Abstract
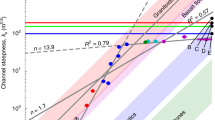
The southern highlands of Mars are dissected by hundreds of valley networks, which are evidence that water once sculpted the surface. Characterizing the mechanisms of valley incision may constrain early Mars climate and the search for ancient life. Previous interpretations of the geological record require precipitation and surface water runoff to form the valley networks, in contradiction with climate simulations that predict a cold, icy ancient Mars. Here we present a global comparative study of valley network morphometry, using a principal-component-based analysis with physical models of fluvial, groundwater sapping and glacial and subglacial erosion. We found that valley formation involved all these processes, but that subglacial and fluvial erosion are the predominant mechanisms. This is supported by predictions from models of steady-state erosion and geomorphological comparisons to terrestrial analogues. The inference of subglacial channels among the valley networks supports the presence of ice sheets that covered the southern highlands during the time of valley network emplacement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets generated during the current study, which include observations, model parameters and longitudinal profile data have been deposited in the Zenodo repository at https://zenodo.org/record/3890557#.XwgnIigzaUl and are included in this article as Supplementary tables.
Code availability
Data analysis codes include the PCA (available as the MATLAB built-in function pca) as well as custom codes specifically generated for data and error extraction, error propagation, confidence analysis and modelling of the synthetic fluvial, glacial, sapping and subglacial valley networks. The authors will provide the custom codes in a MATLAB live script format (.mlx) upon request.
References
Carr, M. H. The Martian drainage system and the origin of valley networks and fretted channels. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 100, 7479–7507 (1995).
Williams, R. M. & Phillips, R. J. Morphometric measurements of Martian valley networks from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. J. Geophys. Research Planet. 106, 23737–23751 (2001).
Gulick, V. C. Origin of the valley networks on Mars: a hydrological perspective. Geomorphology 37, 241–268 (2001).
Hynek, B. M., Beach, M. & Hoke, M. R. Updated global map of Martian valley networks and implications for climate and hydrologic processes. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 115, E090008 (2010).
Carr, M. H. & Clow, G. D. Martian channels and valleys: their characteristics, distribution, and age. Icarus 48, 91–117 (1981).
Laity, J. E. & Malin, M. C. Sapping processes and the development of theater-headed valley networks on the Colorado Plateau. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 96, 203–217 (1985).
Kargel, J. S. & Strom, R. G. Ancient glaciation on Mars. Geology 20, 3–7 (1992).
Lee, P. A Unique Mars/early Mars analog on Earth: the Haughton impact structure Devon Island, Canadian Arctic. In Conference on Early Mars: Geologic and Hydrologic Evolution, Physical and Chemical Environments, and the Implications for Life (eds Clifford, S. M., Treiman, A. H., Newsom, H. E. & Farmer, J. D.) 50 (LPI Contribution no. 916, Lunar and Planetary Institute, 1997).
Craddock, R. A. & Howard, A. D. The case for rainfall on a warm, wet early Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 107, 5111 (2002).
Howard, A. D., Moore, J. M. & Irwin, R. P. An intense terminal epoch of widespread fluvial activity on early Mars: 1. Valley network incision and associated deposits. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 110, E12S14 (2005).
Baker, V. R., Carr, M. H., Gulick, V. C., Williams, C. R. & Marley, M. S. in Mars (eds Kieffer, H. H., Jakosky, B. M., Snyder, C. W. & Matthews, M. S.) 493–522 (Univ. Arizona Press, 1992).
Lamb, M. P. et al. Can springs cut canyons into rock? J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 111, E07002 (2006).
Sharp, R. P. & Malin, M. C. Channels on Mars. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 86, 593–609 (1975).
Wordsworth, R. et al. Global modelling of the early Martian climate under a denser CO2 atmosphere: water cycle and ice evolution. Icarus 222, 1–19 (2013).
Fastook, J. L. & Head, J. W. Glaciation in the Late Noachian Icy Highlands: ice accumulation, distribution, flow rates, basal melting, and top-down melting rates and patterns. Planet. Space Sci. 106, 82–98 (2015).
Grau Galofre, A. & Jellinek, M. A. The geometry and complexity of spatial patterns of terrestrial channel networks: distinctive fingerprints of erosional regimes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 122, 1037–1059 (2017).
Grau Galofre, A., Jellinek, A. M., Osinski, G., Zanetti, M. & Kukko, A. Subglacial drainage patterns of Devon Island, Canada: detailed comparison of river and subglacial channels. Cryosphere 12, 1461–1478 (2018).
Shreve, R. Movement of water in glaciers. J. Glaciol. 11, 205–214 (1972).
