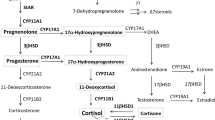
Abstract
Epithelial barriers play an important role in the exchange of nutrients, gases, and other signals between our body and the outside world. However, they protect it also from invasion by potential pathogens. Defective epithelial barriers and associated overshooting immune responses are the basis of many different inflammatory disorders of the skin, the lung, and the intestinal mucosa. The anti-inflammatory activity of glucocorticoids has been efficiently used for the treatment of these diseases. Interestingly, epithelia in these tissues are also a rich source of endogenous glucocorticoids, suggesting that local glucocorticoid synthesis is part of a tissue-specific regulatory circuit. In this review, we summarize current knowledge about the extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis at the epithelial barriers of the intestine, lung and the skin, and discuss their relevance in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases and as therapeutic targets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKay LI, Cidlowski JA. Cross-talk between nuclear factor-κB and the steroid hormone receptors: mechanisms of mutual antagonism. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1210/mend.12.1.0044.
Ray A, Prefontaine KE. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.2.752.
Yang-Yen HF, Chambard JC, Sun YL, Smeal T, Schmidt TJ, Drouin J, et al. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein–protein interaction. Cell. 1990;62:1205–15.
Diamond MI, Miner JN, Yoshinaga SK, Yamamoto KR. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990;249:1266–72.
Erlacher M, Michalak EM, Kelly PN, Labi V, Niederegger H, Coultas L, et al. BH3-only proteins Puma and Bim are rate-limiting for gamma-radiation- and glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of lymphoid cells in vivo. Blood. 2005;106:4131–8.
Boldizsar F, Talaber G, Szabo M, Bartis D, Palinkas L, Nemeth P, et al. Emerging pathways of non-genomic glucocorticoid (GC) signalling in T cells. Immunobiology. 2010;215:521–6.
Turnbull AV, Rivier CL. Regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1–71.
Honma S. The mammalian circadian system: a hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J Physiol Sci. 2018;68:207–19.
Schibler U, Gotic I, Saini C, Gos P, Curie T, Emmenegger Y, et al. Clock-talk: interactions between central and peripheral circadian oscillators in mammals. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2016;80:223–32.
Kalsbeek A, van der Spek R, Lei J, Endert E, Buijs RM, Fliers E. Circadian rhythms in the hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;349:20–29.
Pon LA, Hartigan JA, Orme-Johnson NR. Acute ACTH regulation of adrenal corticosteroid biosynthesis. Rapid accumulation of a phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:13309–16.
Clark BJ, Soo SC, Caron KM, Ikeda Y, Parker KL, Stocco DM. Hormonal and developmental regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1995;9:1346–55.
Arakane F, King SR, Du Y, Kallen CB, Walsh LP, Stocco DM, et al. Phosphorylation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) modulates its steroidogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32656–62.
Ruggiero C, Lalli E. Impact of ACTH signaling on transcriptional regulation of steroidogenic genes. Front Endocrinol. 2016;7:24.
Parker KL, Rice Da, Lala DS, Ikeda Y, Luo X, Wong M, et al. Steroidogenic factor 1: an essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2002;57:19–36.
Parker KL. The roles of steroidogenic factor 1 in endocrine development and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998;145:15–20.
Parker KL, Ikeda Y, Luo X. The roles of steroidogenic factor-1 in reproductive function. Steroids. 1996;61:161–5.
Wang XL, Bassett M, Zhang Y, Su Y, Clyne C, White PC, et al. Transcriptional regulation of human 11β-hydroxylase (hCYP11B1). Endocrinology. 2000;1:3587–94.
Rice DA, Aitken LD, Vandenbark GR, Mouw AR, Franklin A, Schimmer BP, et al. A cAMP-responsive element regulates expression of the mouse steroid 11β-hydroxylase gene. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:14011–5.
Talabér G, Jondal M, Okret S. Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis: immune regulation and aspects on local organ homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;380:89–98.
Hostettler N, Bianchi P, Gennari-Moser C, Kassahn D, Schoonjans K, Corazza N, et al. Local glucocorticoid production in the mouse lung is induced by immune cell stimulation. Allergy. 2012;67:227–34.
Mittelstadt PR, Taves MD, Ashwell JD. Cutting edge: de novo glucocorticoid synthesis by thymic epithelial cells regulates antigen-specific thymocyte selection. J Immunol. 2018;200:1988–94.
Cima I, Corazza N, Dick B, Fuhrer A, Herren S, Jakob S, et al. Intestinal epithelial cells synthesize glucocorticoids and regulate T cell activation. J Exp Med. 2004;200:1635–46.
