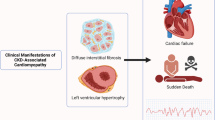
Abstract
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cardiovascular death. Identifying and monitoring cardiovascular complications and hypertension is important for managing patients with CKD or kidney failure and transplant recipients. Biomarkers of myocardial ischaemia, such as troponins and electrocardiography (ECG), have limited utility for diagnosing cardiac ischaemia in patients with advanced CKD. Dobutamine stress echocardiography, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and dipyridamole stress testing can be used to detect coronary disease in these patients. Left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction can be detected and monitored using various techniques with differing complexity and cost, including ECG, echocardiography, nuclear magnetic resonance, CT and myocardial scintigraphy. Atrial fibrillation and other major arrhythmias are common in all stages of CKD, and ambulatory heart rhythm monitoring enables precise time profiling of these disorders. Screening for cerebrovascular disease is only indicated in asymptomatic patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Standardized blood pressure is recommended for hypertension diagnosis and treatment monitoring and can be complemented by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Judicious use of these diagnostic techniques may assist clinicians in detecting the whole range of cardiovascular alterations in patients with CKD and enable timely treatment of CVD in this high-risk population.
Key points
-
Cardiovascular disease is the main comorbidity of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and most patients with CKD die from cardiovascular causes before they progress to kidney failure; detection of anatomical and functional cardiovascular abnormalities and hypertension is important to enable management of these complications.
-
Dobutamine stress echocardiography, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, dipyridamole stress testing and CT angiography are valid methods for detecting coronary disease in patients with CKD or kidney failure.
-
Left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction can be detected and monitored using various techniques with differing cost and complexity, including electrocardiography, echocardiography and nuclear magnetic resonance.
-
Major arrhythmias are common in patients with CKD and kidney failure; ambulatory heart rhythm monitoring enables precise time profiling of these disorders.
-
Screening for cerebrovascular disease is only indicated in asymptomatic patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
-
Standardized blood pressure measurements and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring are recommended for diagnosis and monitoring of hypertension in patients with CKD or kidney failure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foreman, K. J. et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 392, 2052–2090 (2018).
Al-Wahsh, H. et al. Accounting for the competing risk of death to predict kidney failure in adults with stage 4 chronic kidney disease. JAMA Netw. Open 4, e219225 (2021).
Bikbov, B. et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 395, 709–733 (2020).
Tonelli, M. et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 2034–2047 (2006).
Zoccali, C. & Mallamaci, F. Mapping progress in reducing cardiovascular risk with kidney disease: managing volume overload. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13, 1432–1431 (2018).
Zoccali, C., Mallamaci, F. & Picano, E. Detecting and treating lung congestion with kidney failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 757–765 (2022).
de Lemos, J. A. & Hillis, L. D. Diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 7, 2044–2054 (1996).
Sharma, R. et al. Dobutamine stress echocardiography and the resting but not exercise electrocardiograph predict severe coronary artery disease in renal transplant candidates. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 20, 2207–2214 (2005).
Poulikakos, D. & Malik, M. Challenges of ECG monitoring and ECG interpretation in dialysis units. J. Electrocardiol. 49, 855–859 (2016).
Birnbaum, Y., Rankinen, J., Jneid, H., Atar, D. & Nikus, K. The role of ECG in the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute coronary syndromes: an old but indispensable tool. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 24, 109–118 (2022).
Fletcher, G. F. et al. Exercise standards for testing and training. Circulation 128, 873–934 (2013).
Gianrossi, R. et al. Exercise-induced ST depression in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. A meta-analysis. Circulation 80, 87–98 (1989).
Zoccali, C., Bolignano D & Mallamaci, F. in Oxford Textbook of Clinical Nephrology Vol. 1 Ch. 107 (eds Turner, N. N. et al.) 837–852 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2019).
Dubin, R. F. et al. Predictors of high sensitivity cardiac troponin T in chronic kidney disease patients: a cross-sectional study in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort (CRIC). BMC Nephrol. 14, 229 (2013).
Gunsolus, I. et al. Renal dysfunction influences the diagnostic and prognostic performance of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 29, 636–643 (2018).
Herzog, C. A. et al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 80, 572–586 (2011).
