Abstract
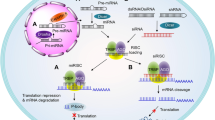
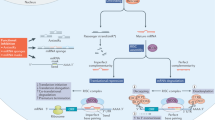
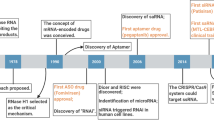
Harnessing RNA interference using small RNA-based drugs has great potential to develop drugs designed to knock down expression of any disease-causing gene, thereby greatly expanding the universe of possible drug targets. However, delivering small RNAs into specific tissues and cells is still a hurdle. Here, we review recent progress in overcoming systemic, local and cellular barriers to RNA drug delivery, focusing on strategies for targeted uptake.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Amarzguioui M, Rossi JJ, Kim D . Approaches for chemically synthesized siRNA and vector-mediated RNAi. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 5974–5981.
Sledz CA, Williams BR . RNA interference in biology and disease. Blood 2005; 106: 787–794.
de Fougerolles A, Vornlocher HP, Maraganore J, Lieberman J . Interfering with disease: a progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007; 6: 443–453.
Song E, Lee SK, Dykxhoorn DM, Novina C, Zhang D, Crawford K et al. Sustained small interfering RNA-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibition in primary macrophages. J Virol 2003; 77: 7174–7181.
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N, Min J et al. RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med 2003; 9: 347–351.
Palliser D, Chowdhury D, Wang QY, Lee SJ, Bronson RT, Knipe DM et al. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature 2006; 439: 89–94.
Robbins M, Judge A, Ambegia E, Choi C, Yaworski E, Palmer L et al. Misinterpreting the therapeutic effects of siRNA caused by immune stimulation. Hum Gene Ther 2008; 19: 991–999.
Kleinman ME, Yamada K, Takeda A, Chandrasekaran V, Nozaki M, Baffi JZ et al. Sequence- and target-independent angiogenesis suppression by siRNA via TLR3. Nature 2008; 452: 591–597.
Ma M, Zhou L, Guo X, Lv Z, Yu Y, Ding C et al. Decreased cofilin1 expression is important for compaction during early mouse embryo development. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 1804–1810.
Bose S, Leclerc GM, Vasquez-Martinez R, Boockfor FR . Administration of connexin43 siRNA abolishes secretory pulse synchronization in GnRH clonal cell populations. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010; 314: 75–83.
Wiese M, Castiglione K, Hensel M, Schleicher U, Bogdan C, Jantsch J . Small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery into murine bone marrow-derived macrophages by electroporation. J Immunol Methods 2010; 353: 102–110.
Honjo K, Takahashi KA, Mazda O, Kishida T, Shinya M, Tokunaga D et al. MDR1a/1b gene silencing enhances drug sensitivity in rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Gene Med 2010; 12: 219–227.
Donze O, Picard D . RNA interference in mammalian cells using siRNAs synthesized with T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: e46.
Tsubouchi A, Sakakura J, Yagi R, Mazaki Y, Schaefer E, Yano H et al. Localized suppression of RhoA activity by Tyr31/118-phosphorylated paxillin in cell adhesion and migration. J Cell Biol 2002; 159: 673–683.
Huang YZ, Zang M, Xiong WC, Luo Z, Mei L . Erbin suppresses the MAP kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 1108–1114.
Zhang M, Bai CX, Zhang X, Chen J, Mao L, Gao L . Downregulation enhanced green fluorescence protein gene expression by RNA interference in mammalian cells. RNA Biol 2004; 1: 74–77.
Gosain AK, Machol JA, Gliniak C, Halligan NL . TGF-beta1 RNA interference in mouse primary dura cell culture: downstream effects on TGF receptors, FGF-2, and FGF-R1 mRNA levels. Plast Reconstr Surg 2009; 124: 1466–1473.
Cheng SQ, Wang WL, Yan W, Li QL, Wang L, Wang WY . Knockdown of survivin gene expression by RNAi induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7721. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: 756–759.
Baker BE, Kestler DP, Ichiki AT . Effects of siRNAs in combination with Gleevec on K-562 cell proliferation and Bcr-Abl expression. J Biomed Sci 2006; 13: 499–507.
Crombez L, Charnet A, Morris MC, Aldrian-Herrada G, Heitz F, Divita G . A non-covalent peptide-based strategy for siRNA delivery. Biochem Soc Trans 2007; 35: 44–46.
Muratovska A, Eccles MR . Conjugate for efficient delivery of short interfering RNA (siRNA) into mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 2004; 558: 63–68.
