Abstract
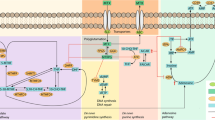
We describe a novel approach to investigate and evaluate combined effect of a large number of clinical and pharmacogenetic factors on treatment outcome. We have used this approach to investigate predictors of methotrexate (MTX)-induced adverse events (AEs) leading to treatment discontinuation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. In total, 333 RA patients were genotyped for 34 polymorphisms in MTX transporters, folate and adenosine pathways. The effect of clinical and pharmacogenetic factors was assessed with penalized regression in the cause-specific Cox proportional hazards model. The predictive capacity was evaluated with the area under time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve where cross-validation was applied. SLC19A1, ABCG2, ADORA3 and TYMS were associated with discontinuation because of AEs in clinical–pharmacogenetic model. Cross-validation showed that both clinical–pharmacogenetic model and nongenetic model had worthless predictive ability for MTX discontinuation because of AEs. These models could be further improved, either with additional polymorphisms or with epigenetic predictors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73: 492–509.
Malik F, Ranganathan P . Methotrexate pharmacogenetics in rheumatoid arthritis: a status report. Pharmacogenomics 2013; 14: 305–314.
Umicevic Mirkov M, Coenen MJ . Pharmacogenetics of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: towards personalized medicine. Pharmacogenomics 2013; 14: 425–444.
Aletaha D, Smolen JS . The rheumatoid arthritis patient in the clinic: comparing more than 1,300 consecutive DMARD courses. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2002; 41: 1367–1374.
Genestier L, Paillot R, Fournel S, Ferraro C, Miossec P, Revillard JP . Immunosuppressive properties of methotrexate: apoptosis and clonal deletion of activated peripheral T cells. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 322–328.
Brzezinska A, Winska P, Balinska M . Cellular aspects of folate and antifolate membrane transport. Acta Biochim Pol 2000; 47: 735–749.
Giacomini KM, Balimane PV, Cho SK, Eadon M, Edeki T, Hillgren KM et al. International Transporter Consortium commentary on clinically important transporter polymorphisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2013; 94: 23–26.
Mikkelsen TS, Thorn CF, Yang JJ, Ulrich CM, French D, Zaza G et al. PharmGKB summary: methotrexate pathway. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2011; 21: 679–686.
Dervieux T, Greenstein N, Kremer J . Pharmacogenomic and metabolic biomarkers in the folate pathway and their association with methotrexate effects during dosage escalation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 3095–3103.
Kremer JM . Toward a better understanding of methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 1370–1382.
Wessels JA, Kooloos WM, De Jonge R, De Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, Linssen A et al. Relationship between genetic variants in the adenosine pathway and outcome of methotrexate treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2830–2839.
Stamp LK, Hazlett J, Roberts RL, Frampton C, Highton J, Hessian PA . Adenosine receptor expression in rheumatoid synovium: a basis for methotrexate action. Arthritis Res Ther 2012; 14: R138.
Aslibekyan S, Brown EE, Reynolds RJ, Redden DT, Morgan S, Baggott JE et al. Genetic variants associated with methotrexate efficacy and toxicity in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from the treatment of early aggressive rheumatoid arthritis trial. Pharmacogenomics J 2014; 14: 48–53.
Senapati S, Singh S, Das M, Kumar A, Gupta R, Kumar U et al. Genome-wide analysis of methotrexate pharmacogenomics in rheumatoid arthritis shows multiple novel risk variants and leads for TYMS regulation. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2014; 24: 211–219.
Lima A, Monteiro J, Bernardes M, Sousa H, Azevedo R, Seabra V et al. Prediction of methotrexate clinical response in Portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients: implication of MTHFR rs1801133 and ATIC rs4673993 polymorphisms. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014: 368681.
Lima A, Seabra V, Bernardes M, Azevedo R, Sousa H, Medeiros R . Role of key TYMS polymorphisms on methotrexate therapeutic outcome in portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients. PLoS One 2014; 9: e108165.
Romao VC, Canhao H, Fonseca JE . Old drugs, old problems: where do we stand in prediction of rheumatoid arthritis responsiveness to methotrexate and other synthetic DMARDs? BMC Med 2013; 11: 17.
Kung TN, Dennis J, Ma Y, Xie G, Bykerk V, Pope J et al. RFC-1 80G>A is a genetic determinant of methotrexate efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis: a HuGE review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 66: 1111–1120.
Owen SA, Hider SL, Martin P, Bruce IN, Barton A, Thomson W . Genetic polymorphisms in key methotrexate pathway genes are associated with response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics J 2013; 13: 227–234.
Lima A, Sousa H, Monteiro J, Azevedo R, Medeiros R, Seabra V . Genetic polymorphisms in low-dose methotrexate transporters: current relevance as methotrexate therapeutic outcome biomarkers. Pharmacogenomics 2014; 15: 1611–1635.
Owen SA, Lunt M, Bowes J, Hider SL, Bruce IN, Thomson W et al. MTHFR gene polymorphisms and outcome of methotrexate treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of key polymorphisms and meta-analysis of C677T and A1298C polymorphisms. Pharmacogenomics J 2013; 13: 137–147.
