Abstract
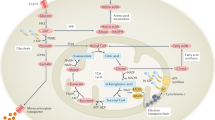
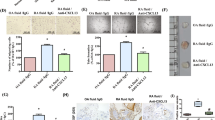
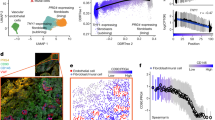
A novel rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid protein, Syntenin-1, and its receptor, Syndecan-1 (SDC-1), are colocalized on RA synovial tissue endothelial cells and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Syntenin-1 exacerbates the inflammatory landscape of endothelial cells and RA FLS by upregulating transcription of IRF1/5/7/9, IL-1β, IL-6, and CCL2 through SDC-1 ligation and HIF1α, or mTOR activation. Mechanistically, Syntenin-1 orchestrates RA FLS and endothelial cell invasion via SDC-1 and/or mTOR signaling. In Syntenin-1 reprogrammed endothelial cells, the dynamic expression of metabolic intermediates coincides with escalated glycolysis along with unchanged oxidative factors, AMPK, PGC-1α, citrate, and inactive oxidative phosphorylation. Conversely, RA FLS rewired by Syntenin-1 displayed a modest glycolytic-ATP accompanied by a robust mitochondrial-ATP capacity. The enriched mitochondrial-ATP detected in Syntenin-1 reprogrammed RA FLS was coupled with mitochondrial fusion and fission recapitulated by escalated Mitofusin-2 and DRP1 expression. We found that VEGFR1/2 and Notch1 networks are responsible for the crosstalk between Syntenin-1 rewired endothelial cells and RA FLS, which are also represented in RA explants. Similar to RA explants, morphological and transcriptome studies authenticated the importance of VEGFR1/2, Notch1, RAPTOR, and HIF1α pathways in Syntenin-1 arthritic mice and their obstruction in SDC-1 deficient animals. Consistently, dysregulation of SDC-1, mTOR, and HIF1α negated Syntenin-1 inflammatory phenotype in RA explants, while inhibition of HIF1α impaired synovial angiogenic imprint amplified by Syntenin-1. In conclusion, since the current therapies are ineffective on Syntenin-1 and SDC-1 expression in RA synovial tissue and blood, targeting this pathway and its interconnected metabolic intermediates may provide a novel therapeutic strategy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this paper and its supplementary information files.
References
Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Prevot C, Sarkar D, Fisher PB. mda-9/Syntenin promotes metastasis in human melanoma cells by activating c-Src. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:15914–9.
Boukerche H, Aissaoui H, Prevost C, Hirbec H, Das SK, Su ZZ, et al. Src kinase activation is mandatory for MDA-9/syntenin-mediated activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Oncogene. 2010;29:3054–66.
Kang BS, Cooper DR, Jelen F, Devedjiev Y, Derewenda U, Dauter Z, et al. PDZ tandem of human syntenin: crystal structure and functional properties. Structure. 2003;11:459–68.
Latysheva N, Muratov G, Rajesh S, Padgett M, Hotchin NA, Overduin M, et al. Syntenin-1 is a new component of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains: mechanisms and consequences of the interaction of syntenin-1 with CD63. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:7707–18.
Grembecka J, Cierpicki T, Devedjiev Y, Derewenda U, Kang BS, Bushweller JH, et al. The binding of the PDZ tandem of syntenin to target proteins. Biochemistry. 2006;45:3674–83.
Luo P, Yang X, Huang S, Feng S, Ou Z. Syntenin overexpression in human lung cancer tissue and serum is associated with poor prognosis. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:159.
Das SK, Guo C, Pradhan AK, Bhoopathi P, Talukdar S, Shen XN, et al. Knockout of MDA-9/Syntenin (SDCBP) expression in the microenvironment dampens tumor-supporting inflammation and inhibits melanoma metastasis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:46848–61.
Holli K, Hietanen P, Saaristo R, Huhtala H, Hakama M, Joensuu H. Radiotherapy after segmental resection of breast cancer with favorable prognostic features: 12-year follow-up results of a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:927–32.
Nault JC, Guyot E, Laguillier C, Chevret S, Ganne-Carrie N, N’Kontchou G, et al. Serum proteoglycans as prognostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013;22:1343–52.
Wiksten JP, Lundin J, Nordling S, Lundin M, Kokkola A, von Boguslawski K, et al. Epithelial and stromal syndecan-1 expression as predictor of outcome in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2001;95:1–6.
Binder Gallimidi A, Nussbaum G, Hermano E, Weizman B, Meirovitz A, Vlodavsky I, et al. Syndecan-1 deficiency promotes tumor growth in a murine model of colitis-induced colon carcinoma. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0174343.
Jaiswal AK, Sadasivam M, Archer NK, Miller RJ, Dillen CA, Ravipati A, et al. Syndecan-1 Regulates Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Controlling Homeostasis of IL-17-Producing gammadelta T Cells. J Immunol. 2018;201:1651–61.