Minakuchi Y, Takeshita F, Kosaka N, Sasaki H, Yamamoto Y, Kouno M et al. Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e109.
Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Muramatsu T . A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3365–3370.
Puebla I, Esseghir S, Mortlock A, Brown A, Crisanti A, Low W . A recombinant H1 histone-based system for efficient delivery of nucleic acids. J Biotechnol 2003; 105: 215–226.
Lv H, Zhang S, Wang B, Cui S, Yan J . Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery. J Control Release 2006; 114: 100–109.
Kedmi R, Ben-Arie N, Peer D . The systemic toxicity of positively charged lipid nanoparticles and the role of Toll-like receptor 4 in immune activation. Biomaterials 2010; 31: 6867–6875.
Wu Y, Navarro F, Lal A, Basar E, Pandey RK, Manoharan M et al. Durable protection from Herpes Simplex Virus-2 transmission following intravaginal application of siRNAs targeting both a viral and host gene. Cell Host Microbe 2009; 5: 84–94.
Lee YS, Pressman S, Andress AP, Kim K, White JL, Cassidy JJ et al. Silencing by small RNAs is linked to endosomal trafficking. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1150–1156.
Zimmermann TS, Lee AC, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Bumcrot D, Fedoruk MN et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2006; 441: 111–114.
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1002–1007.
Geisbert TW, Hensley LE, Kagan E, Yu EZ, Geisbert JB, Daddario-DiCaprio K et al. Postexposure protection of guinea pigs against a lethal ebola virus challenge is conferred by RNA interference. J Infect Dis 2006; 193: 1650–1657.
Villares GJ, Zigler M, Wang H, Melnikova VO, Wu H, Friedman R et al. Targeting melanoma growth and metastasis with systemic delivery of liposome-incorporated protease-activated receptor-1 small interfering RNA. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9078–9086.
Landen Jr CN, Chavez-Reyes A, Bucana C, Schmandt R, Deavers MT, Lopez-Berestein G et al. Therapeutic EphA2 gene targeting in vivo using neutral liposomal small interfering RNA delivery. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6910–6918.
Anderson DG, Akinc A, Hossain N, Langer R . Structure/property studies of polymeric gene delivery using a library of poly(beta-amino esters). Mol Ther 2005; 11: 426–434.
Akinc A, Zumbuehl A, Goldberg M, Leshchiner ES, Busini V, Hossain N et al. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 561–569.
Honma K, Iwao-Koizumi K, Takeshita F, Yamamoto Y, Yoshida T, Nishio K et al. RPN2 gene confers docetaxel resistance in breast cancer. Nat Med 2008; 14: 939–948.
Fujii T, Saito M, Iwasaki E, Ochiya T, Takei Y, Hayashi S et al. Intratumor injection of small interfering RNA-targeting human papillomavirus 18 E6 and E7 successfully inhibits the growth of cervical cancer. Int J Oncol 2006; 29: 541–548.
Mu P, Nagahara S, Makita N, Tarumi Y, Kadomatsu K, Takei Y . Systemic delivery of siRNA specific to tumor mediated by atelocollagen: combined therapy using siRNA targeting Bcl-xL and cisplatin against prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 2978–2990.
Wolfrum C, Shi S, Jayaprakash KN, Jayaraman M, Wang G, Pandey RK et al. Mechanisms and optimization of in vivo delivery of lipophilic siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2007; 25: 1149–1157.
Nishina K, Unno T, Uno Y, Kubodera T, Kanouchi T, Mizusawa H et al. Efficient in vivo delivery of siRNA to the liver by conjugation of alpha-tocopherol. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 734–740.
Lorenz C, Hadwiger P, John M, Vornlocher HP, Unverzagt C . Steroid and lipid conjugates of siRNAs to enhance cellular uptake and gene silencing in liver cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 4975–4977.
Rozema DB, Lewis DL, Wakefield DH, Wong SC, Klein JJ, Roesch PL et al. Dynamic PolyConjugates for targeted in vivo delivery of siRNA to hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 12982–12987.
Kortylewski M, Swiderski P, Herrmann A, Wang L, Kowolik C, Kujawski M et al. In vivo delivery of siRNA to immune cells by conjugation to a TLR9 agonist enhances antitumor immune responses. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 925–932.
McNamara II JO, Andrechek ER, Wang Y, Viles KD, Rempel RE, Gilboa E et al. Cell type-specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 1005–1015.
