Abstract
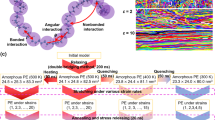
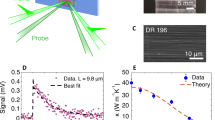
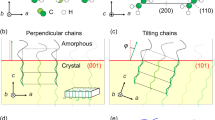
The thermal conductivity of bulk polymeric films can be generally improved by introducing interlaced lamellar or “shish-kebab” crystals along the machine direction (MD) through uniaxial stretching or high-pressure extrusion. However, the thermal pathway along the transverse direction (TD) is disrupted to limit the enhancement of in-plane thermal conductivity as the draw ratio increases. In this paper, a mesh-like crystal structure of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) films is achieved through a two-step biaxial stretching mode to construct a planar-oriented crystal network. The in-plane thermal conductivity increases to 7.3 W m/K at a total draw ratio of 25. This mesh-like crystal network structure was investigated through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and 1-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (1D-WXRD). The evolution mechanism of the crystal network structure is proposed on the basis of single-temperature biaxial stretching modes with different draw ratios. The construction of additional order along the TD to form a planar-oriented crystal network structure by biaxial stretching can provide new insight into improving the in-plane thermal conductivity of bulk polymeric films.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du JG, Wang Z, Yu JL, Ullah S, Yang B, Li CH, et al. Ultrahigh-strength ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)-based fiber electrode for high performance flexible supercapacitors. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1707351.
Lee J, Sul H, Lee W, Pyun KR, Ha I, Kim D, et al. Stretchable skin‐like cooling/heating device for reconstruction of artificial thermal sensation in virtual reality. Adv Funct Mater. 2020:1909171.
Koda T, Toyoshima T, Komatsu T, Takezawa Y, Nishioka A, Miyata K. Ordering simulation of high thermal conductivity epoxy resins. Polym J. 2012;45:444–8.
Zhang X, Zhang J, Xia L, Li C, Wang J, Xu F, et al. Simple and consecutive melt extrusion method to fabricate thermally conductive composites with highly oriented boron nitrides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:22977–84.
Zhang XL, Wu H, Guo SY, Wang YZ. Understanding in crystallization of polyethylene: the role of boron nitride (BN) particles. Rsc Adv. 2015;5:99812–9.
Choi SW, Yoon KH, Jeong S-S. Morphology and thermal conductivity of polyacrylate composites containing aluminum/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos Part A. 2013;45:1–5.
He X, Wang Y. Highly thermally conductive polyimide composite films with excellent thermal and electrical insulating properties. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2020;59:1925–33.
Kuwagaki H, Meguro T, Tatami J, Komeya K. An improvement of thermal conduction of activated carbon by adding graphite. J. Mater Sci. 2003,38:3279–84.
Sawada T, Tsuruoka T, Ueda N, Marubayashi H, Nojima S, Morikawa J, et al. Thermally conductive molecular assembly composed of an oligo(ethylene glycol)-modified filamentous virus with improved solubility and resistance to organic solvents. Polym J. 2020;52:803–11.
Wang X, Ho V, Segalman RA, Cahill DG. Thermal conductivity of high-modulus polymer fibers. Macromolecules. 2013;46:4937–43.
Singh V, Bougher TL, Weathers A, Cai Y, Bi K, Pettes MT, et al. High thermal conductivity of chain-oriented amorphous polythiophene. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014;9:384–90.
Kim GH, Lee D, Shanker A, Shao L, Kwon MS, Gidley D, et al. High thermal conductivity in amorphous polymer blends by engineered interchain interactions. Nat Mater. 2015;14:295–300.
Li J, Zhang C, Chen T, Li L, Li J. Preparation of a THermally Insulating Nanocomposite by Blending Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene with Gas-phase Silica. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015;54:6093–9.
Shen S, Henry A, Tong J, Zheng R, Chen G. Polyethylene nanofibres with very high thermal conductivities. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010;5:251–5.
Henry A, Chen G. High thermal conductivity of single polyethylene chains using molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;101:235502.
Cui K, Ma Z, Tian N, Su F, Liu D, Li L. Multiscale and multistep ordering of flow-induced nucleation of polymers. Chem Rev. 2018;118:1840–86.
Zheng H, Quan Y, Zheng G, Dai K, Liu C, Shen C. Fabrication of a polymer/aligned shish-kebab composite: microstructure and mechanical properties. RSC Adv. 2015;5:60392–60400.
Wang Z, An M, Xu H, Lv Y, Tian F, Gu Q. Structural evolution from shish-kebab to fibrillar crystals during hot-stretching process of gel spinning ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers obtained from low concentration solution. Polymer. 2017;120:244–54.
Lv F, Chen X, Wan C, Su F, Ji Y, Lin Y, et al. Deformation of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene precursor fiber: crystal slip with or without melting. Macromolecules. 2017;50:6385–95.
Ronca S, Igarashi T, Forte G, Rastogi S. Metallic-like thermal conductivity in a lightweight insulator: solid-state processed ultra high molecular weight polyethylene tapes and films. Polymer. 2017;123:203–10.
