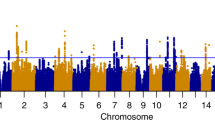
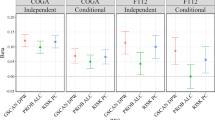
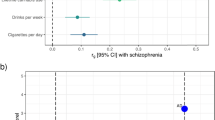
Abstract
We introduce a method for detecting variants in several genes of related function with small effect on a phenotype of interest. Our method uses logistic regression to test whether multiple alleles within a functional set have significantly higher than expected predictive value, even though none individually may have strong individual effects. We illustrate this method by testing seven gene sets (including 48 genes), from a study with1350 single nucleotide polymorphisms in 130 addiction candidate genes studied in a sample of 575 alcohol dependence (AD) cases and 530 controls. We conclude that AD is related to variation in genes participating in Glutamate and γ-amino butyric acid signaling, as has been reported elsewhere, and in stress response pathways, but not with genes in several other systems implicated in other drugs of abuse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sullivan PF, Neale BM, van den Oord E, Miles MF, Neale MC, Bulik CM et al. Candidate genes for nicotine dependence via linkage, epistasis, and bioinformatics. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2004; 126: 23–36.
Sullivan PF, O′Neill FA, Walsh D, Ma Y, Kendler KS, Straub RE . Analysis of epistasis in linked regions in the Irish study of high-density schizophrenia families. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 266–270.
Zammit S, Jones G, Jones SJ, Norton N, Sanders RD, Milham C et al. Polymorphisms in the MAOA, MAOB, and COMT genes and aggressive behavior in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2004; 128: 19–20.
Qin S, Zhao X, Pan Y, Liu J, Feng G, Fu J et al. An association study of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit gene (GRIN1) and NR2B subunit gene (GRIN2B) in schizophrenia with universal DNA microarray. Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 807–814.
Ott U, Reuter M, Hennig J, Vaitl D . Evidence for a common biological basis of the absorption trait, hallucinogen effects, and positive symptoms: epistasis between 5-HT2a and COMT polymorphisms. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 137: 29–32.
Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe’er I et al. Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 753–757.
Sullivan PF, Lin D, Tzeng JY, van den Oord E, Perkins D, Stroup TS et al. Genomewide association for schizophrenia in the CATIE study: results of stage 1. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 570–584.
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O′Donovan MC, Sullivan PF et al. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 2009; 460: 748–752.
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 744–747.
Wang K, Li M, Bucan M . Pathway-based approaches for analysis of genomewide association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81.
Holmans P, Green EK, Pahwa JS, Ferreira MA, Purcell SM, Sklar P et al. Gene ontology analysis of GWA study data sets provides insights into the biology of bipolar disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 85: 13–24.
Dinu V, Zhao H, Miller PL . Integrating domain knowledge with statistical and data mining methods for high-density genomic SNP disease association analysis. J Biomed Inform 2007; 40: 750–760.
Weedon MN, Lango H, Lindgren CM, Wallace C, Evans DM, Mangino M et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies 20 loci that influence adult height. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 575–583.
Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, Craddock N, Deloukas P, Duncanson A et al. Genome-wide association study of 14 000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
Petretto E, Liu ET, Aitman TJ . A gene harvest revealing the archeology and complexity of human disease. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1299–1301.
Prescott CA, Sullivan PF, Myers JM, Patterson DG, Devitt M, Halberstadt LJ et al. The Irish Affected Sib Pair Study of alcohol dependence: study methodology and validation of diagnosis by interview and family history. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2005; 29: 417–429.
Bucholz KK, Cadoret R, Cloninger CR, Dinwiddie SH, Hesselbrock VM, Nurnberger JI, Jr et al. A new, semi-structured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: a report on the reliability of the SSAGA. J Stud Alcohol 1994; 55: 149–158.
Hodgkinson CE, Xu K, Yuan Q, Shen P-H, Heinz E, Ehlers C et al. Addictions biology: haplotype based analysis for 130 candidate genes on a single array. Alcohol Alcohol 2008; 43: 505–515.
Koob GF, Le Moal M . Alcohol. In: Koob GF, Le Moal M (eds). Neurobiology of Addiction. Elsevier: London, 2006; pp. 173–242.
Edenberg HJ, Dick DM, Xuei X, Tian H, Almasy L, Bauer LO et al. Variations in GABRA2, encoding the alpha 2 subunit of the GABA(A) receptor, are associated with alcohol dependence and with brain oscillations. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 705–714.
Dick DM, Edenberg HJ, Xuei X, Goate A, Hesselbrock V, Schuckit M et al. No association of the GABAA receptor genes on chromosome 5 with alcoholism in the collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism sample. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 132B: 24–28.
Sander T, Harms H, Lesch KP, Dufeu P, Kuhn S, Hoehe M et al. Association analysis of a regulatory variation of the serotonin transporter gene with severe alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1997; 21: 1356–1359.
Loh EW, Smith I, Murray R, McLaughlin M, McNulty S, Ball D . Association between variants at the GABAAbeta2, GABAAalpha6 and GABAAgamma2 gene cluster and alcohol dependence in a Scottish population. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 539–544.
