Abstract
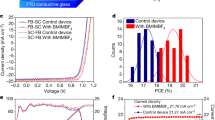
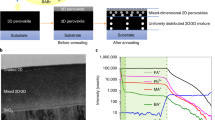
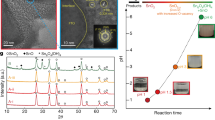
Irreversible ion migration from the perovskite layer to the charge transport layer and metal electrodes causes irreversible efficiency loss in perovskite solar cells. Confining the mobile ions within the perovskite layer is a promising strategy to improve the long-term operational stability of solar cells. Here we inhibit the migration of iodide ions out of the perovskite under light illumination by creating a depletion region inside the perovskite layer. Precise control of the doping depth induces an electric field within the perovskite that counteracts ion migration while enhancing carrier separation. Our devices exhibit a certified power conversion efficiency of 24.6% and maintain over 88% of the initial efficiency after 1,920 h of continuous illumination under maximum power point conditions (65 °C in ambient air, following the ISOS-L-2 protocol). The power conversion efficiency returns to more than 94% of its initial value after overnight recovery. When operating under repeated 12 h light on/off cycles for over 10,000 h (solar simulator at 65 °C and ambient air, following the ISOS-LC-2 protocol), the efficiency loss is less than 2%. We expect this method to open up new and effective avenues towards enhancing the long-term stability of high-performance perovskite photovoltaics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Kojima, A., Teshima, K., Shirai, Y. & Miyasaka, T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 6050–6051 (2009).
Kim, H.-S. et al. Lead iodide perovskite sensitized all-solid-state submicron thin film mesoscopic solar cell with efficiency exceeding 9%. Sci. Rep. 2, 591 (2012).
Lee, M. M., Teuscher, J., Miyasaka, T., Murakami, T. N. & Snaith, H. J. Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338, 643–647 (2012).
Burschka, J. et al. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499, 316–319 (2013).
Jeon, N. J. et al. Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 13, 897–903 (2014).
Chen, W. et al. Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science 350, 944–948 (2015).
Park, J. et al. Controlled growth of perovskite layers with volatile alkylammonium chlorides. Nature 616, 724–730 (2023).
Best Research-Cell-Efficiency Chart (NREL, 2023); https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html
Yuan, Y. & Huang, J. Ion migration in organometal trihalide perovskite and its impact on photovoltaic efficiency and stability. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 286–293 (2016).
Di Girolamo, D. et al. Ion migration-induced amorphization and phase segregation as a degradation mechanism in planar Perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 2000310 (2020).
Yuan, H. F. et al. Degradation of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite structures through light and electron beam driven ion migration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 561–566 (2016).
Domanski, K. et al. Migration of cations induces reversible performance losses over day/night cycling in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 604–613 (2017).
Gottesman, R. et al. Photoinduced reversible structural transformations in free-standing CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite films. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 2332–2338 (2015).
Nie, W. et al. Light-activated photocurrent degradation and self-healing in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 11574 (2016).
Besleaga, C. et al. Iodine migration and degradation of perovskite solar cells enhanced by metallic electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 5168–5175 (2016).
Zhao, Y. C. et al. Mobile-ion-induced degradation of organic hole-selective layers in perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 14517–14523 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. Stabilizing heterostructures of soft perovskite semiconductors. Science 365, 687–691 (2019).
Kato, Y. et al. Silver iodide formation in methyl ammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with silver top electrodes. Adv. Mater. Inter. 2, 1500195 (2015).
De Bastiani, M. et al. Toward stable monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem photovoltaics: a six-month outdoor performance study in a hot and humid climate. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 2944–2951 (2021).
Lin, D. X. et al. Ion migration accelerated reaction between oxygen and metal halide perovskites in light and its suppression by cesium incorporation. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2002552 (2021).
Zhou, W. K. et al. Light-independent ionic transport in inorganic perovskite and ultrastable Cs-based perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 4122–4128 (2017).
Wei, D. et al. Ion-migration inhibition by the cation–π interaction in perovskite materials for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 30, 1707583 (2018).
Cai, Y. et al. Multifunctional enhancement for highly stable and efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2005776 (2021).
Zai, H. et al. Sandwiched electrode buffer for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells with dual back surface fields. Joule 5, 2148–2163 (2021).
Chen, C. et al. Arylammonium-assisted reduction of the open-circuit voltage deficit in wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells: the role of suppressed ion migration. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 2560–2568 (2020).