Sugden, D. E., Denton, G. H. & Marchant, D. R. Subglacial meltwater channel systems and ice sheet overriding, Asgard Range, Antarctica. Geogr. Annal. A 73, 109–121 (1991).
Greenwood, S. L., Clark, C. D. & Hughes, A. L. Formalising an inversion methodology for reconstructing ice-sheet retreat patterns from meltwater channels: application to the British Ice Sheet. J. Quatern. Sci. 22, 637–645 (2007).
Kehew, A. E., Piotrowski, J. A. & Jørgensen, F. Tunnel valleys: concepts and controversies—a review. Earth Sci. Rev. 113, 33–58 (2012).
Hobley, D. E., Howard, A. D. & Moore, J. M. Fresh shallow valleys in the Martian midlatitudes as features formed by meltwater flow beneath ice. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 119, 128–153 (2014).
Kleman, J. & Hättestrand, C. Frozen-bed Fennoscandian and Laurentide ice sheets during the Last Glacial Maximum. Nature 402, 63–66 (1999).
Dyke, A. Last Glacial Maximum and deglaciation of Devon Island, Arctic Canada: support for an Innuitian Ice Sheet. Quatern. Sci. Rev. 18, 393–420 (1999).
Hättestrand, C. & Stroeven, A. P. A relict landscape in the centre of Fennoscandian glaciation: geomorphological evidence of minimal Quaternary glacial erosion. Geomorphology 44, 127–143 (2002).
England, J. et al. The Innuitian Ice Sheet: configuration, dynamics and chronology. Quatern. Sci. Rev. 25, 689–703 (2006).
Walder, J. & Hallet, B. Geometry of former subglacial water channels and cavities. J. Glaciol. 23, 335–346 (1979).
Malin, M. C. & Carr, M. H. Groundwater formation of Martian valleys. Nature 397, 589–591 (1999).
Whipple, K. X. & Tucker, G. E. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model: implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 104, 17661–17674 (1999).
Parker, G., Wilcock, P. R., Paola, C., Dietrich, W. E. & Pitlick, J. Physical basis for quasi-universal relations describing bankfull hydraulic geometry of single-thread gravel bed rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface 112, F04005 (2007).
Perron, J. T., Dietrich, W. E. & Kirchner, J. W. Controls on the spacing of first-order valleys. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface 113, F04016 (2008).
Wordsworth, R. D., Kerber, L., Pierrehumbert, R. T., Forget, F. & Head, J. W. Comparison of ‘warm and wet’ and ‘cold and icy’ scenarios for early Mars in a 3-D climate model. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 120, 1201–1219 (2015).
Schoof, C. Ice-sheet acceleration driven by melt supply variability. Nature 468, 803–806 (2010).
Rennermalm, A. K. et al. Understanding Greenland ice sheet hydrology using an integrated multi-scale approach. Environ. Res. Lett. 8, 015017 (2013).
Christensen, P. R. Water at the poles and in permafrost regions of Mars. Elements 2, 151–155 (2006).
Carr, M. & Head, J. Martian surface/near-surface water inventory: sources, sinks, and changes with time. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 726–732 (2015).
Cuffey, K. M. & Paterson, W. S. B. The Physics of Glaciers (Academic, 2010).
Clifford, S. M. A model for the hydrologic and climatic behavior of water on mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 98, 10973–11016 (1993).
Wordsworth, R. D. The climate of early Mars. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 44, 381–408 (2016).
Palumbo, A. M. & Head, J. W. Early Mars climate history: characterizing a ‘warm and wet’ Martian climate with a 3D global climate model and testing geological predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45, 10249–10258 (2018).
Rosenberg, E. N., Palumbo, A. M., Cassanelli, J. P., Head, J. W. & Weiss, D. K. The volume of water required to carve the Martian valley networks: improved constraints using updated methods. Icarus 317, 379–387 (2019).
Head, J. W. & Pratt, S. Extensive Hesperian-aged south polar ice sheet on Mars: evidence for massive melting and retreat, and lateral flow and ponding of meltwater. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 106, 12275–12299 (2001).
Fastook, J. L., Head, J. W., Marchant, D. R., Forget, F. & Madeleine, J.-B. Early Mars climate near the Noachian–Hesperian boundary: Independent evidence for cold conditions from basal melting of the south polar ice sheet (Dorsa Argentea Formation) and implications for valley network formation. Icarus 219, 25–40 (2012).
Butcher, F. E., Conway, S. J. & Arnold, N. S. Are the Dorsa Argentea on Mars eskers? Icarus 275, 65–84 (2016).
Orosei, R. et al. Radar evidence of subglacial liquid water on Mars. Science 361, 490–493 (2018).