Noti M, Corazza N, Tuffin G, Schoonjans K, Brunner T. Lipopolysaccharide induces intestinal glucocorticoid synthesis in a TNFalpha-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2010;24:1340–6.
Noti M, Corazza N, Mueller C, Berger B, Brunner T. TNF suppresses acute intestinal inflammation by inducing local glucocorticoid synthesis. J Exp Med. 2010;207:1057–66.
Mueller M, Atanasov A, Cima I, Corazza N, Schoonjans K, Brunner T. Differential regulation of glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial versus adrenocortical cell lines. Endocrinology. 2007;148:1445–53.
Mueller M, Cima I, Noti M, Fuhrer A, Jakob S, Dubuquoy L, et al. The nuclear receptor LRH-1 critically regulates extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in the intestine. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2057–62.
Coste A, Dubuquoy L, Barnouin R, Annicotte J-S, Magnier B, Notti M, et al. LRH-1-mediated glucocorticoid synthesis in enterocytes protects against inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:13098–103.
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby C, Brennan T, Wendling O, et al. Synergy between LRH-1 and β-catenin Induces G1cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 2004;15:499–509.
Bayrer JR, Wang H, Nattiv R, Suzawa M, Escusa HS, Fletterick RJ, et al. LRH-1 mitigates intestinal inflammatory disease by maintaining epithelial homeostasis and cell survival. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4055.
Delgado ME, Grabinger T, Brunner T. Cell death at the intestinal epithelial front line. FEBS J. 2016;384:2701–19.
Huang J, Jia R, Brunner T. Local synthesis of immunosuppressive glucocorticoids in the intestinal epithelium regulates anti-viral immune responses. Cell Immunol. 2018;334:1–10.
Cintolo M. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease: maintain or de-escalate therapy. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2016;7:1–16.
Dubuquoy L, Å Jansson E, Deeb S, Rakotobe S, Karoui M, Colombel JF, et al. Impaired expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γin ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1265–76.
Tomashefski JF, Farver CF. Anatomy and histology of the lung. In: Tomashefski JF Jr., Cagle PT, Farver CF FA (arg). Dail and Hammar’s Pulmonary Pathology. New York, NY: Springer; 2008. p. 20–48.
Kato A, Schleimer RP. Beyond inflammation: airway epithelial cells are at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:711–20.
Taylor KM, Ray DW, Sommer P. Glucocorticoid receptors in lung cancer: new perspectives. J Endocrinol. 2016;229:R17–R28.
Bolt RJ, Weissenbruch MM, Van, Lafeber HN. Glucocorticoids and lung development in the fetus and preterm infant. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001;91:76–91.
Nkadi PO, Merritt TA, Pillers DAM. An overview of pulmonary surfactant in the neonate: genetics, metabolism, and the role of surfactant in health and disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2009;97:95–101.
Pazirandeh A, Xue Y, Rafter I, Sjövall J, Jondal MOS. Paracrine glucocorticoid activity produced by mouse thymic epithelial cells. FASEB J. 1999;13:893–901.
Provost PR, Tremblay Y. Genes involved in the glucocorticoid synthesis are transiently expressed in the developing lung. Endocrinology. 2005;146:2239–45.
Nishimura M, Naito S, Yokoi T. Tissuespecific mRNA expression profiles of human nuclear receptor subfamilies. Drug Metab Pharm. 2004;19:135–49.
Bird AD, Mcdougall ARA, Seow B, Hooper SB, Cole TJ. Glucocorticoid regulation of lung development: lessons learned from conditional GR knockout mice. Mol Endocrinol. 2015;29:158–71.
Liggins GC, Howie RN. A controlled trial of antepartum glucocorticoid treatment for prevention of the respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1972;50:515–25.
Chalmers JD, Poole C, Webster S, Tebboth A, Dickinson S, Gayle A. Assessing the healthcare resource use associated with inappropriate prescribing of inhaled corticosteroids for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in GOLD groups A or B: an observational study using the Clinical Practice Research Data. Respir Res. 2018;19:1–9.
Heijink IH, Nawijn MC, Hackett TL. Airway epithelial barrier function regulates the pathogenesis of allergic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;44:620–30.
Gon Y, Hashimoto S. Role of airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol Int. 2018;67:12–17.
Hackett TL, Singhera GK, Shaheen F, Hayden P, Jackson GR, Hegele RG, et al. Intrinsic phenotypic differences of asthmatic epithelium and its inflammatory responses to respiratory syncytial virus and air pollution. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45:1090–1100.
Jiang Z, Zhu L. Update on molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid resistance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2016;37:1–8.
Slominski A, Baker J, Ermak G, Chakraborty A, Pawelek J. Ultraviolet B stimulates production of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) by human melanocytes. FEBS Lett. 1996;399:175–6.
