Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Ultra-large-scale continuous-variable cluster states multiplexed in the time domain
Ultra-large-scale continuous-variable cluster states multiplexed in the time domain
A continuous-variable cluster state containing more than 10,000 entangled modes is deterministically generated and fully characterized. The developed time-domain multiplexing method allows each quantum mode to be manipulated by the same optical components at different times. An efficient scheme for measurement-based quantum computation on this cluster state is presented.
- Shota Yokoyama
- , Ryuji Ukai
- & Akira Furusawa
-
Letter |
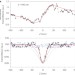 Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Two-, three- and higher multiphoton absorption processes are shown to occur in amyloid protein fibres, which are thought to play a role in various diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. The nonlinear optical behaviour of such proteins may also be useful for fabricating photonics devices.
- Piotr Hanczyc
- , Marek Samoc
- & Bengt Norden
-
-
-
-
Letter |
 Nonlinear laser lithography for indefinitely large-area nanostructuring with femtosecond pulses
Nonlinear laser lithography for indefinitely large-area nanostructuring with femtosecond pulses
A simple, rapid and inexpensive nanolithography technique is demonstrated that exploits nonlinear feedback mechanisms to tightly regulate the formation of nanostructures induced by femtosecond laser pulses. The nonlocal nature of the feedback allows the nanostructures to be seamlessly stitched, resulting in large-area nanostructuring whose periodicity is uniform on a subnanometre scale.
- Bülent Öktem
- , Ihor Pavlov
- & F. Ömer Ilday
-
-
News & Views |
 Nanophotonics for plasma heating
Nanophotonics for plasma heating
Vertically aligned nanowires on a solid surface in conjunction with table-top lasers create an ultrahigh-energy-density plasma with extremely high ionization in the laboratory.
- Lap Van Dao
- & Peter Hannaford
-
Review Article |
 Developments in laser-driven plasma accelerators
Developments in laser-driven plasma accelerators
Laser-driven plasma accelerators have the potential to replace existing particle accelerators, as they are highly efficient systems that are orders of magnitude smaller than conventional particle accelerators. This review discusses recent progress and future challenges in this area.
- S. M. Hooker
-
Letter |
 Miniature chiral beamsplitter based on gyroid photonic crystals
Miniature chiral beamsplitter based on gyroid photonic crystals
A chip-compatible beamsplitter that can separate left- and right-handed circularly polarized light is promising for constructing more sophisticated integrated optical circuits. The prism-shaped device, which operates around the telecommunication wavelength of 1.5 μm, consists of a photonic crystal composed of an array of helical structures.
- Mark D. Turner
- , Matthias Saba
- & Min Gu
-
Letter |
 Relativistic plasma nanophotonics for ultrahigh energy density physics
Relativistic plasma nanophotonics for ultrahigh energy density physics
Femtosecond laser pulses were used to heat dense matter, converting it into an extremely hot plasma. 52-times ionized gold was achieved as well as gigabar pressures, which can be exceeded only in the central hot spots of thermonuclear fusion plasmas.
- Michael A. Purvis
- , Vyacheslav N. Shlyaptsev
- & Jorge J. Rocca
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Superconducting emitters of THz radiation
Superconducting emitters of THz radiation
Recent progress on terahertz-emission devices based on the high-temperature superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ is reviewed. The emission mechanism is explained as a result of collective resonant modes in a stack of intrinsic Josephson junctions. Remarkable features of the linewidth, tunability, the optimum bias condition and the thermal influence are discussed.
- Ulrich Welp
- , Kazuo Kadowaki
- & Reinhold Kleiner
-
Article |
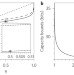 Electromagnetic channel capacity for practical purposes
Electromagnetic channel capacity for practical purposes
The long-standing problem of determining the classical communication capacities of Gaussian bosonic channels is addressed by determining upper and lower bounds for the classical capacities of important active and passive bosonic channels. The results apply to any bosonic thermal-noise channel, including electromagnetic signaling at any frequency.
- Vittorio Giovannetti
- , Seth Lloyd
- & Jeffrey H. Shapiro
-
Article |
 Terahertz polarization pulse shaping with arbitrary field control
Terahertz polarization pulse shaping with arbitrary field control
A terahertz pulse shaper based on optical rectification is proposed. The polarization of the terahertz pulses depends on the polarization selection rules for the rectification process in a GaP crystal. The terahertz pulse shaper can arbitrarily control the chirality, phase, pulse duration and frequency of circularly polarized few-cycle terahertz pulses.
