Abstract
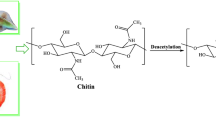
Modified catechol chitosan was synthesized to examine the intricate connections between Fe(III) and catechol under different pH conditions. The conjugation of the catechol moieties, which determines the structure of the hydrogel, was evaluated by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and ultraviolet‒visible spectroscopy. The gel formation was well maintained by the dual cross-linking networks of the electrostatic interactions between catechol chitosan solution (CCS) and Fe3+ along with the covalent catechol-coupling-based coordinate bonds. Three pH conditions of 3, 5, and 7 were applied for ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) treatment as a triggering factor in modifying the uniform hydrogel structure. The hydrogels demonstrated enhanced mechanical strength and cohesiveness at a pH of 5, and rheology analysis was used to determine the storage and loss moduli. Several analysis and characterization techniques were utilized to describe the cross-linking components and confirm the physical properties of the chitosan backbone polymer chain in the modified iron-induced hydrogel frameworks before and after EDTA treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schexnailder P, Schmidt G. Nanocomposite polymer hydrogels. Coll Polym Sci. 2009;287:1–11.
Döring A, Birnbaum W, Kuckling D. Responsive hydrogels–structurally and dimensionally optimized smart frameworks for applications in catalysis, micro-system technology and material science. Chem Soc Rev 2013;42:7391–420.
Daly AC, Riley L, Segura T, Burdick JA. Hydrogel microparticles for biomedical applications. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5:20–43.
Neishabouri A, Soltani Khaboushan A, Daghigh F, Kajbafzadeh AM, Majidi Zolbin M. Decellularization in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: evaluation, modification, and application methods. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2022;10:629.
Zhao W, Jin X, Cong Y, Liu Y, Fu J. Degradable natural polymer hydrogels for articular cartilage tissue engineering. J Chem Tech Biotech. 2013;88:327–39.
Zhu J, Marchant RE. Design properties of hydrogel tissue-engineering scaffolds. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8:607–26.
Narayanaswamy R, Torchilin VP. Hydrogels and their applications in targeted drug delivery. Molecules 2019;24:603.
Bolla PK, Rodriguez VA, Kalhapure RS, Kolli CS, Andrews S, Renukuntla J. A review on pH and temperature responsive gels and other less explored drug delivery systems. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2018;46:416–35.
Hoffman AS. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:18–23.
Leal D, De Borggraeve W, Encinas MV, Matsuhiro B, Müller R. Preparation and characterization of hydrogels based on homopolymeric fractions of sodium alginate and PNIPAAm. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92:157–66.
Herrick WG, Nguyen TV, Sleiman M, McRae S, Emrick TS, Peyton SR. PEG-phosphorylcholine hydrogels as tunable and versatile platforms for mechanobiology. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14:2294–304.
Kamoun EA, Kenawy ERS, Chen X. A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. J Adv Res. 2017;8:217–33.
Krogsgaard M, Behrens MA, Pedersen JS, Birkedal H. Self-healing mussel-inspired multi-pH-responsive hydrogels. Biomacromol. 2013;14:297–301.
Song L, Li L, He T, Wang N, Yang S, Yang X, et al. Peritoneal adhesion prevention with a biodegradable and injectable N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan-aldehyde hyaluronic acid hydrogel in a rat repeated-injury model. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1–13.
Jeon C, Höll WH. Chemical modification of chitosan and equilibrium study for mercury ion removal. Water Res. 2003;37:4770–80.
Kuroiwa T, Takada H, Shogen A, Saito K, Kobayashi I, Uemura K, et al. Cross-linkable chitosan-based hydrogel microbeads with pH-responsive adsorption properties for organic dyes prepared using size-tunable microchannel emulsification technique. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2017;514:69–78.
Park JW, Choi KH, Park KK. Acid-based equilibria and related properties of chitosan. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 1983;4:68–72.
Peniche C, Argüelles‐Monal W, Peniche H, Acosta N. Chitosan: an attractive biocompatible polymer for microencapsulation. Macromol Biosci. 2003;3:511–20.
Ostrowska-Czubenko J, Gierszewska-Drużyńska M. Effect of ionic crosslinking on the water state in hydrogel chitosan membranes. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;77:590–8.
Ravishankar K, Dhamodharan R. Advances in chitosan-based hydrogels: evolution from covalently crosslinked systems to ionotropically crosslinked superabsorbents. React Funct Polym. 2020;149:104517.
Fan X, Fang Y, Zhou W, Yan L, Xu Y, Zhu H, et al. Mussel foot protein inspired tough tissue-selective underwater adhesive hydrogel. Mater Horiz. 2021;8:997–1007.
Lee D, Park JP, Koh MY, Kim P, Lee J, Shin M, et al. Chitosan-catechol: a writable bioink under serum culture media. Biomater Sci. 2018;6:1040–7.
Zheng Z, Bian S, Li Z, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zhai X, et al. Catechol modified quaternized chitosan enhanced wet adhesive and antibacterial properties of injectable thermo-sensitive hydrogel for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;249:116826.
Alves NM, Mano JF. Chitosan derivatives obtained by chemical modifications for biomedical and environmental applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2008;43:401–14.
Yavvari PS, Srivastava A. Robust, self-healing hydrogels synthesised from catechol rich polymers. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3:899–910.
