Abstract
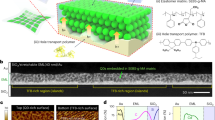
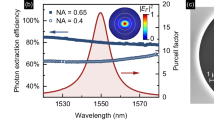
To develop highly sensitive updatable hologram materials, an azobenzene monomer was synthesized herein that supports effective photoisomerization under visible green beam irradiation. Furthermore, an acetylene group was introduced via Sonogashira coupling for higher birefringence. Polymerization was performed on the synthesized azobenzene monomer and on the methyl methacrylate (MMA) monomer, which serves as the skeleton of the film. The structures of all molecules were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and UV-Visible absorption spectroscopy was performed to analyze their optical properties. The holographic writing and rewriting capabilities of the newly synthesized azobenzene side-chain polymer were characterized by using a green laser as a writing beam, which showed that a high diffraction efficiency was reliably achievable under low-energy laser irradiation when evaluated with a four-wave-mixing optical scheme.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabor D. A new microscopic principle. Nature. 1948;777:777–8.
Chen J-S, Chu DP. Improved layer-based method for rapid hologram generation and real-time interactive holographic display applications. Opt Express. 2015;23:18143.
Ichihashi Y, Masuda N, Tsuge M, et al. One-unit system to reconstruct a 3-D movie at a video-rate via electroholography. Opt Express. 2009;17:19691.
Javidi B, Nomura T. Securing information by use of digital holography. Opt Lett. 2000;25:28.
Nishchal NK, Joseph J, Singh K. Securing information using fractional Fourier transform in digital holography. Opt Commun. 2004;235:253–9.
Ghuloum H. 3D Hologram technology in learning environment. Proc 2010 InSITE Conference 2010;693–704.
Yang L, Dong H, Alelaiwi A, Saddik AE. See in 3D: state of the art of 3D display technologies. Multimed Tools Appl. 2016;75:17121–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2981-y.
Fazhi L, Ligong Z, Feng Y, Donglin ZX. Optical testing method and its experiment on freeform surface with computer-generated hologram. Infrared Laser Eng. 2012;41:1052–6.
Fujita S, Fujita S. Photography based on silver halides. An overview. Org Chem Photogr. 2004;3–37.
Shankoff TA. Phase holograms in dichromated gelatin. Appl Opt. 1968;7:2101–5.
Curran RK, Shankoff TA. The mechanism of hologram formation in dichromated gelatin. Opt Soc Am. 1970;9:1651–7.
Lawrence JR, O’Neill FT, Sheridan JT. Photopolymer holographic recording material. Optik. 2001;112:449–63.
Booth BL. Photopolymer material for holography. Appl Opt. 1975;14:593–601.
Ikeda T. Photomodulation of liquid crystal orientations for photonic applications. J Mater Chem. 2003;13:2037–57.
Shishido A. Rewritable holograms based on azobenzene-containing liquid-crystalline polymers. Polym J. 2010;42:525–33.
Saishoji A, Sato D, Shishido A, Ikeda T. Formation of bragg gratings with large angular multiplicity by means of the photoinduced reorientation of azobenzene copolymers. Langmuir 2007;23:320–6.
Yamamoto T, Hasegawa M, Kanazawa A, Shiono T, Ikeda T. Holographic gratings and holographic image storage via photochemical phase transitions of polymer azobenzene liquid-crystal films. J Mater Chem. 2000;10:337–42.
Okano K, Shishido A, Ikeda T. An azotolane liquid-crystalline polymer exhibiting extremely large birefringence and its photoresponsive behavior. Adv Mater. 2006;18:523–7.
Okano K, Tsutsumi O, Shishido A, Ikeda T. Azotolane liquid-crystalline polymers: huge change in birefringence by photoinduced alignment change. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:15368–9.
Zhang Q, Li JM, Niu LH, et al. A rapid response photochromic diarylethene material for rewritable holographic data storage. Chin Sci Bull. 2013;58:74–78.
Cao L, Wang Z, Zong S, Zhang S, Zhang F, Jin G. Volume holographic polymer of photochromic diarylethene for updatable three-dimensional display. J Polym Sci Part B. 2016;54:2050–8.
Kobayashi Y, Abe J. Real-time dynamic hologram of a 3D object with fast photochromic molecules. Adv Opt Mater. 2016;4:1354–7.
Ishii N, Kato T, Abe J. A real-time dynamic holographic material using a fast photochromic molecule. Sci Rep. 2012;2:819.
Tay S, et al. An updatable holographic three-dimensional display. Nature. 2008;451:694–8.
Blanche PA, Bablumian A, Voorakaranam R, et al. Holographic three-dimensional telepresence using large-area photorefractive polymer. Nature. 2010;468:80–83.
Kirby R, Sabat RG, Nunzi JM, Lebel O. Disperse and disordered: a mexylaminotriazine-substituted azobenzene derivative with superior glass and surface relief grating formation. J Mater Chem C. 2014;2:841–7.
Kim K-H, Jeong Y-C. Nanoindentation study of optically patterned surface relief grating of azobenzene polymers. Opt Express. 2016;24:25242.
Zarins E, Balodis K, Ruduss A, et al. Molecular glasses of azobenzene for holographic data storage applications. Opt Mater. 2018;79:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.03.020.
Lyu Z, Wang C, Li H, Pan Y, Xia R. Switchable biphotonic holographic recording in an azobenzene liquid crystal film. Opt Mater Express. 2018;8:2050.
Bugakov M, Sakhno O, Boiko N, Ryabchun A. Polarization gratings in azobenzene-based fully liquid crystalline triblock copolymer. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2019;40:1–6.
Blanche PA. Field guide to holography. SPIE; 2014.
Provenzano C, Pagliusi P, Cipparrone G, Royes J, Piñol M, Oriol L. Polarization holograms in a bifunctional amorphous polymer exhibiting equal values of photoinduced linear and circular birefringences. J Phys Chem B. 2014;118:11849–54.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Industrial Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (10052667, Korea) and the KRICT core project (SS2021-20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there are no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H.J., Joo, KI., Kang, Y.Y. et al. Highly sensitive updatable green hologram recording polymer with photoisomerizable azobenzene with highly birefringent acetylene as the side chain. Polym J 53, 539–547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-020-00447-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-020-00447-x