Abstract
Glaciers in the Himalaya–Karakoram mountain ranges harbour approximately half of the ice volume in High-mountain Asia and modulate the flow of freshwater to almost 869 million people within the Indus, Tarim, Ganges and Brahmaputra river basins. Since the mid-twentieth century, rising temperatures have led to unsustainably high melting rates for many glaciers, particularly in the Himalaya, temporarily increasing summer meltwater run-off but continuously reducing the ice-storage volume. In this Review, we discuss how and why glaciers and meltwater supplies have changed, how they will likely evolve in the future and how these changes impact water resources and water-related hazards. Heterogeneous glacier retreat is changing streamflow patterns, in turn, affecting the incidence of glacial-lake outburst floods and exacerbating the risk of flooding and water shortages associated with future climate change. These changes could negatively impact downstream populations and infrastructure, including the thriving hydropower sector and some of the world’s largest irrigated agriculture systems, by making water flow more extreme and unpredictable. An improved in situ monitoring network for weather, hydrology and glacier change is a crucial requirement for predicting the future of this resource and associated hazards, and their impact on regional water, energy and food security.
Key points
-
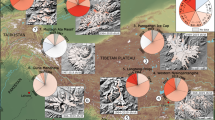
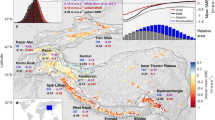
Himalayan glaciers have lost mass at an accelerating rate in recent decades, in contrast with relatively stable Karakoram glaciers.
-
Under a range of climate change scenarios, the run-off of glacier meltwater in the Himalaya and Karakoram is likely to peak in the next few decades.
-
After glacial run-off peaks, run-off will decline as the glaciers in both mountain ranges shrink, although the magnitude and timing of the peak and the rate of subsequent decline are uncertain.
-
Basin run-off regimes will become more rain-dominated as the modulating effect of glaciers decreases, and this is likely to increase the impact of droughts and floods.
-
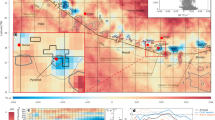
The frequency of glacial-lake outburst floods and run-off floods have increased recently and could increase further in coming decades, threatening existing and planned hydropower infrastructure downstream.
-
A lower-emissions climate change pathway would reduce the rate of glacier loss, increasing the time available for adaptation. This pathway would have considerable socio-economic benefits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$99.00 per year
only $8.25 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Immerzeel, W. W., van Beek, L. P. H. & Bierkens, M. F. P. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328, 1382–1385 (2010).
Immerzeel, W. W. et al. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 577, 364–369 (2020).
Yao, T. et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Change 2, 663–667 (2012).
Rounce, D. R., Hock, R. & Shean, D. E. Glacier mass change in high mountain Asia through 2100 using the open-source Python Glacier Evolution Model (PyGEM). Front. Earth Sci. 7, 331 (2020).
Farinotti, D. et al. A consensus estimate for the ice thickness distribution of all glaciers on Earth. Nat. Geosci. 12, 168–173 (2019). Revealed the ice thickness of global glaciers and provided a baseline data for ice volume on the mountain-range scale.
RGI Consortium. Randolph Glacier Inventory – A Dataset of Global Glacier Outlines: Version 6.0: Technical Report. Global Land Ice Measurements from Space, Colorado, USA. https://doi.org/10.7265/N5-RGI-60 (2017).
Pfeffer, W. T. et al. The Randolph Glacier Inventory: a globally complete inventory of glaciers. J. Glaciol. 60, 537–552 (2014).
Wang, X., Liu, S. & Zhang, J. A new look at roles of the cryosphere in sustainable development. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 10, 124–131 (2019).
Viviroli, D., Kummu, M., Meybeck, M., Kallio, M. & Wada, Y. Increasing dependence of lowland populations on mountain water resources. Nat. Sustain. 3, 917–928 (2020).
Biemans, H. et al. Importance of snow and glacier meltwater for agriculture on the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Nat. Sustain. 2, 594–601 (2019). Quantified the role of meltwater in various major agricultural crops.
Bolch, T. et al. The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 336, 310–314 (2012).
Pritchard, H. D. Asia’s shrinking glaciers protect large populations from drought stress. Nature 569, 649–654 (2019). Identified and quantified the role of Asian glaciers in buffering against droughts.
Rose, A. N., Mckee, J. J., Urban, M. L. & Bright, E. A. LandScan 2017. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN (2018).
Bolch, T. et al. in The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment (eds Wester, P., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A. & Shrestha, A. B.) 209–255 (Springer, 2019).
