Abstract
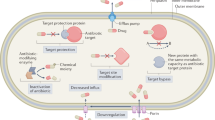
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) are prevalent throughout the world resulting in a major public health burden. In this research, we isolated and identified 28 MDR UPEC from one university hospital in China, investigated MDR and pathogenic mechanisms by PCR, including 55 antibiotic resistance determinants (ARDs) genes, 13 genetic markers of mobile genetic elements (MGEs) and 6 virulence factors (VFs) genes. In these isolates, we identified 23 ARDs genes and 6 genetic markers of MGEs that played a key role in MDR phenotypes. In addition, we found 2 VFs genes, hofQ and ompT, which could be associated with pathogenicity and invasiveness of these strains in urinary tract infections (UTIs).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ronald AR, Nicolle LE, Stamm E, Krieger J, Warren J, Schaeffer A, Naber KG, Hooton TM, Johnson J, Chambers S, Andriole V. Urinary tract infection in adults: research priorities and strategies. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2001;17:343–8.
Totsika M, Moriel DG, Idris A, Rogers BA, Wurpel DJ, Phan MD, Paterson DL, Schembri MA. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli mediated urinary tract infection. Curr Drug Targets. 2012;13:1386–99.
Stamm WE, Norrby SR. Urinary tract infections: disease panorama and challenges. J Infect Dis. 2001;183(Suppl. 1):S1–4.
Barber AE, Norton JP, Spivak AM, Mulvey MA. Urinary tract infections: current and emerging management strategies. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:719–24.
Foxman B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7:653–60.
Flores-Mireles AL, Walker JN, Caparon M, Hultgren SJ. Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13:269–84.
Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am J Med. 2002;113(Suppl. 1A):5s–13s.
Dehbanipour R, Rastaghi S, Sedighi M, Maleki N, Faghri J. High prevalence of multidrug-resistance uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains, Isfahan, Iran. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2016;7:22–6.
Ochoa SA, Cruz-Córdova A, Luna-Pineda VM, Reyes-Grajeda JP, Cázares-Domínguez V, Escalona G, Sepúlveda-González ME, López-Montiel F, Arellano-Galindo J, López-Martínez B, Parra-Ortega I, Giono-Cerezo S, Hernández-Castro R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Xicohtencatl-Cortes J. Multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli clinical strains: phylogenetic groups widely associated with integrons maintain high genetic diversity. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:2042.
Lüthje P, Brauner A. Virulence factors of uropathogenic E. coli and their interaction with the host. Adv Micro Physiol. 2014;65:337–72.
Zowawi HM, Harris PN, Roberts MJ, Tambyah PA, Schembri MA, Pezzani MD, Williamson DA, Paterson DL. The emerging threat of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in urology. Nat Rev Urol. 2015;12:570–84.
Gautam V, Singhal L, Arora S, Jha C, Ray P. Reliability of Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method for detecting carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:2003–4.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: twenty-eighth informational supplement. Document M100-S28. Wayne, PA: CLSI. 2018.
Chen JM, Sun YX, Chen JW, Liu S, Yu JM, Shen CJ, Sun XD, Peng D. Panorama phylogenetic diversity and distribution of type A influenza viruses based on their six internal gene sequences. Virol J. 2009;6:137.
Díez-Aguilar M, Conejo MC, Morosini MI, Palop NT, Gimeno C, Cantón R, Pascual Á. Susceptibility testing and detection of β-lactam resistance mechanisms in Enterobacteriaceae: a multicentre national proficiency study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018;51:612–9.
Jaffe A, Chabbert YA, Semonin O. Role of porin proteins OmpF and OmpC in the permeation of β-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982;22:942–8.
Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Glupczynski Y, Tulkens PM. Aminoglycosides: activity and resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43:727–37.
Xia Q, Wang H, Zhang A, Wang T, Zhang Y. Prevalence of 16S rRNA methylase conferring high-level aminoglycoside resistance in Escherichia coli in China. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011;37:387–8.
Shigemura K, Tanaka K, Yamamichi F, Shirakawa T, Miyake H, Fujisawa M. Does mutation in gyrA and/or parC or efflux pump expression play the main role in fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli urinary tract infections? A statistical analysis study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;40:516–20.
Jesse TW, Englen MD, Pittenger-Alley LG, Fedorka-Cray PJ. Two distinct mutations in gyrA lead to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid resistance in Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens and beef cattle. J Appl Microbiol. 2006;100:682–8.
Poole K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56:20–51.
Tu J, Qi K, Song X, Xue T, Ji H, Shao Y, Liu H, Zhou X, Zhu L. Horizontal transfer and functional evaluation of high pathogenicity islands in Avian Escherichia coli. Pol J Vet Sci. 2017;20:395–402.
Ahmed N, Dobrindt U, Hacker J, Hasnain SE. Genomic fluidity and pathogenic bacteria: applications in diagnostics, epidemiology and intervention. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:387–94.
Sun D, Zhang X, Wang L, Prudhomme M, Xie Z, Martin B, Claverys JP. Transforming DNA uptake gene orthologs do not mediate spontaneous plasmid transformation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2009;191:713–9.
Kanamaru S, Kurazono H, Ishitoya S, Terai A, Habuchi T, Nakano M, Ogawa O, Yamamoto S. Distribution and genetic association of putative uropathogenic virulence factors iroN, iha, kpsMT, ompT and usp in Escherichia coli isolated from urinary tract infections in Japan. J Urol. 2003;170:2490–3.
Marrs CF, Zhang LX, Tallman P, Manning SD, Somsel P, Raz P, Colodner R, Jantunen ME, Siitonen A, Saxen H, Foxman B. Variations in 10 putative uropathogen virulence genes among urinary, faecal and peri-urethral Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 2002;51:138–42.
Hui CY, Guo Y, He QS, Peng L, Wu SC, Cao H, Huang SH. Escherichia coli outer membrane protease OmpT confers resistance to urinary cationic peptides. Microbiol Immunol. 2010;54:452–9.
Sato M, Miyazaki K. Phylogenetic network analysis revealed the occurrence of horizontal gene transfer of 16S rRNA in the genus Enterobacter. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:2225.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by grants from Ningbo Health Branding Subject Fund (PPXK2018–04), Zhejiang Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2011ZB126), Ningbo Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology (2012A610186).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
We obtained the approval letter of Ningbo First Hospital Ethics Committee (Approval No. 2019-R043).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Dh., Lv, Df., Mi, Zh. et al. Investigation of antibiotic resistance determinants and virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Antibiot 73, 314–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0284-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0284-7