Abstract
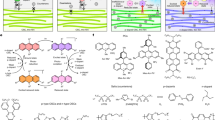
Organosilanes are of vital importance for modern human society, having found widespread applications in functional materials, organic synthesis, drug discovery and life sciences. However, their preparation remains far from trivial, and on-demand synthesis of heteroleptic substituted silicon reagents is a formidable challenge. The generation of silyl radicals from hydrosilanes via direct hydrogen-atom-transfer (HAT) photocatalysis represents the most atom-, step-, redox- and catalyst-economic pathway for the activation of hydrosilanes. Here, in view of the green characteristics of neutral eosin Y (such as its abundance, low cost, metal-free nature, absorption of visible light and excellent selectivity), we show that using it as a direct HAT photocatalyst enables the stepwise custom functionalization of multihydrosilanes, giving access to fully substituted silicon compounds. By exploiting this strategy, we realize preferable hydrogen abstraction of Si–H bonds in the presence of active C–H bonds, diverse functionalization of hydrosilanes (for example, alkylation, vinylation, allylation, arylation, deuteration, oxidation and halogenation), and remarkably selective monofunctionalization of di- and trihydrosilanes.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the Article and its Supplementary Information. Computational raw data are available at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20154056.
References
Lehmann, J. W., Blair, D. J. & Burke, M. D. Towards the generalized iterative synthesis of small molecules. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 0115 (2018).
Woerly, E. M., Roy, J. & Burke, M. D. Synthesis of most polyene natural product motifs using just 12 building blocks and one coupling reaction. Nat. Chem. 6, 484–491 (2014).
Burns, M. et al. Assembly-line synthesis of organic molecules with tailored shapes. Nature 513, 183–188 (2014).
Rossi, R., Bellina, F. & Lessi, M. Selective palladium-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura reactions of polyhalogenated heteroarenes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 354, 1181–1255 (2012).
Lee, J. C. H., McDonald, R. & Hall, D. G. Enantioselective preparation and chemoselective cross-coupling of 1,1-diboron compounds. Nat. Chem. 3, 894–899 (2011).
Liao, K., Negretti, S., Musaev, D. G., Bacsa, J. & Davies, H. M. L. Site-selective and stereoselective functionalization of unactivated C–H bonds. Nature 533, 230–234 (2016).
Xia, J., Zhu, C. & Chen, C. Visible light-promoted metal-free C–H activation: diarylkeone-catalyzed selective benzylic mono- and difluorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 17494–17500 (2013).
Rösch, L., John, P. & Reitmeier, R. Silicon compounds, organic. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 637–669 (Wiley, 2000).
Franz, A. K. & Wilson, S. O. Organosilicon molecules with medicinal applications. J. Med. Chem. 56, 388–405 (2013).
Denmark, S. E. & Regens, C. S. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organosilanols and their salts: practical alternatives to boron- and tin-based methods. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 1486–1499 (2008).
Kubota, K. & Ito, H. in Organosilicon Chemistry: Novel Approaches and Reactions (eds Hiyama, T. & Oestreich, M.) 1–31 (Wiley, 2019).
Yuan, W., Smirnov, P. & Oestreich, M. Custom hydrosilane synthesis based on monosilane. Chem 4, 1443–1450 (2018).
Simonneau, A. & Oestreich, M. Formal SiH4 chemistry using stable and easy-to-handle surrogates. Nat. Chem. 7, 816–822 (2015).
Chatgilialoglu, C. Structural and chemical properties of silyl radicals. Chem. Rev. 95, 1229–1251 (1995).
Oestreich, M., Hermeke, J. & Mohr, J. A unified survey of Si–H and H–H bond activation catalysed by electron-deficient boranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 2202–2220 (2015).
Zhang, X., Fang, J., Cai, C. & Lu, G. Recent advances in synthesis of organosilicons via radical strategies. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32, 1280–1292 (2021).
Zhou, R. et al. Visible-light-mediated metal-free hydrosilylation of alkenes through selective hydrogen atom transfer for Si–H activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 16621–16625 (2017).