Xu Y, Kraemer D, Song B, Jiang Z, Zhou J, Loomis J, et al. Nanostructured polymer films with metal-like thermal conductivity. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1771.
Zhang RC, Huang Z, Sun D. New insights into thermal conductivity of uniaxially stretched high density polyethylene films. Polymer. 2018;154:42–7
Lu T, Kim K, Li X, Zhou J, Chen G, Liu J. Thermal transport in semicrystalline polyethylene by molecular dynamics simulation. J Appl Phys. 2018;123:015107.
Kwon OH, Ha T, Kim DG, Kim BG, Kim YS, Shin TJ, et al. Anisotropy-driven high thermal conductivity in stretchable poly(vinyl alcohol)/hexagonal boron nitride nanohybrid films. ACS Appl Mater interfaces. 2018;10:34625–33.
Hong SY, Lee YH, Park H, Jin SW, Jeong YR, Yun J, et al. Stretchable active matrix temperature sensor array of polyaniline nanofibers for electronic skin. Adv Mater. 2016;28:930–5.
Song WL, Wang P, Cao L, Anderson A, Meziani MJ, Farr AJ, et al. Polymer/boron nitride nanocomposite materials for superior thermal transport performance. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012;51:6498–501.
Gao Y, Müller-Plathe F. Molecular dynamics study on the thermal conductivity of the endgrafted carbon nanotubes filled polyamide-6.6 nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C. 2018;122:1412–21.
Ulbricht M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer. 2006;47:2217–62.
Knoche T, Lund R, Prymak O, Epple M, Ulbricht M. Effect of annealing temperature on pore formation in preparation of advanced polyethylene battery separator membranes. Mater Today Commun. 2016;8:23–30.
Zhang SS. A review on the separators of liquid electrolyte Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2007;164:351–64.
Chen Q, Chen D, Kang J, Cao Y, Chen J. Structure evolution of polyethylene in sequential biaxial stretching along the first tensile direction. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2019;58:12419–30.
Wang XW, Wu PY. Preparation of highly thermally conductive polymer composite at low filler content via a self-assembly process between polystyrene microspheres and boron nitride nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:19934–44.
Chen J, Huang X, Sun B, Jiang P. Highly thermally conductive yet electrically insulating polymer/boron nitride nanosheets nanocomposite films for improved thermal management capability. ACS Nano. 2019;13:337–45.
Yu S, Lee JW, Han TH, Park C, Kwon Y, Hong SM, et al. Copper shell networks in polymer composites for efficient thermal conduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:11618–22.
Hashimoto Y, Nishitsuji S, Kurose T, Ito H. Structural formation of UHMWPE film tracked by real-time retardation measurements during uniaxial/biaxial stretching. Materials. 2018;11:2292.
Loomis J, Ghasemi H, Huang X, Thoppey N, Wang J, Tong JK, et al. Continuous fabrication platform for highly aligned polymer films. Technology. 2014;02:189–99.
Smook JPJ. Influence of draw ratio on morphological and structural changes in hot-drawing of UHMW polyethylene fibers as revealed by DSC. Colloid Polym Sci. 1984;262:712–22.
Tian Y, Zhu CZ, Gong JH, Ma JH, Xu J. Transition from shish-kebab to fibrillar crystals during ultra-high hot stretching of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers: In situ small and wide angle X-ray scattering studies. Eur Polym J. 2015;73:127–36.
McDaniel PB, Deitzel JM, Gillespie JW. Structural hierarchy and surface morphology of highly drawn ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fibers studied by atomic force microscopy and wide angle X-ray diffraction. Polymer. 2015;69:148–58.
An M, Xu H, Lv Y, Gu Q, Tian F, Wang Z. An in situ small-angle X-ray scattering study of the structural effects of temperature and draw ratio of the hot-drawing process on ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers. Rsc Adv. 2016;6:51125–34.
An M, Xu H, Lv Y, Duan T, Tian F, Hong L, et al. Ultra-strong gel-spun ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers filled with chitin nanocrystals. Rsc Adv. 2016;6:20629–36.
Zhang QL, Zhang R, Meng LP, Lin YF, Chen XW, Li XY, et al. Biaxial stretch-induced crystallization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) above glass transition temperature: the necessary of chain mobility. Polymer. 2016;101:15–23.
Wan C, Chen X, Lv F, Chen X, Meng L, Li L. Biaxial stretch-induced structural evolution of polyethylene gel films: crystal melting recrystallization and tilting. Polymer. 2019;164:59–66.
Xiang D, Harkin-Jones E, Linton D. Effect of high temperature, biaxial stretching on the thermal and mechanical properties of HDPE/MWCNT sheet. Proceedings of Pps-30. In: The 30th International Conference of the Polymer Processing Society 1664. 2015.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51573118, U1630139, and 51721091), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT-15R48), State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials Engineering, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, T., Zhou, Y. et al. Enhanced in-plane thermal conductivity of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene films via a new design of a two-step biaxial stretching mode. Polym J 53, 1371–1381 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-021-00516-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-021-00516-9