Abstract
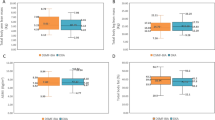
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at increased risk of sarcopenia. Previous studies have proposed equations to estimate muscle mass based on triceps skin-fold thickness and mid-upper arm circumference, with or without adjustment for hand grip strength (HGS). We wished to evaluate their usefulness compared to multifrequency segmental bioimpedance (MFBIA) measured appendicular lean mass (ALM). We audited 160 CKD patients attending outpatient clinics, 65.6% male, median age 73 (62–81.5) years. We calculated muscle mass using six proposed equations based on anthropometric measurements. These equations over estimated muscle mass compared to MFBIA with a mean bias ranging from 3.4 to 35.9 kg. Apart from one equation, there was a systematic bias, with bias increasing with increasing fat mass (ranging from r = 0.17, p = 0.044 to r = 0.65, p < 0.001). For CKD patients we found that most of the previously proposed equations based on anthropometric equations over-estimated muscle mass compared to MFBIA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang XH, Mitch WE. Mechanisms of muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:504–16.
Rosenberg IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. Clin Geriatr Med. 2011;27:337–9.
Heymsfield SB, McManus C, Smith J, Stevens V, Nixon DW. Anthropometric measurement of muscle mass: revised equations for calculating bone-free arm muscle area. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982;36:680–90.
Lee RC, Wang Z, Heo M, Ross R, Janssen I, Heymsfield SB. Total-body skeletal muscle mass: development and cross-validation of anthropometric prediction models. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:796–803.
Noori N, Kovesdy CP, Bross R, Lee M, Oreopoulos A, Benner D, et al. Novel equations to estimate lean body mass in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57:130–9.
Tian X, Chen Y, Yang ZK, Qu Z, Dong J. Novel equations for estimating lean body mass in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr. 2018;28:156–64.
Fürstenberg A, Davenport A. Comparison of multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry assessments in outpatient haemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;57:123–9.
Fürstenberg A, Davenport A. Assessment of body composition in peritoneal dialysis patients using bioelectrical impedance and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33:150–6.
Figueroa-Bonaparte S, Llauger J, Segovia S, Belmonte I, Pedrosa I, Montiel E, et al. Quantitative muscle MRI to follow up late onset Pompe patients: a prospective study. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10898.
Sawant A, House AA, Chesworth BM, Connelly DM, Lindsay R, Gati J, et al. Association between muscle hydration measures acquired using bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging in healthy and haemodialysis population. Physiol Rep. 2015;3:pii: e12219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S.R.S.M. was in receipt of International Society of Nephrology Kidney Research UK training award. All the remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maharjan, S.R.S., Jiang, K., Slee, A. et al. Comparison of multifrequency bioimpedance measured lean mass to that calculated from anthropomometric measurements in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 73, 1200–1202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-019-0415-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-019-0415-z
This article is cited by
-
Change in appendicular lean mass in patients established on peritoneal dialysis as measured by dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2021)