Yang, S. et al. Stabilizing halide perovskite surfaces for solar cell operation with wide-bandgap lead oxysalts. Science 365, 473–478 (2019).
Azmi, R. et al. Damp heat–stable perovskite solar cells with tailored-dimensionality 2D/3D heterojunctions. Science 376, 73–77 (2022).
Cai, M. L. et al. Control of electrical potential distribution for high-performance perovskite solar cells. Joule 2, 296–306 (2018).
Zhang, M. et al. Reconfiguration of interfacial energy band structure for high-performance inverted structure perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 10, 4593 (2019).
Wang, C. et al. Understanding and eliminating hysteresis for highly efficient planar perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700414 (2017).
Wang, Q. et al. Qualifying composition dependent p and n self-doping in CH3NH3PbI3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 163508 (2014).
Yin, W. J., Shi, T. T. & Yan, Y. F. Unusual defect physics in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cell absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 063903 (2014).
Wang, R. et al. Constructive molecular configurations for surface-defect passivation of perovskite photovoltaics. Science 366, 1509–1513 (2019).
Andrade, J. S. Jr, Street, D. A., Shinohara, T., Shibusa, Y. & Arai, Y. Percolation disorder in viscous and nonviscous flow through porous media. Phys. Rev. E 51, 5725–5731 (1995).
Oldenburg, C. M., Mukhopadhyay, S. & Cihan, A. On the use of Darcy’s law and invasion-percolation approaches for modeling large-scale geologic carbon sequestration. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 6, 19–33 (2016).
Larson, R. G., Davis, H. T. & Scriven, L. E. Displacement of residual nonwetting fluid from porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 36, 75–85 (1981).
Ni, Z. et al. Resolving spatial and energetic distributions of trap states in metal halide perovskite solar cells. Science 367, 1352–1358 (2020).
Guo, Z. et al. Long-range hot-carrier transport in hybrid perovskites visualized by ultrafast microscopy. Science 356, 59–62 (2017).
Xing, G. et al. Long-range balanced electron- and hole-transport lengths in organic–inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science 342, 344–347 (2013).
Giovanni, D. et al. Ultrafast long-range spin-funneling in solution-processed Ruddlesden–Popper halide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 10, 3456 (2019).
Guo, Z., Manser, J. S., Wan, Y., Kamat, P. V. & Huang, L. B. Spatial and temporal imaging of long-range charge transport in perovskite thin films by ultrafast microscopy. Nat. Commun. 6, 7471 (2015).
Lu, G. L., Zheng, F., Wang, J. Q. & Shen, W. Z. Thin Al2O3 passivated boron emitter of n-type bifacial c-Si solar cells with industrial process. Prog. Photovoltaics 25, 280–290 (2017).
Yoo, J. J. et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells via improved carrier management. Nature 590, 587–593 (2021).
Zhao, Y. et al. Inactive (PbI2)2RbCl stabilizes perovskite films for efficient solar cells. Science 377, 531–534 (2022).
Kresse, G. & Furthmuller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Lee, K., Murray, E. D., Kong, L. Z., Lundqvist, B. I. & Langreth, D. C. Higher-accuracy van der Waals density functional. Phys. Rev. B 82, 081101 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant nos. 2020YFB1506400 and 2021YFB3800100) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. U20A20245, U21A20171, 11834011 and 12074245). We thank H. Li, Q. Shan for KPFM measurements; R. Wang for TRPL measurements; J. Ding for TOF-SIMS measurements; X. Ding and N. Zhang for XPS and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy measurements; B. Zhu for Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy measurements; Q. Rao for X-ray diffraction measurements; and Z. Bao and Y. Lin for SEM measurement from the Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University. We thank X. Liu from the College of Arts and Sciences, University of Tokyo, for valuable advice on the experiments and paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.S., Q.H., Y.Y. and L.H. conceived the experiments, performed data analysis and wrote the paper. Z.S. led the fabrication of the solar cells. Y.S. and X.L. helped with the sample preparation for characterization. Y.W., Y.Y. and Y.Z. participated the discussion about the feasibility of the experiment. All authors discussed the results and commented on the paper. Q.H. and L.H. directed and supervised the entire research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks Nam-Gyu Park, Michael Saliba and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Characterization, Supplementary Notes 1 and 2, Figs. 1–37 and Tables 1–8.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Z., Han, Q., Luo, X. et al. Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells with regulated depletion region. Nat. Photon. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01383-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01383-5