Abstract
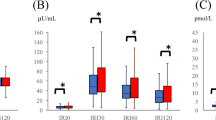
The purpose of the study is to compare surrogate estimates of insulin sensitivity with a directly measured insulin sensitivity index, steady-state plasma glucose (SSPG) from insulin suppression test (IST), in subjects with hypertension. Two hundred and twenty-eight hypertensive patients who received IST for SSPG were included for analysis. Estimates from fasting measurements alone, homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI)), and indices from fasting and/or 2 h samples (ISI0,120 and ISITX) were calculated. In addition to Pearson and partial correlations, variance-component models were used to test the relationship between surrogate estimates of insulin sensitivity and SSPG. A large proportion of variance owing to covariates in the variance-component models indicated the goodness of model fit, irrespective of the independence among variables. SSPG was positively correlated with logarithmic transformation (Log) (HOMA-IR) and negatively correlated with QUICKI, Log (ISI0,120) and ISITX (all P<0.0001). Log (ISI0,120) seemed to have a better correlation with SSPG (r=−0.72) than other measures in partial correlation. The proportion of variance owing to all covariates of Log (ISI0,120) and ISITX were larger than those of Log (HOMA-IR) and QUICKI in the variance-component models. After adjustments for demographic and obesity covariates, the proportion of variance explained by Log (ISI0,120) were largest among the surrogate measures in the variance-component models. Our results showed that ISI0,120 and ISITX correlated better with SSPG than those used fasting measures alone (HOMA-IR and QUICKI). Log (ISI0,120) currently showing the strongest association with SSPG than other estimates is adaptable for use in large studies of hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verdecchia P, Reboldi G, Angeli F, Borgioni C, Gattobigio R, Filippucci L et al. Adverse prognostic significance of new diabetes in treated hypertensive subjects. Hypertension 2004; 43: 963–969.
Saad MF, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Nelson RG, Charles MA, Bennett PH . A two-step model for development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Am J Med 1991; 90: 229–235.
Reaven GM . Insulin resistance/compensatory hyperinsulinemia, essential hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 2399–2403.
Scheen AJ, Paquot N, Castillo MJ, Lefèbvre PJ . How to measure insulin action in vivo. Diabetes Metab Rev 1994; 10: 151–188.
Lansang MC, Williams GH, Carroll JS . Correlation between the glucose clamp technique and the homeostasis model assessment in hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 51–53.
Chen H, Sullivan G, Yue LQ, Katz A, Quon MJ . QUICKI is a useful index of insulin sensitivity in subjects with hypertension. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: E804–E812.
Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, Giorico MA, Oleggini M, Graziadei L et al. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 1987; 317: 350–357.
Yeni-Komshian H, Carantoni M, Abbasi F, Reaven GM . Relationship between several surrogate estimates of insulin resistance and quantification of insulin-mediated glucose disposal in 490 healthy non-daibetic volunteers. Diabetes Care 2000; 23: 171–175.
Abbasi F, Reaven GM . Evaluation of the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index as an estimate of insulin sensitivity in humans. Metabolism 2002; 51: 235–237.
Hjelmesæth J, Midtvedt K, Jenssen T, Hartmann A . Insulin resistance after renal transplantation. Impact of immunosuppressive and antihypertensive therapy. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 2121–2126.
Gutt M, Davis CL, Spitzer SB, Llabre MM, Kumar M, Czarnecki EM et al. Validation of the insulin sensitivity index (ISI0,120): comparison with other measures. Diabetes Res Clin Practice 2000; 47: 177–184.
Ranade K, Hsuing AC, Wu KD, Chang MS, Chen YT, Hebert J et al. Lack of evidence for an association between α-adducin and blood pressure regulation in Asian populations. Am J Hypertens 2000; 13: 704–709.
Hwu CM, Hsiao CF, Sheu WHH, Pei D, Tai TY, Quertermous T et al. Sagittal abdominal diameter is associated with insulin sensitivity in Chinese hypertensive patients and their siblings. J Hum Hypertens 2003; 17: 193–198.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo Jr JL et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560–2572.
Pan WH, Flegal KM, Chang HY, Yeh WT, Yeh CJ, Lee WC . Body mass index and obesity-related metabolic disorders in Taiwanese and US whites and blacks: implications for definitions of overweight and obesity for Asians. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: 31–39.
Hwu CM, Hsiao CF, Kuo SW, Wu KD, Ting CT, Quertermous T et al. Physical inactivity is an important lifestyle determinant of insulin resistance in hypertensive patients. Blood Pressure 2004; 13: 355–361.
Hwu CM, Kwok CF, Chiang SC, Wang PY, Hsiao LC, Lee SH et al. A comparison of insulin suppression tests performed with somatostatin and octreotide with particular reference to tolerability. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2001; 51: 187–193.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: A simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2402–2410.
Almasy L, Blangero J . Multipoint quantitative-trait linkage analysis in general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62: 1198–1211.
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA . Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing. Comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999; 22: 1426–1470.
DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E . Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care 1992; 15: 318–368.
Rutter MK, Meigs JB, Sullivan LM, D'Agostino Jr RB, Wilson PW . Insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and incident cardiovascular events in the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes 2005; 54: 3252–3257.
Hanley AJG, Williams K, Gonzalez C, D'Agostino Jr RB, Wagenknecht LE, Stern MP et al. Prediction of type 2 diabetes using simple measures of insulin resistance. Combined results from the San Antonio Heart Study, the Mexico City Diabetes Study, and the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes 2003; 52: 463–469.
Kim SH, Abbasi F, Reaven GM . Impact of degree of obesity on surrogate estimates of insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1998–2002.
Stumvoll M, Mitrakou A, Jenssen T, Yki-Järvinen H, van Haeften T, Renn W et al. Use of the oral glucose tolerance test to assess insulin release and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000; 23: 295–301.
Mooy JM, Grootenhuis PA, de Vries H, Kostense PJ, Popp-Snijders C, Bouter LM et al. Intra-individual variation of glucose, specific insulin and proinsulin concentrations measured by two oral glucose tolerance tests in a general Caucasian population: the Hoorn Study. Diabetologia 1996; 39: 298–305.
Wu KD, Hsiao CF, Ho LT, Sheu WHH, Pei D, Chuang LM et al. Clustering and heritability of insulin resistance in Chinese and Japanese hypertensive families: a Stanford-Asian Pacific Program in Hypertension and Insulin Resistance Sibling Study. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 529–536.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by grants from the National Science Council ROC (NSC85-2331-B075-109Y, NSC86-2314-B075-099, NSC87-2312-B075-003Y), the National Health Research Institute ROC (DD01-86IX-MG-608S) and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (U01HL54527-0151). Dr Chii-Min Hwu was also supported by the Taipei Veterans General Hospital (VGH-91-15A) and the Shih-Yuan Foundation for the Development of Internal Medicine (Grant No. 93008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwu, C., Hsiao, C., Grove, J. et al. Surrogate estimates of insulin sensitivity in subjects with hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 21, 246–252 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002137
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002137
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dynamic lipidome alterations associated with human health, disease and ageing
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
Measurements of insulin resistance in hypertension: where are we now?
Journal of Human Hypertension (2007)