Goeman JJ . L1 penalized estimation in the Cox proportional hazards model. Biom J 2010; 52: 70–84.
Moons KG, Donders AR, Steyerberg EW, Harrell FE . Penalized maximum likelihood estimation to directly adjust diagnostic and prognostic prediction models for overoptimism: a clinical example. J Clin Epidemiol 2004; 57: 1262–1270.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 2569–2581.
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J, Phan L, Smigielski EM et al. dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 308–311.
Lima A, Bernardes M, Azevedo R, Monteiro J, Sousa H, Medeiros R et al. SLC19A1, SLC46A1 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms as predictors of methotrexate-related toxicity in Portuguese rheumatoid arthritis patients. Toxicol Sci 2014; 142: 196–209.
Hider SL, Thomson W, Mack LF, Armstrong DJ, Shadforth M, Bruce IN . Polymorphisms within the adenosine receptor 2a gene are associated with adverse events in RA patients treated with MTX. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2008; 47: 1156–1159.
Bohanec Grabar P, Leandro-Garcia LJ, Inglada-Perez L, Logar D, Rodriguez-Antona C, Dolzan V . Genetic variation in the SLC19A1 gene and methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharmacogenomics 2012; 13: 1583–1594.
Bohanec Grabar P, Logar D, Lestan B, Dolzan V . Genetic determinants of methotrexate toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a study of polymorphisms affecting methotrexate transport and folate metabolism. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2008; 64: 1057–1068.
Sharma S, Das M, Kumar A, Marwaha V, Shankar S, Singh P et al. Purine biosynthetic pathway genes and methotrexate response in rheumatoid arthritis patients among north Indians. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2009; 19: 823–828.
Yuan HY, Chiou JJ, Tseng WH, Liu CH, Liu CK, Lin YJ et al. FASTSNP: an always up-to-date and extendable service for SNP function analysis and prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34, (Web Server issue): W635–W641.
Xu Z, Taylor JA . SNPinfo: integrating GWAS and candidate gene information into functional SNP selection for genetic association studies. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37, (Web Server issue): W600–W605.
Boyle AP, Hong EL, Hariharan M, Cheng Y, Schaub MA, Kasowski M et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res 2012; 22: 1790–1797.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 2005; 21: 263–265.
Grabar PB, Rojko S, Logar D, Dolzan V . Genetic determinants of methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a study of polymorphisms in the adenosine pathway. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: 931–932.
He C, Holme J, Anthony J . SNP genotyping: the KASP assay. Methods Mol Biol 2014; 1145: 75–86.
Simon RM, Subramanian J, Li MC, Menezes S . Using cross-validation to evaluate predictive accuracy of survival risk classifiers based on high-dimensional data. Brief Bioinform 2011; 12: 203–214.
Foucher Y, Danger R . Time dependent ROC curves for the estimation of true prognostic capacity of microarray data. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 2012; 11: Article 1.
R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014.
Wessels JA, van der Kooij SM, le Cessie S, Kievit W, Barerra P, Allaart CF et al. A clinical pharmacogenetic model to predict the efficacy of methotrexate monotherapy in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 1765–1775.
Fransen J, Kooloos WM, Wessels JA, Huizinga TW, Guchelaar HJ, van Riel PL et al. Clinical pharmacogenetic model to predict response of MTX monotherapy in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis after DMARD failure. Pharmacogenomics 2012; 13: 1087–1094.
Mansiaux Y, Carrat F . Detection of independent associations in a large epidemiologic dataset: a comparison of random forests, boosted regression trees, conventional and penalized logistic regression for identifying independent factors associated with H1N1pdm influenza infections. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014; 14: 1471–2288.
Katchamart W, Koolvisoot A, Aromdee E, Chiowchanwesawakit P, Muengchan C . Associations of rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated peptide antibody with disease progression and treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2015; 35: 1693–1699.
Weisman MH, Furst DE, Park GS, Kremer JM, Smith KM, Wallace DJ et al. Risk genotypes in folate-dependent enzymes and their association with methotrexate-related side effects in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 607–612.
Dervieux T, Furst D, Lein DO, Capps R, Smith K, Caldwell J et al. Pharmacogenetic and metabolite measurements are associated with clinical status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate: results of a multicentred cross sectional observational study. Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64: 1180–1185.
Jekic B, Lukovic L, Bunjevacki V, Milic V, Novakovic I, Damnjanovic T et al. Association of the TYMS 3G/3G genotype with poor response and GGH 354GG genotype with the bone marrow toxicity of the methotrexate in RA patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2013; 69: 377–383.
Plant D, Wilson AG, Barton A . Genetic and epigenetic predictors of responsiveness to treatment in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2014; 10: 329–337.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge collaborators from the Department of Rheumatology, University Medical Centre Ljubljana, Slovenia: Žiga Rotar and Alojzija Hočevar for referring the patients and Saša Čučnik and Katja Lakota for the support with sample collection. This work was financially supported by The Slovenian Research Agency (ARRS Grant No. P1-0170).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenko, B., Lusa, L., Tomsic, M. et al. Clinical–pharmacogenetic predictive models for MTX discontinuation due to adverse events in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics J 17, 412–418 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2016.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2016.36