Hou, J. et al. Visible-light-mediate metal-free difunctionalization of alkenes with CO2 and silanes or C(sp3)–H alkanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 17220–17224 (2018).
Zhou, R. et al. Visible-light-mediated deuteration of silanes with deuterium oxide. Chem. Sci. 10, 7340–7344 (2019).
Zhang, Z. & Hu, X. Arylsilylation of electron-deficient alkenes via cooperative photoredox and nickel catalysis. ACS Catal. 10, 777–782 (2020).
Ghosh, S., Lai, D. & Hajra, A. Visible-light-induced silylation: an update. Org. Biomol. Chem. 19, 2399–2415 (2021).
Qrareya, H., Dondi, D., Ravelli, D. & Fagnoni, M. Decatungstate-photocatalyzed Si–H/C–H activation in silyl hydrides: hydrosilylation of electron-poor alkenes. ChemCatChem 7, 3350–3357 (2015).
Fan, X. et al. Eosin Y as a direct hydrogen atom transfer photocatalysts for the functionalization of C–H bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 8514–8518 (2018).
Fan, X. et al. Neutral-eosin-Y-photocatalyzed silane chlorination using dichloromethane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 12580–12584 (2019).
Kuang, Y. et al. Asymmetric synthesis of 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds from aldehydes via the marriage of hydrogen atom transfer photocatalysis with chiral Lewis acid catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 16859–16863 (2019).
Yan, J. et al. Divergent functionalization of aldehydes photocatalyzed by neutral eosin Y with sulfone reagents. Nat. Commun. 12, 7214 (2021).
Cambié, D., Bottecchia, C., Straathof, N. J. W., Hessel, W. & Noël, T. Applications of continuous-flow photochemistry in organic synthesis, material science and water treatment. Chem. Rev. 116, 10276–10341 (2016).
Obligacion, J. V. & Chirik, P. J. Earth-abundant transition metal catalysts for alkene hydrosilylation and hydroboration. Nat. Rev. 2, 15–34 (2018).
Speier, J. L., Webster, J. A. & Barnes, G. H. The addition of silicon hydrides to olefinic double bonds. Part II. The use of group VIII metal catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79, 974–979 (1957).
Asgari, P. et al. Catalytic hydrogen atom transfer from hydrosilanes to vinylarenes for hydrosilylation and polymerization. Nat. Catal. 2, 164–173 (2019).
Sieburth, S. M., Manly, C. J. & Gammon, D. W. Organosilane insecticides. Part I: biological and physical effects of isosteric replacement of silicon for carbon in etofenprox and MTI-800. Pestic. Sci. 28, 289–307 (1990).
Zhu, J., Cui, W.-C., Wang, S.-Z. & Yao, Z.-J. Radical hydrosilylation of alkynes catalyzed by eosin Y and thiol under visible light irradiation. Org. Lett. 20, 3174–3178 (2018).
Zhu, J., Cui, W.-C., Wang, S.-Z. & Yao, Z.-J. Visible light-driven radical trans-hydrosilylation of electron-neutral and -rich alkenes with tertiary and secondary hydrosilanes. J. Org. Chem. 83, 14600–14609 (2018).
Cheng, C. & Hartwig, J. F. Catalytic silylation of unactivated C–H bonds. Chem. Rev. 115, 8946–8975 (2015).
Dong, J. et al. Manganese-catalysed divergent silylation of alkenes. Nat. Chem. 13, 182–190 (2021).
Ma, Y., Wang, B., Zhang, L. & Hou, Z. Boron-catalyzed aromatic C–H bond silylation with hydrosilanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 3663–3666 (2016).
Toutov, A. A. et al. Silylation of C-H bonds in aromatic heterocycles by an earth-abundant metal catalyst. Nature 518, 80–84 (2015).
McNally, A., Prier, C. K. & MacMillan, D. W. C. Discovery of an α-amino C–H arylation reaction using the strategy of accelerated serendipity. Science 334, 1114–1117 (2011).