Wang K, Buschle-Diller G, Misra RDK. Chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Mater Technol. 2015;30:198–205.
Ren Y, Zhao X, Liang X, Ma PX, Guo B. Injectable hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan, gelatin and dopamine as localized drug delivery system to treat Parkinson’s disease. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;105:1079–87.
Xiong S, Duan L, Cheng X. A novel coumarin-chitosan fluorescent hydrogel for the selective identification of Fe 2+ in aqueous systems. Polym Chem. 2020;11:6066–72.
DeForest CA, Anseth KS. Cytocompatible click-based hydrogels with dynamically tunable properties through orthogonal photoconjugation and photocleavage reactions. Nat Chem. 2011;3:925–31.
Li J, Hu W, Zhang Y, Tan H, Yan X, Zhao L, et al. pH and glucose dually responsive injectable hydrogel prepared by in situ crosslinking of phenylboronic modified chitosan and oxidized dextran. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem. 2015;53:1235–44.
Lee HA, Park E, Lee H. Polydopamine and its derivative surface chemistry in material science: a focused review for studies at KAIST. Adv Mater. 2020;32:1907505.
Guo Z, Ni K, Wei D, Ren Y. Fe 3+-induced oxidation and coordination cross-linking in catechol-chitosan hydrogels under acidic pH conditions. RSC Adv. 2015;5:37377–3738433.
Lee J, Chang K, Kim S, Gite V, Chung H, Sohn D. Phase controllable hyaluronic acid hydrogel with iron (III) ion–catechol induced dual cross-linking by utilizing the gap of gelation kinetics. Macromolecules. 2016;49:7450–9.
Lavertu M, Xia Z, Serreqi AN, Berrada M, Rodrigues A, Wang D, et al. A validated 1 H NMR method for the determination of the degree of deacetylation of chitosan. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003;32:1149–58.
Kim K, Ryu JH, Lee DY, Lee H. Bio-inspired catechol conjugation converts water-insoluble chitosan into a highly water-soluble, adhesive chitosan derivative for hydrogels and LbL assembly. Biomater Sci. 2013;1:783–90.
Zhang D, Ouyang Q, Hu Z, Lu S, Quan W, Li P, et al. Catechol functionalized chitosan/active peptide microsphere hydrogel for skin wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;173:591–606.
Panja S, Hanson S, Wang C. EDTA-inspired polydentate hydrogels with exceptionally high heavy metal adsorption capacity as reusable adsorbents for wastewater purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:25276–85.
Ma J, Zhou G, Chu L, Liu Y, Liu C, Luo S, et al. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with an EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2017;5:843–51.
Zeng H, Hwang DS, Israelachvili JN, Waite JH. Strong reversible Fe 3+-mediated bridging between dopa-containing protein films in water. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:12850–3.
Shen J, Zhou Y, Li S, Gu P, Xue G. Hydrogel-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for degradation of phenol. J Mater Sci. 2019;54:10684–94.
Kaur L, Raj R, Thakur AK, Singh I. Development of chitosan-catechol conjugates as mucoadhesive polymer: assessment of acute oral toxicity in mice. J Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2020;35;2020014.
Hefni HH, Azzam EM, Badr EA, Hussein M, Tawfik SM. Synthesis, characterization and anticorrosion potentials of chitosan-g-PEG assembled on silver nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;83:297–305.
Repo E, Malinen L, Koivula R, Harjula R, Sillanpää M. Capture of Co (II) from its aqueous EDTA-chelate by DTPA-modified silica gel and chitosan. J Hazard Mater. 2011;187:122–32.
Kavianinia I, Plieger PG, Kandile NG, Harding DR. Fixed-bed column studies on a modified chitosan hydrogel for detoxification of aqueous solutions from copper (II). Carbohydr Polym. 2012;90:875–86.
Monteiro OA Jr, Airoldi C. Some studies of crosslinking chitosan–glutaraldehyde interaction in a homogeneous system. Int J Biol Macromol. 1999;26:119–28.
Islam A, Riaz M, Yasin T. Structural and viscoelastic properties of chitosan-based hydrogel and its drug delivery application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;59:119–24.
Wang S, Zhang Z, Chen B, Shao J, Guo Z. Self‐healing hydrogel of poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphite oxide with p H‐sensitive and enhanced thermal properties. J Appl Polym Sci. 2018;135:46143.
Narkar AR, Cannon E, Yildirim-Alicea H, Ahn K. Catechol-functionalized chitosan: optimized preparation method and its interaction with Mucin. Langmuir 2019;35:16013–23.
El-hefian EA, Yahaya AH. Rheological study of chitosan and its blends: an overview. Maejo Int J Sci Technol. 2010;4:210–20.
Soares PI, Machado D, Laia C, Pereira LC, Coutinho JT, Ferreira IMM, et al. Thermal and magnetic properties of chitosan-iron oxide nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;149:382–90.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program administered through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Education (2020R1A6A1A06046728, 2022R1A2C1010580, and 2022R1A6C101A779-23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NQN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. JR: Writing-review and editing. GK: Writing-review and editing. DS: Supervision, Writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, N.Q., Ryu, J., Kolekar, G. et al. Characteristics of ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid treatment on iron(III)-induced modified catechol chitosan hydrogels under different pH conditions. Polym J 55, 1335–1345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-023-00827-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-023-00827-z