Slominski a, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Foecking MF, Wortsman J. Active steroidogenesis in the normal rat skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1474:1–4.
Vukelic S, Stojadinovic O, Pastar I, Rabach M, Krzyzanowska A, Lebrun E, et al. Cortisol synthesis in epidermis is induced by IL-1 and tissue injury. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:10265–75.
Hannen RF, Michael AE, Jaulim A, Bhogal R, Burrin JM, Philpott MP. Steroid synthesis by primary human keratinocytes; implications for skin disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;404:62–7.
Hannen R, Udeh-Momoh C, Upton J, Wright M, Michael A, Gulati A, et al. Dysfunctional skin-derived glucocorticoid synthesis is a pathogenic mechanism of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:1630–7.
Ermak G, Slominski A. Production of POMC, CRH-R1, MC1, and MC2 receptor mRNA and expression of tyrosinase gene in relation to hair cycle and dexamethasone treatment in the C57BL/6 mouse skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997;108:160–5.
Slominski A, Ermak G, Mazurkiewicz JE, Baker JWJ. Characterization of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in human skin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:1020–4.
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Zbytek B, Tobin DJ, Theoharides TC, Rivier J. Key role of CRF in the skin stress response system. Endocr Rev. 2013;34:827–84.
Skobowiat C, Slominski AT. UVB activates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in C57BL/6 mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:1638–48.
Slominski A, Wortsman J, Luger T, Paus R, Solomon S. Corticotropin releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin involvement in the cutaneous response to stress. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:979–1020.
Slominski AT, Manna PR, Tuckey RC. On the role of skin in the regulation of local and systemic steroidogenic activities. Steroids. 2015;103:72–88.
Slominski A, Zbytek B, Nikolakis G, Manna PR, Skobowiat C, Zmijewski M, et al. Steroidogenesis in the skin: implications for local immune functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;137:107–23.
Cirillo N, Prime SS. Keratinocytes synthesize and activate cortisol. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:1499–505.
Thiboutot D, Jabara S, McAllister JM, Sivarajah A, Gilliland K, Cong Z, et al. Human skin is a steroidogenic tissue: steroidogenic enzymes and cofactors are expressed in epidermis, normal sebocytes, and an immortalized sebocyte cell line (SEB-1). J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:905–14.
Patel MV, McKay IA, Burrin JM. Transcriptional regulators of steroidogenesis, DAX-1 and SF-1, are expressed in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1559–65.
Slominski A, Zjawiony J, Wortsman J, Semak I, Stewart J, Pisarchik A, et al. A novel pathway for sequential transformation of 7-dehydrocholesterol and expression of the P450scc system in mammalian skin. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:4178–88.
Zmijewski MA, Slominski AT. Neuroendocrinology of the skin: an overview and selective analysis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011;3:3–10.
Slominski AT, Kim T-K, Li W, Yi A-K, Postlethwaite A, Tuckey RC. The role of CYP11A1 in the production of vitamin D metabolites and their role in the regulation of epidermal functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;144:28–39.
Elder JT. Genome-wide association scan yields new insights into the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Genes Immun. 2009;10:201–9.
Liu Y, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM. Psoriasis: genetic associations and immune system changes. Genes Immun. 2007;8:1–12.
Garcia VE, Chang M, Brandon R, Li Y, Matsunami N, Callis-Duffin KP, et al. Detailed genetic characterization of the interleukin-23 receptor in psoriasis. Genes Immun. 2008;9:546–55.
Kulig P, Musiol S, Freiberger SN, Schreiner B, Gyülveszi G, Russo G, et al. IL-12 protects from psoriasiform skin inflammation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13466.
Sevilla LM, Pérez P. Roles of the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in skin pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1906.
Whirledge S, DeFranco DB. Glucocorticoid signaling in health and disease: Insights from tissue-specific GR knockout mice. Endocrinology. 2018;159:46–61.
Sevilla LM, Latorre V, Sanchis A, Pérez P. Epidermal inactivation of the glucocorticoid receptor triggers skin barrier defects and cutaneous inflammation. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:361–70.
Boix J, Carceller E, Sevilla LM, Marcos-Garcés V, Pérez P. The mineralocorticoid receptor plays a transient role in mouse skin development. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25:69–71.
Bigas J, Sevilla LM, Carceller E, Boix J, Pérez P. Epidermal glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors act cooperatively to regulate epidermal development and counteract skin inflammation article. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:588.
Krutmann J, Morita A. Mechanisms of ultraviolet (UV) B and UVA phototherapy. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:70–2.
Walker D, Jacobe H. Phototherapy in the age of biologics. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:190–8.