Carlino, C., Kuppuswamy, S., McCray, L., Aggarwal, K. & Alpert, M. A. Comparative feasibility of dobutamine stress echocardiography performed with and without intravenous contrast in patients with class III obesity. Echocardiography 39, 20–27 (2022).
Kurt, M. et al. Impact of contrast echocardiography on evaluation of ventricular function and clinical management in a large prospective cohort. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53, 802–810 (2009).
Hlatky, M. A., Shilane, D., Hachamovitch, R. & Dicarli, M. F., SPARC Investigators. Economic outcomes in the study of myocardial perfusion and coronary anatomy imaging roles in coronary artery disease registry: the SPARC study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63, 1002–1008 (2014).
Wang, L. W. et al. Cardiac testing for coronary artery disease in potential kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review of test accuracy studies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 57, 476–487 (2011).
Cai, Q., Mukku, V. & Ahmad, M. Coronary artery disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: a clinical update. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 9, 331–339 (2014).
El-Mahalawy, N., Abdel-Salam, Z., Samir, A., Mohasseb, W. & Nammas, W. Left ventricular transient ischemic dilation during dobutamine stress echocardiography predicts multi-vessel coronary artery disease. J. Cardiol. 54, 255–261 (2009).
Sørensen, I. M. H. et al. Regional distribution and severity of arterial calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease stages 1–5: a cross-sectional study of the Copenhagen chronic kidney disease cohort. BMC Nephrol. 21, 534 (2020).
Jansz, T. T. et al. Coronary artery calcification as a marker for coronary artery stenosis: comparing kidney failure to the general population. Kidney Med. 3, 386–394.e1 (2021).
Cheng, X. S. et al. Coronary computed tomography angiography in diagnosing obstructive coronary artery disease in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 11, 44–51 (2021).
Liu, A. et al. Adenosine stress and rest T1 mapping can differentiate between ischemic, infarcted, remote, and normal myocardium without the need for gadolinium contrast agents. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 9, 27–36 (2016).
Emrich, T., Halfmann, M., Schoepf, U. J. & Kreitner, K.-F. CMR for myocardial characterization in ischemic heart disease: state-of-the-art and future developments. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 5, 14 (2021).
Poli, F. E. et al. The reliability and feasibility of non-contrast adenosine stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance T1 mapping in patients on haemodialysis. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 22, 43 (2020).
Miller, T. et al. Ferumoxytol-enhanced coronary magnetic resonance angiography compared to invasive coronary angiography for detection of epicardial coronary artery disease. Kidney Med. 3, 139–141 (2021).
De Lima, J. J. G. et al. Coronary angiography is the best predictor of events in renal transplant candidates compared with noninvasive testing. Hypertension 42, 263–268 (2003).
O’Lone, E. et al. Defining myocardial infarction in trials of people receiving hemodialysis: consensus report from the SONG-HD MI Expert Working Group. Kidney Int. 103, 1028–1037 (2023).
Esquitin, R. et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy by electrocardiography and echocardiography in the African American Study of Kidney Disease Cohort Study. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 6, 193–200 (2012).
Cordeiro, A. C. et al. Reliability of electrocardiographic surrogates of left ventricular mass in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Hypertens. 32, 439–445 (2014).
Cuspidi, C. et al. Do combined electrocardiographic and echocardiographic markers of left ventricular hypertrophy improve cardiovascular risk estimation? J. Clin. Hypertens. 18, 846–854 (2016).
Ho, C. Y. & Solomon, S. D. A clinician’s guide to tissue doppler imaging. Circulation 113, e396–e398 (2006).
Ureña-Torres, P. et al. Valvular heart disease and calcification in CKD: more common than appreciated. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 35, 2046–2053 (2020).
Mitchell, C. et al. Guidelines for performing a comprehensive transthoracic echocardiographic examination in adults: recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 32, 1–64 (2019).
Tsao, C. W. et al. Left ventricular structure and risk of cardiovascular events: a Framingham Heart Study cardiac magnetic resonance study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 4, e002188 (2015).
Tripepi, G. et al. Prognostic values of left ventricular mass index in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 36, 665–672 (2021).