- Masaaki Sato
- , Takuya Higuchi
- & Makoto Kuwata-Gonokami
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Squeezing more out of LIGO
Squeezing more out of LIGO
Further sensitivity improvements are required before advanced optical interferometers will be able to measure gravitational waves. A team has now shown that introducing quantum squeezing of light may help to detect these elusive waves.
- Ulrik L. Andersen
-
News & Views |
 Echoes of past solitons
Echoes of past solitons
Caging pairs of propagating solitons in a fibre ring resonator allows scientists to observe the solitons travelling astronomical distances, revealing the effects of extremely tiny forces exerted by the leading soliton on the trailing one.
- Franco Prati
-
Article |
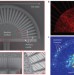 Compact spectrometer based on a disordered photonic chip
Compact spectrometer based on a disordered photonic chip
A miniature spectrometer has been developed that employs light scattering in a photonic chip with a random structure. It generates wavelength-dependent speckle patterns, which are detected and analysed to recover the spectrum of the input signal. It has a resolution of 0.75 nm in the 1,500 nm wavelength region.
- Brandon Redding
- , Seng Fatt Liew
- & Hui Cao
-
Letter |
 Circularly polarized light detection by a chiral organic semiconductor transistor
Circularly polarized light detection by a chiral organic semiconductor transistor
An organic field effect transistor featuring the chiral molecule helicene acts as a photodetector that is able to distinguish between left- and right-handed circularly polarized light.
- Ying Yang
- , Rosenildo Correa da Costa
- & Alasdair J. Campbell
-
Letter |
 Enhanced sensitivity of the LIGO gravitational wave detector by using squeezed states of light
Enhanced sensitivity of the LIGO gravitational wave detector by using squeezed states of light
Squeezed states of light have been experimentally demonstrated to improve the performance of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) in astrophysically relevant frequency regions. This enhanced performance may help to reach the sensitivity required for detecting gravitational waves.
- J. Aasi
- , J. Abadie
- & J. Zweizig
-
Article |
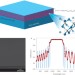 Tenfold reduction of Brownian noise in high-reflectivity optical coatings
Tenfold reduction of Brownian noise in high-reflectivity optical coatings
By employing monocrystalline semiconductor materials as high-quality optical coatings, the long-standing challenge of minimizing the optical phase noise produced by Brownian motion in a multilayer has been overcome. A thermally limited noise floor consistent with a tenfold reduction in mechanical damping relative to that in the best dielectric multilayers is achieved.
- Garrett D. Cole
- , Wei Zhang
- & Markus Aspelmeyer
-
Letter |
 Nonlinear Abbe theory
Nonlinear Abbe theory
Nonlinear optics can overcome the diffraction limit through the presence and interaction of many photons. Abbe's diffraction theory is now generalized to include spatial nonlinearity, and wave mixing is treated as a self-induced structured illumination, thereby allowing a standard imaging system to be nonlinearly enhanced beyond its conventional limits.
- Christopher Barsi
- & Jason W. Fleischer
-
Letter |
 An ultrafast terahertz scanning tunnelling microscope
An ultrafast terahertz scanning tunnelling microscope
An ultrafast terahertz (THz) scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) with subpicosecond time resolution and nanometre spatial resolution has been developed. THz pulses are coupled to the metal tip of a commercial STM and THz-pulse-induced tunnelling is observed in the STM. The THz-STM can directly image ultrafast carrier capture by a single InAs nanodot.
- Tyler L. Cocker
- , Vedran Jelic
- & Frank A. Hegmann
-
Article |
 Photonic streaking of attosecond pulse trains
Photonic streaking of attosecond pulse trains
An all-optical photonic streaking measurement is demonstrated that provides direct experimental access to individual attosecond pulses. The effects of non-adiabatic electron dynamics and plasma formation on the generated attosecond pulse train are directly observed when the pulse train is applied to harmonic generation in gases.
- Kyung Taec Kim
- , Chunmei Zhang
- & F. Quéré
-
Article |
 Ultraweak long-range interactions of solitons observed over astronomical distances
Ultraweak long-range interactions of solitons observed over astronomical distances
Recirculating temporal optical cavity solitons in a coherently driven passive optical fibre ring resonator allows pairs of solitons to interact over distances 8,000 times their width. This finding highlights the extreme stability, robustness and coherence of the process, and of solitons in general.
- Jae K. Jang
- , Miro Erkintalo
- & Stéphane Coen
-
-
News & Views |
 Two become one
Two become one
Scientists experimentally demonstrate a scheme that allows the number of qubits encoded per photon to be varied while keeping the overall quantum information constant. They also propose the inverse 'splitting' process.
- Jonas Schou Neergaard-Nielsen
-
News & Views |
 The effect of field gradient on SERS
The effect of field gradient on SERS
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy is normally associated with the enhanced electric fields that arise near metal nanoparticle surfaces. The contribution of field gradients has been unclear, but new research provides insights into their effect.