Brun, F., Berthier, E., Wagnon, P., Kääb, A. & Treichler, D. A spatially resolved estimate of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balances from 2000 to 2016. Nat. Geosci. 10, 668–673 (2017). Quantified glacier mass changes in a consistently and spatially continuous way over High-mountain Asia.
Shean, D. E. et al. A systematic, regional assessment of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balance. Front. Earth Sci. 7, 363 (2020).
Maurer, J. M., Schaefer, J. M., Rupper, S. & Corley, A. Acceleration of ice loss across the Himalayas over the past 40 years. Sci. Adv. 5, v7266 (2019). Identified and quantified accelerated glacier mass losses over the recent decades from 1975 to 2016.
Sakai, A. Brief communication: Updated GAMDAM glacier inventory over high-mountain Asia. Cryosphere 13, 2043–2049 (2019).
Kargel, J. S., Cogley, J. G., Leonard, G. J., Haritashya, U. & Byers, A. Himalayan glaciers: the big picture is a montage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 14709–14710 (2011).
Kääb, A., Treichler, D., Nuth, C. & Berthier, E. Brief communication: Contending estimates of 2003–2008 glacier mass balance over the Pamir–Karakoram–Himalaya. Cryosphere 9, 557–564 (2015).
Wiltshire, A. J. Climate change implications for the glaciers of the Hindu Kush, Karakoram and Himalayan region. Cryosphere 8, 941–958 (2014).
Kääb, A., Berthier, E., Nuth, C., Gardelle, J. & Arnaud, Y. Contrasting patterns of early twenty-first-century glacier mass change in the Himalayas. Nature 488, 495–498 (2012).
Hewitt, K. The Karakoram anomaly? Glacier expansion and the ‘Elevation Effect,’ Karakoram Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 25, 332–340 (2005).
Bolch, T., Pieczonka, T., Mukherjee, K. & Shea, J. Brief communication: Glaciers in the Hunza catchment (Karakoram) have been nearly in balance since the 1970s. Cryosphere 11, 531–539 (2017).
Hock, R. et al. in IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate (eds Pörtner, H. O. et al.) 131–202 (IPCC, 2019).
Carrivick, J. L. & Tweed, F. S. A global assessment of the societal impacts of glacier outburst floods. Glob. Planet. Change 144, 1–16 (2016).
Azam, M. F. et al. Review of the status and mass changes of Himalayan-Karakoram glaciers. J. Glaciol. 64, 61–74 (2018).
King, O., Bhattacharya, A., Bhambri, R. & Bolch, T. Glacial lakes exacerbate Himalayan glacier mass loss. Sci. Rep. 9, 18145 (2019).
Huss, M. & Hock, R. Global-scale hydrological response to future glacier mass loss. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 135–140 (2018). Predicted annual and seasonal changes in glacier melt under various climate change scenarios.
Huss, M. et al. Toward mountains without permanent snow and ice. Earths Future 5, 418–435 (2017).
Immerzeel, W. W., Wanders, N., Lutz, A. F., Shea, J. M. & Bierkens, M. F. P. Reconciling high-altitude precipitation in the upper Indus basin with glacier mass balances and runoff. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 19, 4673–4687 (2015).
Immerzeel, W. W., van Beek, L. P. H., Konz, M., Shrestha, A. B. & Bierkens, M. F. P. Hydrological response to climate change in a glacierized catchment in the Himalayas. Clim. Change 110, 721–736 (2012).
Ragettli, S., Immerzeel, W. W. & Pellicciotti, F. Contrasting climate change impact on river flows from high-altitude catchments in the Himalayan and Andes Mountains. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 9222–9227 (2016).
Farinotti, D., Immerzeel, W. W., de Kok, R. J., Quincey, D. J. & Dehecq, A. Manifestations and mechanisms of the Karakoram glacier Anomaly. Nat. Geosci. 13, 8–16 (2020).
Bhambri, R., Hewitt, K., Kawishwar, P. & Pratap, B. Surge-type and surge-modified glaciers in the Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 7, 15391 (2017).
Bhambri, R. et al. The hazardous 2017–2019 surge and river damming by Shispare Glacier, Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 10, 4685 (2020).
Nie, Y. et al. An inventory of historical glacial lake outburst floods in the Himalayas based on remote sensing observations and geomorphological analysis. Geomorphology 308, 91–106 (2018).
Houze, R. A., Mcmurdie, L. A., Rasmussen, K. L., Kumar, A. & Chaplin, M. M. Multiscale aspects of the storm producing the June 2013 flooding in Uttarakhand, India. Mon. Weather Rev. 145, 4447–4466 (2017).
Martha, T. et al. Landslides triggered by the June 2013 extreme rainfall event in parts of Uttarakhand state, India. Landslides 12, 135–146 (2015).