Tripepi, G. et al. Reappraisal in two European cohorts of the prognostic power of left ventricular mass index in chronic kidney failure. Kidney Int. 91, 704–710 (2017).
Lang, R. M., Mor-Avi, V., Sugeng, L., Nieman, P. S. & Sahn, D. J. Three-dimensional echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 48, 2053–2069 (2006).
Christensen, J. et al. Left ventricular structure and function in patients with chronic kidney disease assessed by 3D echocardiography: the CPH-CKD ECHO study. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 38, 1233–1244 (2022).
Kakiouzi, V. et al. The prognostic value of speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with end stage renal disease on dialysis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 38, 2605–2614 (2022).
Jahn, L. et al. Speckle tracking echocardiography and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risk in chronic kidney disease patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 44, 690–703 (2019).
Guglielmo, M. & Pontone, G. Clinical implications of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging fibrosis. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 24, I123–I126 (2022).
Price, A. M. et al. Myocardial characterization in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease: a study of prevalence, patterns and outcomes. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 19, 295 (2019).
Zhou, H. et al. Texture analysis of native T1 images as a novel method for noninvasive assessment of uremic cardiomyopathy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 54, 290–300 (2021).
Aoki, J. et al. Clinical and pathologic characteristics of dilated cardiomyopathy in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 67, 333–340 (2005).
Rankin, A. J. et al. Global longitudinal strain by feature-tracking cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging predicts mortality in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 14, 2187–2196 (2021).
Gimpel, C. et al. Magnetic resonance tissue phase mapping demonstrates altered left ventricular diastolic function in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Radiol. 47, 169–177 (2017).
Weinreb, J. C. et al. Use of intravenous gadolinium-based contrast media in patients with kidney disease: consensus statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Radiology 298, 28–35 (2021).
Saravanan, P. & Davidson, N. C. Risk assessment for sudden cardiac death in dialysis patients. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 3, 553–559 (2010).
Steinberg, J. S. et al. 2017 ISHNE-HRS expert consensus statement on ambulatory ECG and external cardiac monitoring/telemetry. Heart Rhythm. 14, e55–e96 (2017).
Kim, E. D., Soliman, E. Z., Coresh, J., Matsushita, K. & Chen, L. Y. Two-week burden of arrhythmias across CKD severity in a large community-based cohort: the ARIC study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 32, 629–638 (2021).
Rantanen, J. M. et al. Arrhythmias in patients on maintenance dialysis: a cross-sectional study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 75, 214–224 (2020).
Koplan, B. A. et al. Implantable loop recorder monitoring and the incidence of previously unrecognized atrial fibrillation in patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 7, 189–199 (2022).
Kelly, D. M. et al. Chronic kidney disease and cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 52, e328–e346 (2021).
Lyerly, M. J. & Chow, D. Neuroimaging considerations in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 30, 105930 (2021).
Fugate, J. E. & Rabinstein, A. A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol. 14, 914–925 (2015).
Ganesh, K. et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 3, 502–507 (2018).
Kute, V. B. et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome – an under recognized manifestation of chronic kidney disease. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 17, 318–320 (2013).
Gerhard-Herman, M. D. et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 135, e686–e725 (2017).
Aboyans, V. et al. 2017 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. Heart J. 39, 763–816 (2018).
Johansen, K. L. et al. Central and peripheral arterial diseases in chronic kidney disease: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney Int. 100, 35–48 (2021).
Høyer, C., Sandermann, J. & Petersen, L. J. The toe-brachial index in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 58, 231–238 (2013).
[No authors listed] The AIUM practice parameter for the performance of an ultrasound examination of the extracranial cerebrovascular system. J. Ultrasound Med. 41, e21–e27 (2022).
Conte, M. S. et al. Global vascular guidelines on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 69, 3S–125S.e40 (2019).
Ali, F., Mangi, M. A., Rehman, H. & Kaluski, E. Use of carbon dioxide as an intravascular contrast agent: a review of current literature. World J. Cardiol. 9, 715–722 (2017).
Vlachopoulos, C. et al. The role of vascular biomarkers for primary and secondary prevention. A position paper from the European Society of Cardiology working group on peripheral circulation. Atherosclerosis 241, 507–532 (2015).