Dassie JP, Liu XY, Thomas GS, Whitaker RM, Thiel KW, Stockdale KR et al. Systemic administration of optimized aptamer-siRNA chimeras promotes regression of PSMA-expressing tumors. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 839–849.
Zhou J, Li H, Li S, Zaia J, Rossi JJ . Novel dual inhibitory function aptamer-siRNA delivery system for HIV-1 therapy. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1481–1489.
Zhou J, Swiderski P, Li H, Zhang J, Neff CP, Akkina R et al. Selection, characterization and application of new RNA HIV gp 120 aptamers for facile delivery of Dicer substrate siRNAs into HIV infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: 3094–3109.
Wheeler L, Trifonova R, Vrbanac V, Basar E, McKernan S, Xu Z et al. CD4 aptamer-siRNA chimeras inhibit HIV infection in primary CD4+ cells in vitro and in polarized human cervicovaginal explants and prevent vaginal transmission in humanized mice. J Clin Invest 2011 (in press).
Song E, Zhu P, Lee SK, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 709–717.
Yao Y, Sun T, Huang S, Dou S, Lin L, Mao C et al. Targeted Delivery of PLK1-siRNA by Single-Chain Antibody Suppresses Her2+ Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis. 2011. Submitted.
Shimaoka M, Takagi J, Springer TA . Conformational regulation of integrin structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 2002; 31: 485–516.
Peer D, Zhu P, Carman CV, Lieberman J, Shimaoka M . Selective gene silencing in activated leukocytes by targeting siRNAs to the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 4095–4100.
Kumar P, Ban HS, Kim SS, Wu H, Pearson T, Greiner DL et al. T cell-specific siRNA delivery suppresses HIV-1 infection in humanized mice. Cell 2008; 134: 577–586.
Subramanya S, Kim SS, Abraham S, Yao J, Kumar M, Kumar P et al. Targeted delivery of small interfering RNA to human dendritic cells to suppress dengue virus infection and associated proinflammatory cytokine production. J Virol 2010; 84: 2490–2501.
Schiffelers RM, Ansari A, Xu J, Zhou Q, Tang Q, Storm G et al. Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e149.
Hu-Lieskovan S, Heidel JD, Bartlett DW, Davis ME, Triche TJ . Sequence-specific knockdown of EWS-FLI1 by targeted, nonviral delivery of small interfering RNA inhibits tumor growth in a murine model of metastatic Ewing′s sarcoma. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8984–8992.
Davis ME . The first targeted delivery of siRNA in humans via a self-assembling, cyclodextrin polymer-based nanoparticle: from concept to clinic. Mol Pharm 2009; 6: 659–668.
Davis ME, Zuckerman JE, Choi CH, Seligson D, Tolcher A, Alabi CA et al. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature 2010; 464: 1067–1070.
Peer D, Park EJ, Morishita Y, Carman CV, Shimaoka M . Systemic leukocyte-directed siRNA delivery revealing cyclin D1 as an anti-inflammatory target. Science 2008; 319: 627–630.
Kim SS, Peer D, Kumar P, Subramanya S, Wu H, Asthana D et al. RNAi-mediated CCR5 silencing by LFA-1-targeted nanoparticles prevents HIV infection in BLT mice. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 370–376.
Sato Y, Murase K, Kato J, Kobune M, Sato T, Kawano Y et al. Resolution of liver cirrhosis using vitamin A-coupled liposomes to deliver siRNA against a collagen-specific chaperone. Nature Biotech 2008; 4: 431–442.
Pirollo KF, Rait A, Zhou Q, Hwang SH, Dagata JA, Zon G et al. Materializing the potential of small interfering RNA via a tumor-targeting nanodelivery system. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2938–2943.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by grants from the Alon Foundation, the Marie Curie IRG-FP7 of the European Union, Levy Family Trust and ISF (181/10) to DP, the Breast Cancer Research Program of the US Department of Defense to JL, and by a joint BSF grant (2009107) to DP and JL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
D Peer declares financial interest in Quiet Therapeutics; J Lieberman is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peer, D., Lieberman, J. Special delivery: targeted therapy with small RNAs. Gene Ther 18, 1127–1133 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.56
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.56
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NAxtra magnetic nanoparticles for low-cost, efficient isolation of mammalian DNA and RNA
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The race to develop oral SERDs and other novel estrogen receptor inhibitors: recent clinical trial results and impact on treatment options
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2022)
-
Role of MicroRNAs, Aptamers in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2017)
-
Oncogene Knockdown via Active Loading of Small RNAs into Extracellular Vesicles by Sonication
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2016)