Ahlers, R., Budds, J., Joshi, D., Merme, V. & Zwarteveen, M. Framing hydropower as green energy: assessing drivers, risks and tensions in the Eastern Himalayas. Earth Syst. Dyn. 6, 195–204 (2015).
Schwanghart, W., Worni, R., Huggel, C., Stoffel, M. & Korup, O. Uncertainty in the Himalayan energy–water nexus: estimating regional exposure to glacial lake outburst floods. Environ. Res. Lett. 11, 74005 (2016).
Brun, F. et al. Heterogeneous influence of glacier morphology on the mass balance variability in High Mountain Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 124, 1331–1345 (2019).
Pandey, P. Inventory of rock glaciers in Himachal Himalaya, India using high-resolution Google Earth imagery. Geomorphology 340, 103–115 (2019).
Böhner, J. General climatic controls and topoclimatic variations in Central and High Asia. Boreas 35, 279–295 (2006).
Bookhagen, B. & Burbank, D. W. Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: Spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. 115, F3019 (2010).
Maussion, F. et al. Precipitation seasonality and variability over the Tibetan Plateau as resolved by the High Asia Reanalysis. J. Clim. 27, 1910–1927 (2014).
Guo, W. et al. The second Chinese glacier inventory: data, methods and results. J. Glaciol. 61, 357–372 (2015).
Rankl, M., Kienholz, C. & Braun, M. Glacier changes in the Karakoram region mapped by multimission satellite imagery. Cryosphere 8, 977–989 (2014).
Minora, U. et al. 2001–2010 glacier changes in the Central Karakoram National Park: a contribution to evaluate the magnitude and rate of the “Karakoram anomaly”. Cryosphere Discuss. 7, 2891–2941 (2013).
Bhambri, R. et al. Heterogeneity in glacier response in the upper Shyok valley, northeast Karakoram. Cryosphere 7, 1385–1398 (2013).
Agarwal, V. et al. Area and mass changes of Siachen Glacier (East Karakoram). J. Glaciol. 63, 148–163 (2017).
Lin, H., Li, G., Cuo, L., Hooper, A. & Ye, Q. A decreasing glacier mass balance gradient from the edge of the Upper Tarim Basin to the Karakoram during 2000–2014. Sci. Rep. 7, 6712 (2017).
Nie, Y. et al. A regional-scale assessment of Himalayan glacial lake changes using satellite observations from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 189, 1–13 (2017). Revealed the distribution, evolution and regional heterogeneity of all Himalayan glacial lakes and detected rapid lake expansion.
Treydte, K. S. et al. The twentieth century was the wettest period in northern Pakistan over the past millennium. Nature 440, 1179–1182 (2006).
Mukhopadhyay, B. & Khan, A. Rising river flows and glacial mass balance in central Karakoram. J. Hydrol. 513, 192–203 (2014).
de Kok, R. J., Tuinenburg, O. A., Bonekamp, P. N. J. & Immerzeel, W. W. Irrigation as a potential driver for anomalous glacier behavior in High Mountain Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 2047–2054 (2018).
Pepin, N. et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Change 5, 424–430 (2015).
Scherler, D., Wulf, H. & Gorelick, N. Global assessment of supraglacial debris-cover extents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 11798–11805 (2018).
Kraaijenbrink, P. D. A., Bierkens, M. F. P., Lutz, A. F. & Immerzeel, W. W. Impact of a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius on Asia’s glaciers. Nature 549, 257–260 (2017). Developed a state-of-the-art model to quantify glacier change under various climate change scenarios.
Scherler, D., Bookhagen, B. & Strecker, M. R. Spatially variable response of Himalayan glaciers to climate change affected by debris cover. Nat. Geosci. 4, 156–159 (2011).
Mölg, N., Bolch, T., Rastner, P., Strozzi, T. & Paul, F. A consistent glacier inventory for Karakoram and Pamir derived from Landsat data: distribution of debris cover and mapping challenges. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 10, 1807–1827 (2018).
Brun, F. et al. Ice cliff contribution to the tongue-wide ablation of Changri Nup Glacier, Nepal, central Himalaya. Cryosphere 12, 3439–3457 (2018).
Miles, E. S. et al. Glacial and geomorphic effects of a supraglacial lake drainage and outburst event, Everest region, Nepal Himalaya. Cryosphere 12, 3891–3905 (2018).
Mccarthy, M., Pritchard, H., Willis, I. & King, E. Ground-penetrating radar measurements of debris thickness on Lirung Glacier, Nepal. J. Glaciol. 63, 543–555 (2017).