Tzoulaki, I., Siontis, K. C., Evangelou, E. & Ioannidis, J. P. A. Bias in associations of emerging biomarkers with cardiovascular disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 173, 664–671 (2013).
Arnett, D. K. et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 74, e177–e232 (2019).
Visseren, F. L. J. et al. 2021 ESC guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 42, 3227–3337 (2021).
Tripepi, G. et al. Pulse wave velocity and prognosis in end-stage kidney disease. Hypertension 71, 1126–1132 (2018).
Hametner, B. et al. Oscillometric estimation of aortic pulse wave velocity. Blood Press. Monit. 18, 173–176 (2013).
Baulmann, J. et al. A new oscillometric method for assessment of arterial stiffness: comparison with tonometric and piezo-electronic methods. J. Hypertens. 26, 523–528 (2008).
Schwartz, J. E., Feig, P. U. & Izzo, J. L. Pulse wave velocities derived from cuff ambulatory pulse wave analysis. Hypertension 74, 111–116 (2019).
Ku, E., Lee, B. J., Wei, J. & Weir, M. R. Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 74, 120–131 (2019).
Stergiou, G. S. et al. 2021 European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for office and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. J. Hypertens. 39, 1293–1302 (2021).
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Blood Pressure Working Group. 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 99, S1–S87 (2021).
Cheung, A. K. et al. International consensus on standardized clinic blood pressure measurement – a call to action. Am. J. Med. 136, 438–445 (2023).
McManus, R. J., Caulfield, M. & Williams, B. NICE hypertension guideline 2011: evidence based evolution. BMJ 344, e181 (2012).
Piper, M. A. et al. Diagnostic and predictive accuracy of blood pressure screening methods with consideration of rescreening intervals: a systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 162, 192–204 (2015).
Parati, G. et al. Hypertension in chronic kidney disease Part 1. Out-of-office blood pressure monitoring: methods, thresholds, and patterns. Hypertension 67, 1093–1101 (2016).
Andersen, M. J., Khawandi, W. & Agarwal, R. Home blood pressure monitoring in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 45, 994–1001 (2005).
Agarwal, R., Peixoto, A. J., Santos, S. F. & Zoccali, C. Pre- and postdialysis blood pressures are imprecise estimates of interdialytic ambulatory blood pressure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1, 389–398 (2006).
Bansal, N. et al. Blood pressure and risk of all-cause mortality in advanced chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis. Hypertension 65, 93–100 (2015).
Minutolo, R. et al. Prognostic role of ambulatory blood pressure measurement in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 171, 1090–1098 (2011).
Tripepi, G. et al. Prognostic value of 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and of night/day ratio in nondiabetic, cardiovascular events-free hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 68, 1294–1302 (2005).
Mallamaci, F. et al. Nocturnal hypertension and altered night–day BP profile and atherosclerosis in renal transplant patients. Transplantation 100, 2211–2218 (2016).
Agarwal, R. et al. Assessment and management of hypertension in patients on dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 25, 1630–1646 (2014).
Sarafidis, P. A. et al. Hypertension in dialysis patients: a consensus document by the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA-m) working group of the European Renal Association–European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) and the Hypertension and the Kidney working group of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 32, 620–640 (2017).
Yadlowsky, S. et al. Clinical implications of revised pooled cohort equations for estimating atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Ann. Intern. Med. 169, 20–29 (2018).
SCORE2 working group and ESC Cardiovascular risk collaboration. SCORE2 risk prediction algorithms: new models to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 42, 2439–2454 (2021).
Lees, J. S. et al. Assessment of cystatin C level for risk stratification in adults with chronic kidney disease. JAMA Netw. Open. 5, e2238300 (2022).
Matsushita, K. et al. Incorporating kidney disease measures into cardiovascular risk prediction: development and validation in 9 million adults from 72 datasets. EClinicalMedicine 27, 100552 (2020).
CKD Prognosis Consortium. Predicted 10 year risk of atherosclerotic CVD. CKD Prognosis Consortium https://ckdpcrisk.org/ckdpatchpce/ (2019).
CKD Prognosis Consortium. Predicted 10 year risk of cardiovascular mortality. CKD Prognosis Consortium https://ckdpcrisk.org/ckdpatchscore/ (2019).