Irwin, R. P., Howard, A. D., Craddock, R. A. & Moore, J. M. An intense terminal epoch of widespread fluvial activity on early Mars: 2. Increased runoff and paleolake development. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 110, E12S15 (2005).
Ansan, V., Mangold, N., Masson, P., Gailhardis, E. & Neukum, G. Topography of valley networks on Mars from Mars Express High Resolution Stereo Camera digital elevation models. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 113, E07006 (2008).
Carr, M. H. & Malin, M. C. Meter-scale characteristics of Martian channels and valleys. Icarus 146, 366–386 (2000).
Rains, R. B. et al. Subglacial tunnel channels, Porcupine Hills, Southwest Alberta, Canada. Quatern. Int. 90, 57–65 (2002).
Sissons, J. A subglacial drainage system by the Tinto Hills, Lanarkshire. Trans. Edin. Geol. Soc. 18, 175–193 (1961).
Pieri, D. C. Martian valleys—morphology, distribution, age, and origin. Science 210, 895–897 (1980).
Smith, D. E. et al. Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter: experiment summary after the first year of global mapping of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 106, 23689–23722 (2001).
Horton, R. E. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 56, 275–370 (1945).
Stepinski, T. & Stepinski, A. Morphology of drainage basins as an indicator of climate on early Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planet. 110, E12S12 (2005).
Bue, B. D. & Stepinski, T. F. Automated classification of landforms on Mars. Computat. Geosci. 32, 604–614 (2006).
Acknowledgements
A.G.G., A.M.J. and G.R.O. were supported through the NSERC Discovery grant program. A.G.G. also received support through an NSERC CREATE-funded fellowship and through an Exploration Fellowship from the School of Earth and Space Exploration, ASU. Arctic fieldwork was supported through PCSP and NSERC Northern Research Supplement Grants to G.R.O. Our appreciation goes to C. Schoof, R. Phillips, K. Whipple and P. Christensen for their insightful comments, and to the MJ-CJ research group for continued support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.G.G. and A.M.J conceived the study. A.G.G. carried out all the calculations, performed the data analysis summarized in Figs. 2–4 and took the lead in writing the paper with A.M.J. G.O. provided critical comments related particularly to geological controls on the history of Mars surface processes. All the authors contributed to constructing the discussion and implications for Mars’ hydrosphere and early climate.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Primary handling editor: Stefan Lachowycz.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
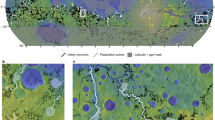
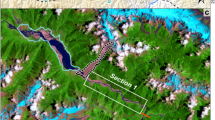
Extended Data Fig. 1 PCA endmember examples.
Examples of the four groups of valley networks as derived from the PCA classification: Warrego valles, fluvial (a), unnamed valley (M68), glacial (b), Abus vallis, sapping (c), and Pallacopas valles, subglacial (d). Images show colorized elevation (MOLA, Goddard Space Flight Center) overlying a THEMIS (ASU/NASA) mosaic.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary methods including Figs. 1–13 and Table 1.
Supplementary Data 1
Main dataset. The table is structured so that each row is a valley network and columns include the ID number, valley name (if applicable), latitude/longitude, and the six metrics and their respective error.
Supplementary Data 2
This table includes two sheets. The first is the table of parameters, where each row is a parameter, and columns are the parameter symbol, definition, units, values (lower, average, and upper bounds), and references. The second sheet contains the metric predictions (upper, average, and lower values).
Supplementary Data 3
PCA classification and confidence results of the study. Rows correspond to valley networks, whereas columns give their ID, name, latitude/longitude, the distances to each of the synthetic valley network erosional groups, the relative distances, distances minus statistical threshold, and the final classification result (1 is fluvial, 2 is glacial, 3 is sapping, 4 is subglacial, 5 is undifferentiated). The last column, confidence, goes from highest (1) to lowest (4).
Supplementary Data 4
Longitudinal profile observations and undulation interpretations. Rows correspond to valley networks, columns are valley network ID, name, and a description of the longitudinal profile undulations and interpretations.
Supplementary Data 5
Sensitivity analysis for the principal component results. The first sheet contains the sensitivity analysis summary, columns are the sample size and the five metrics. The second sheet contains a total of 35 individual analysis for different sample sizes, as indicated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grau Galofre, A., Jellinek, A.M. & Osinski, G.R. Valley formation on early Mars by subglacial and fluvial erosion. Nat. Geosci. 13, 663–668 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-020-0618-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-020-0618-x
This article is cited by
-
Drainage divide migration and implications for climate and biodiversity
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2024)
-
High Arctic channel incision modulated by climate change and the emergence of polygonal ground
Nature Communications (2023)
-
The importance of lake breach floods for valley incision on early Mars
Nature (2021)