- Christine M. Aikens
- , Lindsey R. Madison
- & George C. Schatz
-
News & Views |
 Boson sampling on a chip
Boson sampling on a chip
Small-scale quantum computers made from an array of interconnected waveguides on a glass chip can now perform a task that is considered hard to undertake on a large scale by classical means.
- T. C. Ralph
-
Letter |
 Quantum-dense metrology
Quantum-dense metrology
Researchers demonstrate a laser interferometer that achieves simultaneous nonclassical readout of two conjugated observables. Because their system uses steady-state entanglement, it does not require any conditioning or post-selection. By distinguishing between scientific and parasitic signals, its sensitivity exceeds the standard quantum limit by about 6 dB.
- Sebastian Steinlechner
- , Jöran Bauchrowitz
- & Roman Schnabel
-
Letter |
 Towards isolated attosecond pulses at megahertz repetition rates
Towards isolated attosecond pulses at megahertz repetition rates
A fibre-laser-pumped optical parametric amplifier for high-harmonic generation has been used to realize a megahertz-repetition-rate source of extreme-ultraviolet continua, with evidence of isolated attosecond pulses at 0.6 MHz. This technique could potentially enable a vast array of new applications, such as attosecond-resolution coincidence and photoelectron spectroscopy.
- Manuel Krebs
- , Steffen Hädrich
- & Andreas Tünnermann
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Plasmon-boosted magneto-optics
Plasmon-boosted magneto-optics
Enhancing magneto-optic effects may help to reduce the size of photonic devices. Recent research by several groups shows that the features of metal optical components can be exploited to enhance typically weak magneto-optic effects.
- Ming Liu
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Versatile nanophotonics
Versatile nanophotonics
Nanophotonics is of both fundamental and applied importance. This field has a wide range of applications, including light-emitting devices and optical integrated circuits.
- Noriaki Horiuchi
-
Letter |
 Towards quantum-dot arrays of entangled photon emitters
Towards quantum-dot arrays of entangled photon emitters
An array of pyramidal site-controlled InGaAs1−δNδ quantum dots is grown on a GaAs substrate to reduce the fine-structure splitting of the intermediate single-exciton energy levels to less than 4 μeV. The quantum dots emit polarization-entangled photons at a maximum fidelity of 0.721 ± 0.043 without external manipulation of the electronic states.
- Gediminas Juska
- , Valeria Dimastrodonato
- & Emanuele Pelucchi
-
Letter |
 Certified quantum non-demolition measurement of a macroscopic material system
Certified quantum non-demolition measurement of a macroscopic material system
The first true quantum non-demolition measurement of atomic spins by paramagnetic Faraday rotation in a quantum atom–light interface is described. By using an ensemble of 87Rb atoms, quantum state preparation and information–damage trade-off are observed beyond their classical limits by 7 and 12 standard deviations, respectively.
- R. J. Sewell
- , M. Napolitano
- & M. W. Mitchell
-
Letter |
 Experimental boson sampling
Experimental boson sampling
The boson-sampling problem is experimentally solved by implementing Aaronson and Arkhipov's model of computation with photons in integrated optical circuits. These results set a benchmark for a type of quantum computer that can potentially outperform a conventional computer by using only a few photons and linear optical elements.
- Max Tillmann
- , Borivoje Dakić
- & Philip Walther
-
Letter |
 Joining the quantum state of two photons into one
Joining the quantum state of two photons into one
Quantum information circuits for ‘quantum joining’ are proposed, in which two qubits of information encoded in the polarization of two photons are re-encoded into the polarization and path degrees of freedom of a single photon, while keeping the overall quantum information constant. The inverse ‘splitting’ process is also proposed.
- Chiara Vitelli
- , Nicolò Spagnolo
- & Lorenzo Marrucci
-
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Applied physics
- Astronomy and astrophysics
- Atomic and molecular physics
- Biological physics
- Chemical physics
- Condensed-matter physics
- Electronics, photonics and device physics
- Fluid dynamics
- Information theory and computation
- Nuclear physics
- Optical physics
- Particle physics
- Plasma physics
- Quantum physics
- Space physics
- Statistical physics, thermodynamics and nonlinear dynamics
- Techniques and instrumentation

 Optically pumped room-temperature GaAs nanowire lasers
Optically pumped room-temperature GaAs nanowire lasers Extended storage times
Extended storage times Bright terahertz sources
Bright terahertz sources Rocking phase bistability
Rocking phase bistability Total control of ultracold atoms
Total control of ultracold atoms