Minami, K., Ohmatsu, K. & Ooi, T. Hydrogen-atom-transfer-mediated acceptorless dehydrogenative cross-coupling enabled by multiple catalytic functions of zwitterionic triazolium amidate. ACS Catal. 12, 1971–1976 (2022).
Chandrasekhar, V., Boomishankar, R. & Nagendran, S. Recent developments in the synthesis and structure of organosilanols. Chem. Rev. 104, 5847–5910 (2004).
Wang, K. et al. Selective manganese-catalyzed oxidation of hydrosilanes to silanols under neutral reaction conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 6380–6384 (2019).
Liang, H., Wang, L.-J., Ji, Y.-X., Wang, H. & Zhang, B. Selective electrochemical hydrolysis of hydrosilanes to silanols via anodically generated silyl cations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 1839–1844 (2021).
Murakami, K., Hirano, K., Yorimitsu, H. & Oshima, K. Silver-catalyzed transmetalation between chlorosilanes and aryl and alkenyl Grignard reagents for the synthesis of tetraorganosilanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 5833–5835 (2008).
Agarwal, P. & Bertozzi, C. R. Site-specific antibody-drug conjugates: the nexus of biorthogonal chemistry, protein engineering and drug development. Bioconjug. Chem. 26, 176–192 (2015).
Tamao, K., Yamaguchi, S. & Shiro, M. Oligosiloles: first synthesis based on a novel endo-endo mode intramolecular reductive cyclization of diethynylsilanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 11715–11722 (1994).
Muzafarov, A. M. (ed.) Silicon Polymers (Springer, 2011).
Brook, M. A. New control over silicone synthesis using SiH chemistry: the Piers–Rubinsztajn reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 8458–8469 (2018).
Lee, H.-J., Kwak, C., Kim, D.-P. & Kim, H. Continuous-flow Si–H functionalizations of hydrosilanes via sequential organolithium reactions catalyzed by potassium tert-butoxide. Green Chem. 23, 1193–1199 (2021).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support provided by the Ministry of Education (MOE) of Singapore (MOET2EP10120-0014, J.W.; MOET2EP10120-0007, X.L.), the National University of Singapore (R-143-000-B60-114, J.W.) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21688102, G.C.). We thank D. Ravelli (University of Pavia) for insightful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.F. and M.Z. contributed equally to the work; their names are listed alphabetically by family name. J.W. conceived the project and directed the research. X.F. and M.Z. designed and performed the experiments. Y.G. and G.C. performed the DFT calculations. Y.L. performed the GC-MS analysis for H2 source investigation. X.F., M.Z., Q.Z., Y.Z., J. Yu, H.L., W.X., Y.C.T., J. Yan and S.C. conducted experiments to demonstrate the substrate scope. J.W., X.F., M.Z., Z.L., Y.G. and G.C. wrote the paper. All authors commented on the final paper and contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.W., F.X. and M.Z. are inventors on an International Patent Application (PCT/SG2022/050462) submitted by the National University of Singapore that covers the synthesis of functional silanes from multihydrosilanes by neutral eosin Y HAT photocatalysis. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Chemistry thanks Junha Jeon, Paul Rablen and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–64, Tables 1–31, synthetic procedural details, mechanistic studies, proposed mechanisms, high-resolution mass spectrometry, IR data, NMR data and spectra.
Supplementary Data
Cartesian coordinates of computational structures.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Zhang, M., Gao, Y. et al. Stepwise on-demand functionalization of multihydrosilanes enabled by a hydrogen-atom-transfer photocatalyst based on eosin Y. Nat. Chem. 15, 666–676 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01155-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01155-8
This article is cited by
-
Dinuclear gold-catalyzed divergent dechlorinative radical borylation of gem-dichloroalkanes
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Arenium-ion-catalysed halodealkylation of fully alkylated silanes
Nature (2023)
-
Ligand-modulated nickel-catalyzed regioselective silylalkylation of alkenes
Nature Communications (2023)