graduate Fellowship (to CEP and CJB), the Albert J Ryan Foundation (to CEP and CJB), and NIH training Grant #HDO7200-15 (CJB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petre-Draviam, C., Williams, E., Burd, C. et al. A central domain of cyclin D1 mediates nuclear receptor corepressor activity. Oncogene 24, 431–444 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208200
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208200
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of CCND1 Gene c.870G>A Polymorphism with Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-ControlStudy and a Meta-Analysis
Pathology & Oncology Research (2017)
-
AR function in promoting metastatic prostate cancer
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2014)
-
FBI-1 functions as a novel AR co-repressor in prostate cancer cells
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)
-
Cyclin D1 repressor domain mediates proliferation and survival in prostate cancer
Oncogene (2009)
-
Cyclin D1 promotes anchorage-independent cell survival by inhibiting FOXO-mediated anoikis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)