Foster, M. C. et al. Cardiovascular risk factor burden, treatment, and control among adults with chronic kidney disease in the United States. Am. Heart J. 166, 150–156.e1 (2013).
Zoccali, C. et al. Cardiovascular complications in chronic kidney disease – a review from the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group (EURECA-m) of the European Renal Association (ERA). Cardiovasc. Res., https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvad083 (2023).
Colbert, G., Jain, N., de Lemos, J. A. & Hedayati, S. S. Utility of traditional circulating and imaging-based cardiac biomarkers in patients with predialysis CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 515–529 (2015).
Michos, E. D. et al. Prognostic value of cardiac troponin in patients with chronic kidney disease without suspected acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 161, 491–501 (2014).
Stewart, G. A. et al. Electrocardiographic abnormalities and uremic cardiomyopathy. Kidney Int. 67, 217–226 (2005).
Deo, R. et al. Electrocardiographic measures and prediction of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular death in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 27, 559–569 (2016).
Liu, Y., Ping, J., Qiu, L., Sun, C. & Chen, M. Comparative analysis of ischemic changes in electrocardiogram and coronary angiography results. Medicine 100, e26007 (2021).
Bangalore, S. et al. Management of coronary disease in patients with advanced kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1608–1618 (2020).
Dahan, M. et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of combined dipyridamole-exercise thallium imaging in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 54, 255–262 (1998).
Schmidt, A., Stefenelli, T., Schuster, E. & Mayer, G. Informational contribution of noninvasive screening tests for coronary artery disease in patients on chronic renal replacement therapy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37, 56–63 (2001).
Collet, J.-P. et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 42, 1289–1367 (2021).
Ng, S. M. et al. Feasibility, diagnostic performance and clinical value of an abbreviated echocardiography protocol in an out-patient cardiovascular setting: a pilot study. Echo Res. Pract. 9, 8 (2022).
Jankowski, J., Floege, J., Fliser, D., Böhm, M. & Marx, N. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. Circulation 143, 1157–1172 (2021).
Pecoits-Filho, R. & Barberato, S. H. Echocardiography in chronic kidney disease: diagnostic and prognostic implications. Nephron Clin. Pract. 114, c242–c247 (2010).
Chamsi-Pasha, M. A., Sengupta, P. P. & Zoghbi, W. A. Handheld echocardiography: current state and future perspectives. Circulation 136, 2178–2188 (2017).
Koratala, A. & Reisinger, N. POCUS for nephrologists: basic principles and a general approach. Kidney360 2, 1660–1668 (2021).
Zoccali, C. et al. A randomized multicenter trial on a lung ultrasound-guided treatment strategy in patients on chronic hemodialysis with high cardiovascular risk. Kidney Int. 100, 1325–1333 (2021).
Ledwidge, M. et al. Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure. JAMA 310, 66–74 (2013).
House, A. A. et al. Heart failure in chronic kidney disease: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney Int. 95, 1304–1317 (2019).
Moyer, V. A. Screening for peripheral artery disease and cardiovascular disease risk assessment with the ankle–brachial index in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 159, 342–348 (2013).
Sanchis, I. M. et al. Presymptomatic screening for intracranial aneurysms in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14, 1151–1160 (2019).
Kobayashi, M. et al. Relationship between silent brain infarction and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 24, 201–207 (2008).
Nakatani, T. et al. Silent cerebral infarction in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 23, 86–90 (2003).
Eldehni, M. T., Odudu, A. & McIntyre, C. W. Randomized clinical trial of dialysate cooling and effects on brain white matter. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26, 957–965 (2015).
Hillal, A., Ullberg, T. & Ramgren, B. Computed tomography in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: neuroimaging predictors of hematoma expansion and outcome. Insights Imaging 13, 180 (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors researched the data for the article and contributed substantially to discussion of the content. C.Z., P.B.M. and F.M. wrote the article. All authors reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Nephrology thanks Debasish Banerjee, Georg Schlieper and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zoccali, C., Mark, P.B., Sarafidis, P. et al. Diagnosis of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 19, 733–746 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-023-00747-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-023-00747-4
This article is cited by
-
Impact of resistance exercise on patients with chronic kidney disease
BMC Nephrology (2024)