Jiang, S. et al. Glacier change, supraglacial debris expansion and glacial lake evolution in the Gyirong River Basin, central Himalayas, between 1988 and 2015. Remote Sens. 10, 986 (2018).
Kirkbride, M. P. & Deline, P. The formation of supraglacial debris covers by primary dispersal from transverse englacial debris bands. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 38, 1779–1792 (2013).
Sakai, A., Nishimura, K., Kadota, T. & Takeuchi, N. Onset of calving at supraglacial lakes on debris-covered glaciers of the Nepal Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 55, 909–917 (2009).
King, O., Dehecq, A., Quincey, D. & Carrivick, J. Contrasting geometric and dynamic evolution of lake and land-terminating glaciers in the central Himalaya. Glob. Planet. Change 167, 46–60 (2018).
Watson, C. S. et al. Mass loss from calving in Himalayan proglacial lakes. Front. Earth Sci. 7, 342 (2020).
Tsutaki, S. et al. Contrasting thinning patterns between lake- and land-terminating glaciers in the Bhutanese Himalaya. Cryosphere 13, 2733–2750 (2019).
Liu, Q. et al. Interannual flow dynamics driven by frontal retreat of a lake-terminating glacier in the Chinese Central Himalaya. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 546, 116450 (2020).
Wang, X. et al. Glacial lake inventory of high-mountain Asia in 1990 and 2018 derived from Landsat images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 12, 2169–2182 (2020).
Bhambri, R. et al. Ice-dams, outburst floods, and movement heterogeneity of glaciers, Karakoram. Glob. Planet. Change 180, 100–116 (2019).
Lutz, A. F., Immerzeel, W. W., Shrestha, A. B. & Bierkens, M. F. P. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Change 4, 587–592 (2014).
Radić, V. et al. Regional and global projections of twenty-first century glacier mass changes in response to climate scenarios from global climate models. Clim. Dyn. 42, 37–58 (2014).
Radić, V. & Hock, R. Glaciers in the Earth’s hydrological cycle: assessments of glacier mass and runoff changes on global and regional scales. Surv. Geophys. 35, 813–837 (2014).
Irvine-Fynn, T. D. L. et al. Supraglacial ponds regulate runoff from Himalayan debris-covered glaciers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 11,894–11,904 (2017).
Gao, X., Ye, B., Zhang, S., Qiao, C. & Zhang, X. Glacier runoff variation and its influence on river runoff during 1961–2006 in the Tarim River Basin, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 53, 880–891 (2010).
Lutz, A. F., Immerzeel, W. W., Kraaijenbrink, P. D., Shrestha, A. B. & Bierkens, M. F. Climate change impacts on the upper Indus hydrology: sources, shifts and extremes. PLoS ONE 11, e165630 (2016).
Wijngaard, R. R. et al. Future changes in hydro-climatic extremes in the Upper Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra River basins. PLoS ONE 12, e190224 (2017).
Kaser, G., Grosshauser, M. & Marzeion, B. Contribution potential of glaciers to water availability in different climate regimes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 20223–20227 (2010).
Racoviteanu, A. E., Armstrong, R. & Williams, M. W. Evaluation of an ice ablation model to estimate the contribution of melting glacier ice to annual discharge in the Nepal Himalaya. Water Resour. Res. 49, 5117–5133 (2013).
Luo, Y. et al. Contrasting streamflow regimes induced by melting glaciers across the Tien Shan–Pamir–North Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 8, 16470 (2018).
Soncini, A. et al. Future hydrological regimes in the upper Indus basin: A case study from a high-altitude glacierized catchment. J. Hydrometeorol. 16, 306–326 (2015).
Zhang, L., Su, F., Yang, D., Hao, Z. & Tong, K. Discharge regime and simulation for the upstream of major rivers over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118, 8500–8518 (2013).
Hasson, S., Böhner, J. & Lucarini, V. Prevailing climatic trends and runoff response from Hindukush–Karakoram–Himalaya, upper Indus Basin. Earth Syst. Dyn. 8, 337–355 (2017).
Tao, H., Gemmer, M., Bai, Y., Su, B. & Mao, W. Trends of streamflow in the Tarim River basin during the past 50 years: Human impact or climate change? J. Hydrol. 400, 1–9 (2011).
Anand, J., Gosain, A. K., Khosa, R. & Srinivasan, R. Regional scale hydrologic modeling for prediction of water balance, analysis of trends in streamflow and variations in streamflow: The case study of the Ganga River basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 16, 32–53 (2018).
Khandu, F. E., Schumacher, M., Awange, J. L. & Müller Schmied, H. Exploring the influence of precipitation extremes and human water use on total water storage (TWS) changes in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 52, 2240–2258 (2016).