Jaiswal AK, Sadasivam M, Aja S, Hamad ARA. Lack of Syndecan-1 produces significant alterations in whole-body composition, metabolism and glucose homeostasis in mice. World J Diabetes. 2020;11:126–36.
Meyer A, Sienes RE, Nijim W, Zanotti B, Umar S, Volin MV et al. Syntenin-1-mediated arthritogenicity is advanced by reprogramming RA metabolic macrophages and Th1 cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023.
Van Raemdonck K, Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Volin MV, Elshabrawy HA, Romay B et al. IL-34 reprograms glycolytic and osteoclastic RA macrophages via Syndecan-1 and M-CSFR. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021.
Lewis MJ, Barnes MR, Blighe K, Goldmann K, Rana S, Hackney JA, et al. Molecular Portraits of Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Identify Clinical and Treatment Response Phenotypes. Cell reports. 2019;28:2455–2470 e2455.
Barre PE, Redini F, Boumediene K, Vielpeau C, Pujol JP. Semiquantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of syndecan-1 and -4 messages in cartilage and cultured chondrocytes from osteoarthritic joints. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000;8:34–43.
Meyer A, Sienes R, Zanotti B, van Raemdonck K, Palasiewicz K, Mass DP, et al. Dysregulation of IL-34 ligation to SDC-1 mitigates collagen-induced arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19:1070–2.
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Pope RM, Mandelin AM 2nd, Shahrara S. Characterization of CCL19 and CCL21 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:914–22.
Pickens SR, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Pope RM, Talarico NE, Mandelin AM 2nd, et al. Characterization of interleukin-7 and interleukin-7 receptor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2884–93.
Chamberlain ND, Vila OM, Volin MV, Volkov S, Pope RM, Swedler W, et al. TLR5, a novel and unidentified inflammatory mediator in rheumatoid arthritis that correlates with disease activity score and joint TNF-alpha levels. J Immunol. 2012;189:475–83.
Elshabrawy HA, Volin MV, Essani AB, Chen Z, McInnes IB, Van Raemdonck K, et al. IL-11 facilitates a novel connection between RA joint fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. 2018;21:215–28.
Chen Z, Kim SJ, Essani AB, Volin MV, Vila OM, Swedler W, et al. Characterising the expression and function of CCL28 and its corresponding receptor, CCR10, in RA pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1898–906.
Kim SJ, Chen Z, Chamberlain ND, Volin MV, Swedler W, Volkov S, et al. Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Fostered Directly by Toll-like Receptor 5 Ligation and Indirectly Through Interleukin-17 Induction. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2024–36.
Humby F, Lewis M, Ramamoorthi N, Hackney JA, Barnes MR, Bombardieri M, et al. Synovial cellular and molecular signatures stratify clinical response to csDMARD therapy and predict radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:761–72.
Wei K, Korsunsky I, Marshall JL, Gao A, Watts GFM, Major T, et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature. 2020;582:259–64.
Wang J, Conlon D, Rivellese F, Nerviani A, Lewis MJ, Housley W, et al. Synovial Inflammatory Pathways Characterize Anti-TNF-Responsive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74:1916–27.
van Riel PL, Renskers L. The Disease Activity Score (DAS) and the Disease Activity Score using 28 joint counts (DAS28) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:S40–S44.
Rivellese F, Surace AEA, Goldmann K, Sciacca E, Cubuk C, Giorli G, et al. Rituximab versus tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: synovial biopsy-based biomarker analysis of the phase 4 R4RA randomized trial. Nat Med. 2022;28:1256–68.
Alexander CM, Reichsman F, Hinkes MT, Lincecum J, Becker KA, Cumberledge S, et al. Syndecan-1 is required for Wnt-1-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Nat Genet. 2000;25:329–32.
Van Raemdonck K, Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Meyer A, Volin MV, Chang HJ, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages instigates CCL21-induced arthritis. Immunol Cell Biol. 2022;100:127–35.
Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Van Raemdonck K, Volin MV, Romay B, Amin MA, et al. IRAK4 inhibition: a promising strategy for treating RA joint inflammation and bone erosion. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:2199–210.
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. AMPK and HIF signaling pathways regulate both longevity and cancer growth: the good news and the bad news about survival mechanisms. Biogerontology. 2016;17:655–80.
Li H, Satriano J, Thomas JL, Miyamoto S, Sharma K, Pastor-Soler NM, et al. Interactions between HIF-1alpha and AMPK in the regulation of cellular hypoxia adaptation in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;309:F414–428.
Hwang AB, Ryu EA, Artan M, Chang HW, Kabir MH, Nam HJ, et al. Feedback regulation via AMPK and HIF-1 mediates ROS-dependent longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:E4458–4467.
Tae N, Lee S, Kim O, Park J, Na S, Lee JH. Syntenin promotes VEGF-induced VEGFR2 endocytosis and angiogenesis by increasing ephrin-B2 function in endothelial cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:38886–901.