Song J, Koller DL, Foroud T, Carr K, Zhao J, Rice J et al. Association of GABA(A) receptors and alcohol dependence and the effects of genetic imprinting. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2003; 117B: 39–45.
Noble EP, Zhang X, Ritchie T, Lawford BR, Grosser SC, Young RM et al. D2 dopamine receptor and GABA(A) receptor beta3 subunit genes and alcoholism. Psychiatry Res 1998; 81: 133–147.
Mohler H . GABA(A) receptor diversity and pharmacology. Cell Tissue Res 2006; 326: 505–516.
Tsai G, Coyle JT . The role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the pathophysiology of alcoholism. Annu Rev Med 1998; 49: 173–184.
Chandler LJ, Carpenter-Hyland E, Hendricson AW, Maldve RE, Morrisett RA, Zhou FC et al. Structural and functional modifications in glutamateric synapses following prolonged ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2006; 30: 368–376.
Rujescu D, Soyka M, Dahmen N, Preuss U, Hartmann AM, Giegling I et al. GRIN1 locus may modify the susceptibility to seizures during alcohol withdrawal. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 133B: 85–87.
Wernicke C, Samochowiec J, Schmidt LG, Winterer G, Smolka M, Kucharska-Mazur J et al. Polymorphisms in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 1 and 2B subunits are associated with alcoholism-related traits. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 54: 922–928.
Ron D . Signaling cascades regulating NMDA receptor sensitivity to ethanol. Neuroscientist 2004; 10: 325–336.
Kalluri HS, Mehta AK, Ticku MK . Up-regulation of NMDA receptor subunits in rat brain following chronic ethanol treatment. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998; 58: 221–224.
Schumann G, Johann M, Frank J, Preuss U, Dahmen N, Laucht M et al. Systematic analysis of glutamatergic neurotransmission genes in alcohol dependence and adolescent risky drinking behavior. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008; 65: 826–838.
Prendergast MA, Little HJ . Adolescence, glucocorticoids and alcohol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2007; 86: 234–245.
Oswald LM, Wand GS . Opioids and alcoholism. Physiol Behav 2004; 81: 339–358.
Morrow AL, Porcu P, Boyd KN, Grant KA . Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis modulation of GABAergic neuroactive steroids influences ethanol sensitivity and drinking behavior. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2006; 8: 463–477.
Schuckit MA, Gold E, Risch C . Plasma cortisol levels following ethanol in sons of alcoholics and controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1987; 44: 942–945.
Zimmerman U, Spring K, Koller G, Holsboer F, Soyka M . Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system regulation in recently detoxified alcoholics is not altered by one week of treatment with acamprosate. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004; 37: 98–102.
Barr CS, Dvoskin RL, Yuan Q, Lipsky RH, Gupte M, Hu X et al. CRH haplotype as a factor influencing cerebrospinal fluid levels of corticotropin-releasing hormone, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity, temperament, and alcohol consumption in rhesus macaques. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008; 65: 934–944.
Blomeyer D, Treutlein J, Esser G, Schmidt MH, Schumann G, Laucht M . Interaction between CRHR1 gene and stressful life events predicts adolescent heavy alcohol use. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 63: 146–151.
Treutlein J, Kissling C, Frank J, Wiemann S, Dong L, Depner M et al. Genetic association of the human corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1 (CRHR1) with binge drinking and alcohol intake patterns in two independent samples. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 594–602.
Enoch MA, Shen PH, Ducci F, Yuan Q, Liu J, White KV et al. Common genetic origins for EEG, alcoholism and anxiety: the role of CRH-BP. PLoS One 2008; 3: e3620.
Kertes DA, Kalsi G, Prescott CA, Kendler KS, Riley B . Neurotransmitter and neuromodulator genes associated with a history of depressive symptoms in individuals with alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2011; 35: 1–11.
Claes SJ . Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in psychiatry: from stress to psychopathology. Ann Med 2004; 36: 50–61.
Silva SM, Paula-Barbosa MM, Madeira MD . Prolonged alcohol intake leads to reversible depression of corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin immunoreactivity and mRNA levels in the parvocellular neurons of the paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res 2002; 954: 82–93.
Koob GF, Le Moal M . Review. Neurobiological mechanisms for opponent motivational processes in addiction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2008; 363: 3113–3123.
Grant BF, Stinson FS, Dawson DA, Chou SP, Dufour MC, Compton W et al. Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independent mood and anxiety disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61: 807–816.
Comings DE, Gade-Andavolu R, Gonzalez N, Wu S, Muhleman D, Blake H et al. Comparison of the role of dopamine, serotonin, and noradrenaline genes in ADHD, ODD and conduct disorder: multivariate regression analysis of 20 genes. Clin Genet 2000; 57: 178–196.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the study participants and their families for their time and effort. FA O’Neill, the Northern Ireland Blood Transfusion Service of the British National Health Service and the Irish Garda provided assistance in obtaining control blood samples. Funding: this work was funded by U.S. National Institutes of Health Grant R01-AA-11408 and P20 AA017828, with support from the Irish Health Research Board.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reimers, M., Riley, B., Kalsi, G. et al. Pathway based analysis of genotypes in relation to alcohol dependence. Pharmacogenomics J 12, 342–348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.10
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.10