Pavel S. Light therapy (with UVA-1) for SLE patients: is it a good or bad idea? Rheumatology. 2006;45:653–5.
Uva L, Miguel D, Pinheiro C, Antunes J, Cruz D, Ferreira J, et al. Mechanisms of action of topical corticosteroids in psoriasis. Int J Endocrinol. 2012;2012:561018.
Papp KA, Guenther L, Boyden B, Grønhøj Larsen F, Harvima RJ, Guilhou JJ, et al. Early onset of action and efficacy of a combination of calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate in the treatment of psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:48–54.
Devaux S, Castela A, Archier E, Gallini A, Joly P, Misery L, et al. Topical vitamin D analogues alone or in association with topical steroids for psoriasis: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:52–60.
Fleming C, Ganslandt C, Guenther L, Johannesson A, Buckley C, Simon JC, et al. Calcipotriol plus betamethasone dipropionate gel compared with its active components in the same vehicle and the vehicle alone in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris: a randomised, parallel group, double-blind, exploratory study. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:465–71.
Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, Feldman SR, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451–85.
Zhang Y, Leung DYM, Goleva E. Vitamin D enhances glucocorticoid action in human monocytes: Involvement of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor and mediator complex subunit 14. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:14544–53.
Hidalgo AA, Trump DL, Johnson CS. Glucocorticoid regulation of the vitamin D receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;121:372–5.
Cutolo M, Paolino S, Sulli A, Smith V, Pizzorni C, Seriolo B. Vitamin D, steroid hormones, and autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1317:39–46.
Taves MD, Hamden JE, Soma KK. Local glucocorticoid production in lymphoid organs of mice and birds: Functions in lymphocyte development. Horm Behav. 2017;88:4–14.
Kostadinova FI, Hostettler N, Bianchi P, Brunner T. Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in mucosal tissues and its implication in mucosal immune homeostasis and tumor development. In: Qian X (Ed.). In Glucocorticoids—New Recognition of Our Familiar Friend; 2012.
Kostadinova F, Schwaderer J, Sebeo V, Brunner T. Why does the gut synthesize glucocorticoids? Ann Med. 2014;46:490–7.
Hong SN, Joung JG, Bae JS, Lee CS, Koo JS, Park SJ, et al. RNA-seq reveals transcriptomic differences in inflamed and noninflamed intestinal mucosa of Crohn’s disease patients compared with normal mucosa of healthy controls. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23:1098–108.
Hussey M, Holleran G, Smith S, Sherlock M, McNamara D. The role and regulation of the 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme system in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:3385–90.
Stegk JP, Ebert B, Martin HJ, Maser E. Expression profiles of human 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases type 1 and type 2 in inflammatory bowel diseases. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;301:104–8.
Terao M, Katayama I. Local cortisol/corticosterone activation in skin physiology and pathology. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84:11–16.
Terao M, Itoi S, Matsumura S, Yang L, Murota H, Katayama I. Local glucocorticoid activation by 11b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 in keratinocytes the role in hapten-induced dermatitis. Am J Pathol. 2016;186:1499–510.
Itoi-Ochi S, Terao M, Murota H, Katayama I. Local corticosterone activation by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 in keratinocytes: the role in narrow-band UVB-induced dermatitis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2016;8:1–12.
Murota H, Itoi S, Terao M, Matsui S, Kawai H, Satou Y, et al. Topical cholesterol treatment ameliorates hapten-evoked cutaneous hypersensitivity by sustaining expression of 11b-HSD1 in epidermis. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:68–70.
Terao M, Murota H, Kimura A, Kato A, Ishikawa A, Igawa K, et al. 11b-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 Is a novel regulator of skin homeostasis and a candidate target for promoting tissue repair. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:1–11.
Clarke L, Kirwan J. Efficacy, safety and mechanism of action of modified-release prednisone in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4:159–66.
Buttgereit F. Novel glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid receptor ligands: teaching old drugs new tricks. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:41.
Ursini F, Naty S, Bruno C, Grembiale RD. Old but good: modified-release prednisone in rheumatoid arthritis. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017;12:124–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate all scientific discussions with colleagues in the field of extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis and nuclear receptors over the past 20 years, which contributed to this review. This work was supported by a research grant from the German Science Foundation (DFG, BR3369/9-1) to TB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, T.S., Merk, V.M. & Brunner, T. Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis at epithelial barriers. Genes Immun 20, 627–640 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-019-0058-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-019-0058-z
This article is cited by
-
Butterflies in the gut: the interplay between intestinal microbiota and stress
Journal of Biomedical Science (2023)
-
Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid biosynthesis: implications for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders
Genes & Immunity (2020)