Das SK, Bhutia SK, Azab B, Kegelman TP, Peachy L, Santhekadur PK, et al. MDA-9/syntenin and IGFBP-2 promote angiogenesis in human melanoma. Cancer Res. 2013;73:844–54.
Javadi J, Heidari-Hamedani G, Schmalzl A, Szatmari T, Metintas M, Aspenstrom P et al. Syndecan-1 Overexpressing Mesothelioma Cells Inhibit Proliferation, Wound Healing, and Tube Formation of Endothelial Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13.
Xiao W, Oldham WM, Priolo C, Pandey AK, Loscalzo J. Immunometabolic Endothelial Phenotypes: Integrating Inflammation and Glucose Metabolism. Circ Res. 2021;129:9–29.
Wong BW, Marsch E, Treps L, Baes M, Carmeliet P. Endothelial cell metabolism in health and disease: impact of hypoxia. EMBO J. 2017;36:2187–203.
Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Volin MV, Romay B, Rahat R, Tetali C et al. Metabolic regulation of RA macrophages is distinct from RA fibroblasts and blockade of glycolysis alleviates inflammatory phenotype in both cell types. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021.
Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Volin MV, Zanotti B, Al-Awqati M, Sweiss N et al. IRAK4 inhibitor mitigates joint inflammation by rebalancing metabolism malfunction in RA macrophages and fibroblasts. Life Sci. 2021; 120114.
Koedderitzsch K, Zezina E, Li L, Herrmann M, Biesemann N. TNF induces glycolytic shift in fibroblast like synoviocytes via GLUT1 and HIF1A. Sci Rep. 2021;11:19385.
Palasiewicz K, Umar S, Romay B, Zomorrodi RK, Shahrara S Tofacitinib therapy intercepts macrophage metabolic reprogramming instigated by SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. Eur J Immunol. 2021.
Kayakabe K, Kuroiwa T, Sakurai N, Ikeuchi H, Kadiombo AT, Sakairi T, et al. Interleukin-6 promotes destabilized angiogenesis by modulating angiopoietin expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1571–9.
Elshabrawy HA, Chen Z, Volin MV, Ravella S, Virupannavar S, Shahrara S. The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis. 2015;18:433–48.
Nakahara H, Song J, Sugimoto M, Hagihara K, Kishimoto T, Yoshizaki K, et al. Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody therapy reduces vascular endothelial growth factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:1521–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Sadiq Umar for assistance with RA FLS culture and Ms. Pei-Yu Wu for her excellent scientific advice, and the Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry Midwestern University Core Facility, Downers Grove, IL for analyzing the fluorescent stainings. Moreover, we would like to acknowledge Dr. Caroline Alexander (University of Wisconsin–Madison) for generously providing us with SDC-1-/- mice [30]. Schematic figures were illustrated by biorender.com.
Funding
This work was supported in part by awards from the Department of Veteran’s Affairs MERIT Award BX002286, CX002565, IK6BX006474, the National Institutes of Health NIH R01 AI167155, NIH R41 AI147697, and the Innovative Research Award from the Rheumatology Research Foundation (RRF, no number assigned).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Dr. Shahrara had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study conception and design: AM, SZ, SS Acquisition of data: AM, SZ, WN, AB, VP, BZ, MV, ML, CP, SS Analysis and interpretation of data: AM, SZ, WN, AB, VP, BZ, MV, MAA, ML, CP, IM, SA, JAK, NS, SS Providing crucial reagents: MAA, SA, JAK, NS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research Ethics Approval
RA patients were collected according to the protocol approved by the University of Illinois at Chicago Institutional Ethics Review Board (protocol# 2021-1494). All animal studies were approved by the University of Illinois at Chicago Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol# 22-008). To ensure a robust and unbiased experimental design, samples were obtained from RA patients or mice of both genders. Mice used within the same experimental group were age and sex-matched. Rigor and reproducibility were maintained through well-powered studies and multiple distinct approaches to confirm the results. Power was calculated using parameters of α=0.05, and power=90%.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
41423_2023_1108_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary figure 1. Blood Syntenin-1 and SDC-1 relative levels are unaffected by RA therapy and glycolytic metabolites can modulate inflammatory factors and oxidative metabolites in Syntenin-1 rep
41423_2023_1108_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary figure 3. GLUT1 is co-expressed on Vimentin+fibroblasts and VWF+endothelial cells in Syntenin-1 arthritic joints
41423_2023_1108_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary figure 4. HK2 is co-expressed on Vimentin+fibroblasts and VWF+endothelial cells in Syntenin-1 arthritic joints
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, A., Zack, S.R., Nijim, W. et al. Metabolic reprogramming by Syntenin-1 directs RA FLS and endothelial cell-mediated inflammation and angiogenesis. Cell Mol Immunol 21, 33–46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01108-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01108-8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PTEN: an emerging target in rheumatoid arthritis?
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)