Zhang, F., Thapa, S., Immerzeel, W., Zhang, H. & Lutz, A. Water availability on the Third Pole: A review. Water Secur. 7, 100033 (2019).
Chen, X., Long, D., Hong, Y., Zeng, C. & Yan, D. Improved modeling of snow and glacier melting by a progressive two-stage calibration strategy with GRACE and multisource data: How snow and glacier meltwater contributes to the runoff of the Upper Brahmaputra River basin? Water Resour. Res. 53, 2431–2466 (2017).
Sharif, M., Archer, D. R., Fowler, H. J. & Forsythe, N. Trends in timing and magnitude of flow in the Upper Indus Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 17, 1503–1516 (2013).
Masood, M., Yeh, P. J. F., Hanasaki, N. & Takeuchi, K. Model study of the impacts of future climate change on the hydrology of Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 19, 747–770 (2015).
Su, F. et al. Hydrological response to future climate changes for the major upstream river basins in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 136, 82–95 (2016).
Nepal, S., Krause, P., Flügel, W. A., Fink, M. & Fischer, C. Understanding the hydrological system dynamics of a glaciated alpine catchment in the Himalayan region using the J2000 hydrological model. Hydrol. Process. 28, 1329–1344 (2014).
Wortmann, M., Bolch, T., Menz, C., Tong, J. & Krysanova, V. Comparison and correction of high-mountain precipitation data based on glacio-hydrological modeling in the Tarim River headwaters (High Asia). J. Hydrometeorol. 19, 777–801 (2018).
Nepal, S. Impacts of climate change on the hydrological regime of the Koshi river basin in the Himalayan region. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 10, 76–89 (2016).
Pellicciotti, F., Buergi, C., Immerzeel, W. W., Konz, M. & Shrestha, A. B. Challenges and uncertainties in hydrological modeling of remote Hindu Kush–Karakoram–Himalayan (HKH) basins: suggestions for calibration strategies. Mt. Res. Dev. 32, 39–50 (2012).
Momblanch, A., Holman, I. & Jain, S. Current practice and recommendations for modelling global change impacts on water resource in the Himalayas. Water 11, 1303 (2019).
Quincey, D. J. et al. Optical remote sensing techniques in high-mountain environments: application to glacial hazards. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 29, 475–505 (2005).
Cook, K. L., Andermann, C., Gimbert, F., Adhikari, B. R. & Hovius, N. Glacial lake outburst floods as drivers of fluvial erosion in the Himalaya. Science 362, 53–57 (2018). Quantified the role of GLOFs in fluvial erosion and geomorphological evolution using in situ observations.
Chen, C., Zhang, L., Xiao, T. & He, J. Barrier lake bursting and flood routing in the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon in October 2018. J. Hydrol. 583, 124603 (2020).
Chen, X. et al. Dam-break risk analysis of the Attabad landslide dam in Pakistan and emergency countermeasures. Landslides 14, 675–683 (2017).
Osti, R., Bhattarai, T. N. & Miyake, K. Causes of catastrophic failure of Tam Pokhari moraine dam in the Mt. Everest region. Nat. Hazards 58, 1209–1223 (2011).
Nie, Y., Liu, W., Liu, Q., Hu, X. & Westoby, M. J. Reconstructing the Chongbaxia Tsho glacial lake outburst flood in the Eastern Himalaya: Evolution, process and impacts. Geomorphology. 370, 107393 (2020).
Byers, A. C. et al. A rockfall-induced glacial lake outburst flood, Upper Barun Valley, Nepal. Landslides 16, 533–549 (2019).
Westoby, M. J. et al. Modelling outburst floods from moraine-dammed glacial lakes. Earth Sci. Rev. 134, 137–159 (2014).
Gardelle, J., Arnaud, Y. & Berthier, E. Contrasted evolution of glacial lakes along the Hindu Kush Himalaya mountain range between 1990 and 2009. Glob. Planet. Change 75, 47–55 (2011).
Allen, S. K., Rastner, P., Arora, M., Huggel, C. & Stoffel, M. Lake outburst and debris flow disaster at Kedarnath, June 2013: hydrometeorological triggering and topographic predisposition. Landslides 13, 1479–1491 (2016).
Rounce, D. R., Byers, A. C., Byers, E. A. & Mckinney, D. C. Brief communication: Observations of a glacier outburst flood from Lhotse Glacier, Everest area, Nepal. Cryosphere 11, 443–449 (2017).
Gurung, D. R. et al. Lemthang Tsho glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) in Bhutan: cause and impact. Environ. Risk Assess. Remediat. 1, 56–64 (2017).
