Abstract
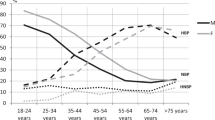
Although isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) increases the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke, more than any other hypertension subtype, the prevalence and risk factors associated with ISH in the Korean population are not known. The 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey was a cross-sectional and nationally representative survey conducted in 2001. The prevalence of ISH by age and body mass index (BMI) was examined in 6601 Korean adults over 20 years of age. After adjusting for age, 4.32±0.32% of Korean adults had ISH, 5.28±0.37% had isolated diastolic hypertension and 5.82±0.36% had systolic/diastolic hypertension. The overall prevalence of ISH was found to increase directly with advancing age and increasing BMI. Although the ISH was found to be more common in men overall (4.81±0.50% in men, 4.12±0.37% in women), it was more common in women over 70 years of age. Independent variables associated with risk for ISH included advanced age, BMI, triglyceride (TG) levels, monthly income and alcohol intake. However, gender, fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, residential area, education level and smoking were found not to be significantly associated with ISH risk. The findings of the present study demonstrate that the prevalence of untreated ISH in Korea was lower than in Western countries. Age, BMI, TG levels, monthly income and alcohol intake were associated with ISH.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Important death cause in Korea. Seoul: Korea National Statistical Office, 2004.
Kim S, Moon S, Popkin BM . The nutrition transition in South Korea. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 71: 44–53.
Whelton PK, He J, Appel LJ, Cutler JA, Havas S, Kotchen TA et al. Primary prevention of hypertension: clinical and public health advisory from The National High Blood Pressure Education Program. JAMA 2002; 288: 1882–1888.
Neaton JD, Grimm Jr RH, Prineas RJ, Stamler J, Grandits GA, Elmer PJ et al. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study. Final results. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study Research Group. JAMA 1993; 270: 713–724.
Kannel WB, Gordon T, Schwartz MJ . Systolic versus diastolic blood pressure and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Cardiol 1971; 27: 335–346.
Antikainen R, Jousilahti P, Tuomilehto J . Systolic blood pressure, isolated systolic hypertension and risk of coronary heart disease, strokes, cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in the middle-aged population. J Hypertens 1998; 16: 577–583.
Kim BG, Park JT, Ahn Y, Kimm K, Shin C . Geographical difference in the prevalence of isolated systolic hypertension in middle-aged men and women in Korea: the Korean Health and Genome Study. J Hum Hypertens 2005; 19: 877–883.
Kim JS, Jones DW, Kim SJ, Hong YP . Hypertension in Korea: a national survey. Am J Prev Med 1994; 10: 200–204.
1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. Guidelines subcommittee. J Hypertens 1999; 17: 151–183.
Huang J, Wildman RP, Gu D, Muntner P, Su S, He J . Prevalence of isolated systolic and isolated diastolic hypertension subtypes in China. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 955–962.
Joffres MR, Hamet P, MacLean DR, L’Italien GJ, Fodor G . Distribution of blood pressure and hypertension in Canada and the United States. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 1099–1105.
Denolle T, Gallois H, L’Hostis P, Cimarosti I . Characteristics of patients with isolated systolic hypertension in relation to body mass index. The PREHSI study. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 2002; 95: 683–686.
Ko GT, Cockram CS, Chow CC, Chan WB, So WY, Ma R et al. Effects of body mass index, plasma glucose and cholesterol levels on isolated systolic hypertension. Int J Cardiol 2005; 101: 429–433.
Franklin SS, Jacobs MJ, Wong ND, L’Italien GJ, Lapuerta P . Predominance of isolated systolic hypertension among middle-aged and elderly US hypertensives: analysis based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III. Hypertension 2001; 37: 869–874.
Beltran A, McVeigh G, Morgan D, Glasser SP, Neutel JM, Weber M et al. Arterial compliance abnormalities in isolated systolic hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 1007–1011.
Schiffrin EL . Vascular stiffening and arterial compliance. Implications for systolic blood pressure. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 39S–48S.
Blacher J, Safar ME . Large-artery stiffness, hypertension and cardiovascular risk in older patients. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2005; 2: 450–455.
Staessen JA, Gasowski J, Wang JG, Thijs L, Den Hond E, Boissel JP et al. Risks of untreated and treated isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: meta-analysis of outcome trials. Lancet 2000; 355: 865–872.
Multiple risk factor intervention trial. Risk factor changes and mortality results. Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group. JAMA 1982; 248: 1465–1477.
Asmar R . Benefits of blood pressure reduction in elderly patients. J Hypertens Suppl 2003; 21: S25–S30.
He J, Whelton PK . Elevated systolic blood pressure as a risk factor for cardiovascular and renal disease. J Hypertens Suppl 1999; 17: S7–S13.
Hozawa A, Ohkubo T, Nagai K, Kikuya M, Matsubara M, Tsuji I et al. Prognosis of isolated systolic and isolated diastolic hypertension as assessed by self-measurement of blood pressure at home: the Ohasama study. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 3301–3306.
Perry Jr HM, Davis BR, Price TR, Applegate WB, Fields WS, Guralnik JM et al. Effect of treating isolated systolic hypertension on the risk of developing various types and subtypes of stroke: the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP). Jama 2000; 284: 465–471.
Gupta R, Guptha S, Gupta VP, Prakash H . Prevalence and determinants of hypertension in the urban population of Jaipur in western India. J Hypertens 1995; 13: 1193–1200.
Wilking SV, Belanger A, Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Steel K . Determinants of isolated systolic hypertension. JAMA 1988; 260: 3451–3455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Support for research
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Kim, S., Choi, Y. et al. The prevalence and risk factors associated with isolated untreated systolic hypertension in Korea: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. J Hum Hypertens 21, 107–113 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002119
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002119
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Isolated systolic hypertension and its associated risk factors in Iranian middle age and older population: a population-based study
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2022)
-
Examining sex disparity in the association of waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and BMI with hypertension among older adults in India
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Systolic hypertension: an increasing clinical challenge in Asia
Hypertension Research (2015)
-
Comparison of Risk Factors Associated With Hypertension Subtypes by Classification Tree Method in Tongshan County of Jiangsu Province, China
American Journal of Hypertension (2009)
-
Hypertension in the Asia-Pacific region
Journal of Human Hypertension (2008)