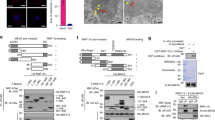
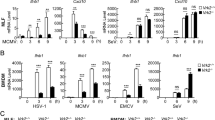
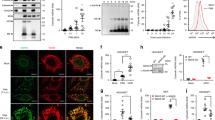
Abstract
The mitochondrial virus-induced signaling adaptor (VISA, also called mitochondrial antiviral signaling, MAVS) protein is a central adaptor in the innate immune response to cytosolic viral RNA. Viral infection causes the aggregation of VISA, which is important for its recruitment of downstream signaling components. How VISA aggregation is regulated remains unknown. Here, we found that sorting nexin 8 (SNX8) is a positive regulator of the RNA virus-triggered induction of downstream effector genes and innate immune response. The brains and lungs of Snx8−/− mice infected with RNA viruses exhibited lower serum cytokine levels and higher viral titers than those of wild-type mice, resulting in higher lethality. Mechanistically, viral infection induced the translocation of SNX8 from the cytosol to mitochondria and its increased association with VISA, leading to VISA aggregation, its recruitment of downstream signaling components and the induction of downstream antiviral genes. Our findings suggest that SNX8 is a critical component of the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR)-mediated innate immune response by modulating VISA aggregation and activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
06 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00682-z
References
Akira, S., Uematsu, S. & Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124, 783–801 (2006).
Gurtler, C. & Bowie, A. G. Innate immune detection of microbial nucleic acids. Trends Microbiol. 21, 413–420 (2013).
Kato, H. et al. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 441, 101–105 (2006).
Yoneyama, M. & Fujita, T. RNA recognition and signal transduction by RIG-I-like receptors. Immunol. Rev. 227, 54–65 (2009).
Yoneyama, M. et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 730–737 (2004).
Kawai, T. et al. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 6, 981–988 (2005).
Meylan, E. et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 437, 1167–1172 (2005).
Seth, R. B., Sun, L., Ea, C. K. & Chen, Z. J. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 122, 669–682 (2005).
Xu, L. G. et al. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol. Cell 19, 727–740 (2005).
Hou, F. et al. MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response. Cell 146, 448–461 (2011).
Lei, C. Q. et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta regulates IRF3 transcription factor-mediated antiviral response via activation of the kinase TBK1. Immunity 33, 878–889 (2010).
Mao, A. P. et al. Virus-triggered ubiquitination of TRAF3/6 by cIAP1/2 is essential for induction of interferon-beta (IFN-beta) and cellular antiviral response. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 9470–9476 (2010).
McWhirter, S. M., Tenoever, B. R. & Maniatis, T. Connecting mitochondria and innate immunity. Cell 122, 645–647 (2005).
Wang, Y. Y. et al. WDR5 is essential for assembly of the VISA-associated signaling complex and virus-triggered IRF3 and NF-kappaB activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 815–820 (2010).
Hu, M. M. & Shu, H. B. Cytoplasmic mechanisms of recognition and defense of microbial nucleic acids. Annu Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 34, 357–379 (2018).
Hu, M. M. & Shu, H. B. Multifaceted roles of TRIM38 in innate immune and inflammatory responses. Cell Mol. Immunol. 14, 331–338 (2017).
Liu, B. et al. The ubiquitin E3 ligase TRIM31 promotes aggregation and activation of the signaling adaptor MAVS through Lys63-linked polyubiquitination. Nat. Immunol. 18, 214–224 (2017).
Wei, J. et al. SNX8 mediates IFNgamma-triggered noncanonical signaling pathway and host defense against Listeria monocytogenes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 13000–13005 (2017).
Wei, J. et al. SNX8 modulates innate immune response to DNA virus by mediating trafficking and activation of MITA. PLoS Pathog. 14, e1007336 (2018).
Johannes, L. & Wunder, C. The SNXy flavours of endosomal sorting. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 884–886 (2011).
Luo, W. W. & Shu, H. B. Delicate regulation of the cGAS-MITA-mediated innate immune response. Cell Mol. Immunol. 15, 666–675 (2018).
Hu, M. M., Liao, C. Y., Yang, Q., Xie, X. Q. & Shu, H. B. Innate immunity to RNA virus is regulated by temporal and reversible sumoylation of RIG-I and MDA5. J. Exp. Med. 214, 973–989 (2017).
Zhou, Q. et al. The ER-associated protein ZDHHC1 is a positive regulator of DNA virus-triggered, MITA/STING-dependent innate immune signaling. Cell Host Microbe 16, 450–461 (2014).
Zhang, J., Hu, M. M., Shu, H. B. & Li, S. Death-associated protein kinase 1 is an IRF3/7-interacting protein that is involved in the cellular antiviral immune response. Cell Mol. Immunol. 11, 245–252 (2014).
Liu, Y. et al. ZDHHC11 modulates innate immune response to DNA virus by mediating MITA-IRF3 association. Cell Mol. Immunol. 15, 907–916 (2018).
Jiang, L. Q. et al. IFITM3 inhibits virus-triggered induction of type I interferon by mediating autophagosome-dependent degradation of IRF3. Cell Mol. Immunol. 15, 858–867 (2018).
Hu, M. M. et al. Sumoylation promotes the stability of the DNA sensor cGAS and the adaptor STING to regulate the kinetics of response to DNA virus. Immunity 45, 555–569 (2016).
Yang, Q. et al. TRIM32-TAX1BP1-dependent selective autophagic degradation of TRIF negatively regulates TLR3/4-mediated innate immune responses. PLoS Pathog. 13, e1006600 (2017).
Zhong, B. et al. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 29, 538–550 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the State Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0505800, 2016YFA0502102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31830024, 31800728, 31630045, 31521091, 31671465, and 31771555).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.B.S., Q.Y., J.W. and W.G. conceived and designed the study; W.G., J.W., X.Z., R.Z. and H.L., performed the experiments; and H.B.S., Q.Y., M.M.H., and S.L. analyzed the data. Q.Y., W.G., J.W. and H.B.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Wei, J., Zhong, X. et al. SNX8 modulates the innate immune response to RNA viruses by regulating the aggregation of VISA. Cell Mol Immunol 17, 1126–1135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0285-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0285-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SNX8 enables lysosome reformation and reverses lysosomal storage disorder
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Mitochondrial DNA-triggered innate immune response: mechanisms and diseases
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
USP18 positively regulates innate antiviral immunity by promoting K63-linked polyubiquitination of MAVS
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Genome-wide bioinformatic analyses predict key host and viral factors in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis
Communications Biology (2021)
-
SARS-CoV-2 membrane glycoprotein M antagonizes the MAVS-mediated innate antiviral response
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)