Veh, G., Korup, O., von Specht, S., Roessner, S. & Walz, A. Unchanged frequency of moraine-dammed glacial lake outburst floods in the Himalaya. Nat. Clim. Change 9, 379–383 (2019).
Fujita, K., Sakai, A., Nuimura, T., Yamaguchi, S. & Sharma, R. R. Recent changes in Imja Glacial Lake and its damming moraine in the Nepal Himalaya revealed by in situ surveys and multi-temporal ASTER imagery. Environ. Res. Lett. 4, 45205 (2009).
Haritashya, U. K. et al. Evolution and controls of large glacial lakes in the Nepal Himalaya. Remote Sens. 10, 798 (2018).
Allen, S. K. et al. Translating the concept of climate risk into an assessment framework to inform adaptation planning: Insights from a pilot study of flood risk in Himachal Pradesh, Northern India. Environ. Sci. Policy 87, 1–10 (2018).
Lala, J. M., Rounce, D. R. & Mckinney, D. C. Modeling the glacial lake outburst flood process chain in the Nepal Himalaya: reassessing Imja Tsho’s hazard. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 22, 3721–3737 (2018).
Rounce, D. R., Mckinney, D. C., Lala, J. M., Byers, A. C. & Watson, C. S. A new remote hazard and risk assessment framework for glacial lakes in the Nepal Himalaya. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 20, 3455–3475 (2016).
Khanal, N. R. et al. A comprehensive approach and methods for glacial lake outburst flood risk assessment, with examples from Nepal and the transboundary area. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 31, 219–237 (2015).
Immerzeel, W. W., Pellicciotti, F. & Bierkens, M. F. P. Rising river flows throughout the twenty-first century in two Himalayan glacierized watersheds. Nat. Geosci. 6, 742–745 (2013).
Harrison, S. et al. Climate change and the global pattern of moraine-dammed glacial lake outburst floods. Cryosphere 12, 1195–1209 (2018).
Rashid, I., Majeed, U., Jan, A. & Glasser, N. F. The January 2018 to September 2019 surge of Shisper Glacier, Pakistan, detected from remote sensing observations. Geomorphology 351, 106957 (2020).
Kirschbaum, D. et al. The state of remote sensing capabilities of cascading hazards over High Mountain Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 7, 197 (2019).
Hewitt, K. Glaciers of the Karakoram Himalaya: Glacial Environments, Processes, Hazards and Resources (Springer, 2014).
Round, V., Leinss, S., Huss, M., Haemmig, C. & Hajnsek, I. Surge dynamics and lake outbursts of Kyagar Glacier, Karakoram. Cryosphere 11, 723–739 (2017).
Chen, Y., Xu, C., Chen, Y., Li, W. & Liu, J. Response of glacial-lake outburst floods to climate change in the Yarkant River basin on northern slope of Karakoram Mountains, China. Quat. Int. 226, 75–81 (2010).
Somos-Valenzuela, M. A., Mckinney, D. C., Rounce, D. R. & Byers, A. C. Changes in Imja Tsho in the Mount Everest region of Nepal. Cryosphere 8, 1661–1671 (2014).
Rounce, D. R., Quincey, D. J. & Mckinney, D. C. Debris-covered glacier energy balance model for Imja–Lhotse Shar Glacier in the Everest region of Nepal. Cryosphere 9, 2295–2310 (2015).
Wang, X. et al. Monitoring and simulation of hydrothermal conditions indicating the deteriorating stability of a perennially frozen moraine dam in the Himalayas. J. Glaciol. 64, 407–416 (2018).
Atta-Ur-Rahman & Khan, A. N. Analysis of 2010-flood causes, nature and magnitude in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 66, 887–904 (2012).
Wester, P., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A. & Shrestha, A. B. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People (Springer, 2019).
Zhang, Q. et al. Magnitude, frequency and timing of floods in the Tarim River basin, China: Changes, causes and implications. Glob. Planet. Change 139, 44–55 (2016).
Elalem, S. & Pal, I. Mapping the vulnerability hotspots over Hindu-Kush Himalaya region to flooding disasters. Weather Clim. Extremes 8, 46–58 (2015).
Goswami, B. N., Venugopal, V., Sengupta, D., Madhusoodanan, M. S. & Xavier, P. K. Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 314, 1442–1445 (2006).
Lutz, A. F. et al. South Asian river basins in a 1.5 °C warmer world. Reg. Environ. Change 19, 833–847 (2019).
Dankers, R. et al. First look at changes in flood hazard in the Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project ensemble. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 3257–3261 (2014).
