Volume 2
-
No. 12 December 2021
Year in ReviewThis month we present a dedicated Focus on 2021 in Review issue that includes news, analysis and comment on the most exciting advances and biggest challenges of the past year, together with a selection of the most popular primary research articles published in Nature Cancer over the last 12 months.
See our December Editorial and associated Focus content.
-
No. 11 November 2021
The proteogenomics landscape of non-small cell lung cancerProteogenomic analysis of patient-derived samples provides insights into the biology and molecular classification of non-small cell lung cancer and identifies potential cancer-cell intrinsic and immune vulnerabilities.
See Lehtiö et al.
-
No. 10 October 2021
Understanding resistance to brain tumor microenvironment–targeted therapyResistance to inhibitionof CSF1R in breast cancer metastasis to the brain is driven by compensatory activation of the CSF2Rb–STAT5 axis in macrophages, which can be alleviated by combined targeting of CSF1R and STAT5.
See Klemm et al.
-
No. 9 September 2021
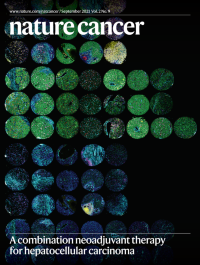
Profiling immune responses to combination neoadjuvant therapy for hepatocellular carcinomaHigh-dimensional profiling of tumor biopsies identifies features of the immune microenvironment associated with response to neoadjuvant treatment with a combination of the targeted kinase inhibitor cabozantinib and the immune-checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab, in a phase 1b clinical trial for hepatocellular carcinoma.
See Ho et al.
-
No. 8 August 2021
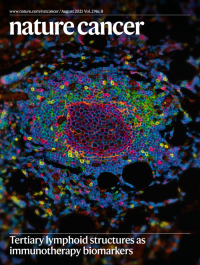
Tertiary lymphoid structures as immunotherapy biomarkersThe presence of mature tertiary lymphoid structures, which are composed of a T cell zone and a B cell zone that forms a germinal center, is an independent predictor of response to immune-checkpoint blockers in multiple cohorts of patients with cancer.
See Vanhersecke et al.
-
No. 7 July 2021
Cross-resistance between targeted therapy and immunotherapyAcquired resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors in melanoma confers cross-resistance to immune-checkpoint blockade by fostering a cancer cell–instructed immunoevasive tumor microenvironment. The hourglass represents the time before therapy and after relapse on therapy, and the bottleneck imposed by targeted therapy that ultimately selects for cross-resistant clones.
See Haas et al.
-
No. 6 June 2021
Mutational signatures of endogenous DNA damageWhole-genome sequencing identifies characteristic mutational signatures attributed to CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of specific DNA replication/repair pathway genes, which may be useful as biomarkers for ongoing and potentially targetable processes in tumor development.
See Zou et al.
-
No. 5 May 2021
Restoring anti-tumor immunity with autophagy inhibitionInhibiting autophagy by targeting the ATG1–ULK1 pathway restores impaired immunoproteasome activity and antigen presentation, to enhance T cell recognition of lung tumor cells expressing a mutant form of the tumor suppressor LKB1.
See Deng et al.. See also related News & Views article by Thorburn & Towers.
-
No. 4 April 2021
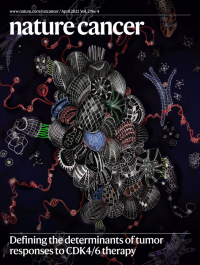
Defining the determinants of tumor responses to CDK4/6 therapyThe thermostability of the kinase CDK6 and the protein complexes that it forms determine the tumor response to CDK4/6 inhibitors and CDK4/6-directed degraders. Here, thermo-unstable CDK6 is depicted in the cytosol as a multi-protein complex that includes the chaperone HSP90 and adaptor CDC37 and is accessible to a small-molecule inhibitor.
See Wu et al., and also the related News & Views article by Caksia and Aplin.
-
No. 3 March 2021
Advancing Cancer TherapyIn this issue, we are launching a Series on Cancer Therapy comprising commissioned Reviews and Perspectives that highlight emerging concepts, recent advances and the challenges ahead in cancer therapy, and a selection of primary research articles on this topic published in Nature Cancer.
See our March Editorial, as well as the Review articles by Esposito et al. and by Mukhopadhyay et al.
-
No. 2 February 2021
Parsing glioblastoma heterogeneity for redefined classificationAnalysis of glioblastoma heterogeneity can classify the disease according to four fundamental functional properties, depicted here as branches of one tree. Genetic alterations common to these four subtypes are within the glioblastoma trunk, but each subtype diverges through distinct genetic lesions and gene-expression programs that incorporate prognostic and therapeutic attributes.
See Garofano et al. See also the articles by Richards et al. and Castellan et al., and the related News & Views by Hubert and Lathia
-
No. 1 January 2021
One year of Nature CancerThis month we celebrate one year of Nature Cancer with a specially curated collection of Nature Cancer articles and a new type of commissioned Clinical Outlook articles.
See Editorial and the One Year of Nature Cancer collection