Volume 20
-
No. 12 December 2021
Elastic magnetic composites for bioelectronicsMicromagnets dispersed in a polymer matrix are used to realize a soft magnetoelastic generator with high magnetomechanical coupling factor, used for wearable and implantable power generation and sensing applications.
See Zhou et al.
-
No. 11 November 2021
Nano-strutted tube-in-tube carbon latticeA nanoscale tube-in-tube sandwich structure is generated by a two-step templating-pyrolysis process, which strengthens the log-pile carbon architecture and slows down the decrease of stiffness with decreasing density.
See Ye et al.
-
No. 10 October 2021
Simulating 3D network polymer formationA computational platform describing the spatial and temporal interactions of monomers during the formation of network polymers provides structure–property relationships that are used to synthesize 3D network polymers with tailored functionalities.
See De Keer et al.
-
No. 9 September 2021
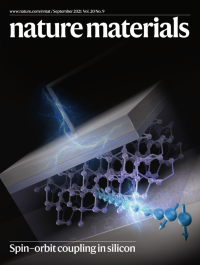
Spin-orbit coupling in siliconSilicon is a light element with high lattice inversion symmetry, and so is not expected to possess a substantial spin–orbit interaction (SOI), which is desirable for spintronics. Here, a silicon-based heterostructure is demonstrated to have a gate-tuneable Rashba-type SOI.
See Lee et al. and Marrows
-
No. 8 August 2021
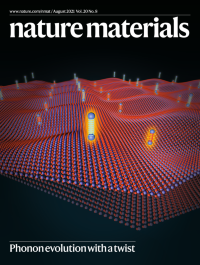
Phonon evolution with a twistRaman measurements of twisted bilayer MoS2 as a function of twist angles, with theoretical support, reveal phonon renormalization in this moiré superlattice.
See Quan et al.
-
No. 7 July 2021
High-rate nanofluidic energy absorptionPorous materials can absorb energy by water infiltration, but studies at industrially relevant high-rate intrusions are rare. Here, high-rate experiments are performed on ZIFs showing high energy storage capacity, while molecular simulations allow design rules to be formulated for absorption materials.
See Sun et al.
-
No. 6 June 2021
Hot and bright graphene plasmonsThe optical emission of graphene under pumping with femtosecond laser pulses contains a strong component linked to plasmon emission from the hot electrons in the system.
See Kim et al.
-
No. 5 May 2021
Ultrafast non-thermal lattice control of magnetic interactionsNon-thermal lattice control of exchange interactions allows for picosecond coherent switching between competing antiferromagnetic and weakly ferromagnetic order.
See Afanasiev et al.
-
No. 4 April 2021
Chirality-driven wound repairMicroporous annealed-particle degradable scaffolds have been developed and shown to induce type 2 innate and adaptive immune response that facilitated skin wound healing.
See Griffin et al. and Stelzel and Doloff
-
No. 3 March 2021
Water-responsive peptide crystalsExperiments and molecular dynamics simulations show that the dehydration-induced actuation of nanoporous tripeptide crystals is a result of pore contraction caused by the strengthening of the water hydrogen-bonding network inside the pore, which creates mechanical stress that deforms the crystal lattice.
See Piotrowska et al.
-
No. 2 February 2021
Bioengineering tools to generate organoidsType-1 innate lymphoid cells have been shown to drive intestinal epithelial proliferation and extracellular matrix remodelling through TGF-β1 secretion, which could exacerbate inflammatory bowel disease comorbidities such as cancer and fibrosis.
See Jowett et al.
-
No. 1 January 2021
Nanoscale lithography of metal–organic frameworksThe low dielectric constants and high porosity of MOFs are of interest for applications in electronics and sensors, but patterning techniques for these materials are in their infancy. Here, direct X-ray and electron-beam lithography at sub-50-nm resolution are reported that leave porosity and crystallinity intact.
See Tu et al. and Faustini