Mohammed, K. et al. Extreme flows and water availability of the Brahmaputra River under 1.5 and 2 °C global warming scenarios. Clim. Change 145, 159–175 (2017).
Mirza, M. M. Q., Warrick, R. A. & Ericksen, N. J. The implications of climate change on floods of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers in Bangladesh. Clim. Change 57, 287–318 (2003).
Yang, Y. C. E., Wi, S., Ray, P. A., Brown, C. M. & Khalil, A. F. The future nexus of the Brahmaputra River Basin: climate, water, energy and food trajectories. Glob. Environ. Change 37, 16–30 (2016).
Khan, A. J., Koch, M. & Tahir, A. A. Impacts of climate change on the water availability, seasonality and extremes in the Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Sustainability 12, 1283 (2020).
Hennig, T. & Harlan, T. Shades of green energy: geographies of small hydropower in Yunnan, China and the challenges of over-development. Glob. Environ. Change 49, 116–128 (2018).
Zarfl, C., Lumsdon, A. E., Berlekamp, J., Tydecks, L. & Tockner, K. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 77, 161–170 (2015).
Lehner, B. et al. High-resolution mapping of the world’s reservoirs and dams for sustainable river-flow management. Front. Ecol. Environ. 9, 494–502 (2011).
Gernaat, D. E. H. J., Bogaart, P. W., Vuuren, D. P. V., Biemans, H. & Niessink, R. High-resolution assessment of global technical and economic hydropower potential. Nat. Energy 2, 821–828 (2017).
Hirabayashi, Y., Kanae, S., Emori, S., Oki, T. & Kimoto, M. Global projections of changing risks of floods and droughts in a changing climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 53, 754–772 (2010).
Dimri, A. P. et al. A review of atmospheric and land surface processes with emphasis on flood generation in the Southern Himalayan rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 556, 98–115 (2016).
Wen, S. et al. Population exposed to drought under the 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warming in the Indus River Basin. Atmos. Res. 218, 296–305 (2019).
Jonell, T. N., Carter, A., Böning, P., Pahnke, K. & Clift, P. D. Climatic and glacial impact on erosion patterns and sediment provenance in the Himalayan rain shadow, Zanskar River, NW India. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 129, 820–836 (2017).
Padhy, M. K. & Saini, R. P. A review on silt erosion in hydro turbines. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 12, 1974–1987 (2008).
Molden, D. J., Vaidya, R. A., Shrestha, A. B., Rasul, G. & Shrestha, M. S. Water infrastructure for the Hindu Kush Himalayas. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 30, 60–77 (2014).
Maavara, T. et al. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 1, 103–116 (2020).
Hennig, T. Damming the transnational Ayeyarwady basin. Hydropower and the water-energy nexus. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 65, 1232–1246 (2016).
Hennig, T. Energy, hydropower, and geopolitics — Northeast India and its neighbors: A critical review of the establishment of India’s largest hydropower base. ASIEN 134, 121–142 (2015).
Pandit, M. K. & Grumbine, R. E. Potential effects of ongoing and proposed hydropower development on terrestrial biological diversity in the Indian Himalaya. Conserv. Biol. 26, 1061–1071 (2012).
Nepal, S., Neupane, N., Belbase, D., Pandey, V. P. & Mukherji, A. Achieving water security in Nepal through unravelling the water-energy-agriculture nexus. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 37, 67–93 (2019).
Chellaney, B. Water: Asia’s New Battleground (Georgetown Univ. Press, 2011).
Hofste, R. W. et al. Aqueduct 3.0: Updated Decision-Relevant Global Water Risk Indicators (Water Resources Institute, 2019).
International Monetary Fund. Issues in Managing Water Challenges and Policy Instruments: Regional Perspectives and Case Studies (International Monetary Fund, 2015).
Schleussner, C., Donges, J. F., Donner, R. V. & Schellnhuber, H. J. Armed-conflict risks enhanced by climate-related disasters in ethnically fractionalized countries. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 9216–9221 (2016).
Yatagai, A. et al. APHRODITE: Constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 93, 1401–1415 (2012).
Hummel, S. Relative water scarcity and country relations along cross-boundary rivers: evidence from the Aral Sea basin. Int. Stud. Q. 61, 795–808 (2017).
Briscoe, J., Qamar, U., Contijoch, M., Amir, P. & Blackmore, D. Pakistan’s Water Economy: Running Dry (World Bank, 2005).
Macdonald, A. M. et al. Groundwater quality and depletion in the Indo-Gangetic Basin mapped from in situ observations. Nat. Geosci. 9, 762–766 (2016).
Richey, A. S. et al. Quantifying renewable groundwater stress with GRACE. Water Resour. Res. 51, 5217–5238 (2015).
Amir, P. & Habib, Z. Estimating the Impacts of Climate Change on Sectoral Water Demand in Pakistan (LEAD Pakistan, 2015).
Kirby, M., Ahmad, M., Mainuddin, M., Khaliq, T. & Cheema, M. J. M. Agricultural production, water use and food availability in Pakistan: Historical trends, and projections to 2050. Agric. Water Manag. 179, 34–46 (2017).
Young, W. J. et al. Pakistan: Getting More from Water (Water Security Diagnostic, 2019).
Thevs, N. Water scarcity and allocation in the Tarim Basin: decision structures and adaptations on the local level. J. Curr. Chin. Aff. 40, 113–137 (2011).
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). AQUASTAT. FAO http://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/aquastat/en/ (2020)
Frenken, K. Irrigation in Southern and Eastern Asia in figures - AQUASTAT Survey - 2011 (FAO, 2012).
Xia, J. et al. Evaluating the dynamics of groundwater depletion for an arid land in the Tarim Basin, China. Water 11, 186 (2019).
Pang, Z., Huang, T. & Chen, Y. Diminished groundwater recharge and circulation relative to degrading riparian vegetation in the middle Tarim River, Xinjiang Uygur, Western China. Hydrol. Process. 24, 147–159 (2010).
Quereshi, A. S. & Sarwar, A. Managing salinity in the Indus Basin of Pakistan. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 7, 111–117 (2009).
Podgorski, J. E. et al. Extensive arsenic contamination in high-pH unconfined aquifers in the Indus Valley. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700935 (2017).
Farinotti, D., Round, V., Huss, M., Compagno, L. & Zekollari, H. Large hydropower and water-storage potential in future glacier-free basins. Nature 575, 341–344 (2019).
Mukherji, A., Molden, D., Nepal, S., Rasul, G. & Wagnon, P. Himalayan waters at the crossroads: issues and challenges. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 31, 151–160 (2015).
Molden, D. et al. Advancing regional and transboundary cooperation in the conflict-prone Hindu Kush–Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 37, 502–508 (2017).
Wijngaard, R. R. et al. Climate change vs. socio-economic development: understanding the future South Asian water gap. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 22, 6297–6321 (2018).
Gao, J., Yao, T., Valérie, M., Hans, C. S. & Wang, W. Collapsing glaciers threaten Asia’s water supplies. Nature 565, 19–21 (2019).
Pritchard, H. D. et al. Towards Bedmap Himalayas: development of an airborne ice-sounding radar for glacier thickness surveys in High-Mountain Asia. Ann. Glaciol. 61, 35–45 (2020).
Rounce, D. R., King, O., Mccarthy, M., Shean, D. E. & Salerno, F. Quantifying debris thickness of debris-covered glaciers in the Everest region of Nepal through inversion of a subdebris melt model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth 123, 1094–1115 (2018).
Dahal, P. R., Paudyal, K. R. & Rajaure, S. Geophysical study on moraine dam of Imja Glacial Lake in Eastern Nepal using electrical resistivity tomography method. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 55, 15–22 (2018).
Frey, H. et al. Estimating the volume of glaciers in the Himalayan–Karakoram region using different methods. Cryosphere 8, 2313–2333 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Fanny Brun for providing data on glacier change in Fig. 2 and Lu Zeng for technical support in creating Figs. 3,6. This study was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. XDA20030301), the second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (grant 2019QZKK0603), the Chinese Academy of Sciences Light of West China and Key Lab of Mountain Environment Programs, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 41571104 and 41971153) and Foundation of Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. 2017425).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.N., H.D.P., Q.L. and T.H. researched data for the article. Y.N., H.D.P., Q.L., T.H., W.W. and X.W. wrote the article. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment thanks Tobias Bolch, who co-reviewed with Owen King, and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, Y., Pritchard, H.D., Liu, Q. et al. Glacial change and hydrological implications in the Himalaya and Karakoram. Nat Rev Earth Environ 2, 91–106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-00124-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-00124-w
This article is cited by
-
Drainage divide migration and implications for climate and biodiversity
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2024)
-
Characteristic Changes in the Strengthening Western Disturbances over Karakoram in Recent Decades
Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (2024)
-
Assessing potential risk of glacier avalanches to hydropower infrastructure in the Himalayan region
Natural Hazards (2024)
-
Runoff components and the contributions of precipitation and temperature in a highly glacierized river basin in Central Asia
Frontiers of Earth Science (2023)
-
Black Carbon Size in Snow of Chinese Altai Mountain in Central Asia
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2023)