Abstract
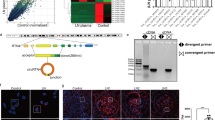
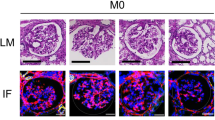
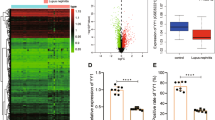
Mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis (MsPGN) is an inflammatory disease, but both the nature of disease progression and its regulation remain unclear. In the present study, we monitored the course of anti-Thy1 nephritis from days 1 to 5 and established gene expression profiles at each time point using microarrays to explore the development of inflammation. According to the gene expression profiles, macrophage infiltration (triggered by CCL2 activation) was evident on day 1 and enhanced inflammation over the next few days. We screened for genes with expression levels similar to CCL2 and found that the upregulation of the circadian gene albumin D-site-binding protein (DBP) was involved in CCL2 activation in mesangial cells. More importantly, CCL2 expression showed oscillatory changes similar to DBP, and DBP induced peak CCL2 expression at 16:00 a clock on day 1 in the anti-Thy1 nephritis model. We knocked down DBP through transfection with a small interfering RNA (siRNA) and used RNA sequencing to identify the DBP-regulated TNF-α-CCL2 pathway. We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) and the dual luciferase assay to show that DBP bound to the TRIM55 promoter, regulating gene expression and in turn controlling the TNF-α-CCL2 pathway. In conclusion, DBP-regulated circadian CCL2 expression by the TRIM55-TNF pathway in injured mesangial cells at an early stage, which promoted macrophage recruitment and in turn triggered infiltration and inflammation in a model of anti-Thy1 nephritis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, X. et al. Change of MAX interactor 1 expression in an anti-Thy1 nephritis model and its effect on mesangial cell proliferation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 27, 391–400 (2011).
Gao, L. et al. Sublytic complement C5b-9 complexes induce thrombospondin-1 production in rat glomerular mesangial cells via PI3-k/Akt: association with activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 144, 326–334 (2006).
Cantaluppi, V. et al. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect from complement-mediated mesangial injury in experimental anti-Thy1.1 glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 30, 410–422 (2015).
Aizawa, K. et al. Renoprotective effect of epoetin beta pegol by the prevention of M2 macrophage recruitment in Thy-1 rats. J. Nephrol. 27, 395–401 (2014).
Miyasato, K. et al. CD28 superagonist-induced regulatory T cell expansion ameliorates mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis in rats. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 15, 50–57 (2011).
Bozek, K. et al. Regulation of clock-controlled genes in mammals. PLoS ONE 4, e4882 (2009).
Yamajuku, D. et al. Cellular DBP and E4BP4 proteins are critical for determining the period length of the circadian oscillator. FEBS Lett. 585, 2217–2222 (2011).
Chen, W. D. et al. Circadian CLOCK mediates activation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling and renal fibrosis through cyclooxygenase 2. Am. J. Pathol. 185, 3152–3163 (2015).
Yuan, J. et al. Upregulation of D site of albumin promoter binding protein in the brain of patients with intractable epilepsy. Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 2486–2492 (2015).
Lee, Y. H. et al. Multiple, functional DBP sites on the promoter of the cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase P450 gene, CYP7. Proposed role in diurnal regulation of liver gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14681–14689 (1994).
Becker, T. et al. Clock gene expression in different synovial cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Acta Histochem. 116, 1199–1207 (2014).
Yoshida, K. et al. TNF-alpha modulates expression of the circadian clock gene Per2 in rheumatoid synovial cells. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 42, 276–280 (2013).
Chen, Y. M. et al. Pentoxifylline attenuates proteinuria in anti-thy1 glomerulonephritis via downregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB and Smad2/3 signaling. Mol. Med. 21, 276–284 (2015).
Roussel, B. D. et al. Age and albumin D site-binding protein control tissue plasminogen activator levels: neurotoxic impact. Brain: J. Neurol. 132, 2219–2230 (2009).
Wan, Y. G. et al. Contrasting dose-effects of multi-glycoside of Tripterygium wilfordii HOOK. f. on glomerular inflammation and hepatic damage in two types of anti-Thy1.1 glomerulonephritis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 118, 433–446 (2012).
Gao, J. et al. Genetic variants of MCP-1 and CCR2 genes and IgA nephropathy risk. Oncotarget 7, 77950–77957 (2016).
Topaloglu, R. et al. Clinicopathological and immunohistological features in childhood IgA nephropathy: a single-centre experience. Clin. Kidney J. 6, 169–175 (2013).
Li, P. et al. Therapeutic mechanism of Saikosaponin-d in anti-Thy1 mAb 1-22-3-induced rat model of glomerulonephritis. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 101, e111–e118 (2005).
Daniel, C. et al. Thrombospondin-2 therapy ameliorates experimental glomerulonephritis via inhibition of cell proliferation, inflammation, and TGF-beta activation. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 297, F1299–F1309 (2009).
Wittmann, S. et al. The mTOR inhibitor everolimus attenuates the time course of chronic anti-Thy1 nephritis in the rat. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 108, e45–e56 (2008).
Kramer, S. et al. Low-dose mTOR inhibition by rapamycin attenuates progression in anti-thy1-induced chronic glomerulosclerosis of the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 294, F440–F449 (2008).
Hua, K. F. et al. Osthole mitigates progressive IgA nephropathy by inhibiting reactive oxygen species generation and NF-kappaB/NLRP3 pathway. PLoS. One. 8, e77794 (2013).
Zoja, C. et al. Effects of MCP-1 inhibition by bindarit therapy in a rat model of polycystic kidney disease. Nephron 129, 52–61 (2015).
Abraham A. P., et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) deficiency attenuates experimental crescentic anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. Nephrology 23, 183–189 (2016).
Matoba, K. et al. Rho-kinase mediates TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in mesangial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 402, 725–730 (2010).
Ozato, K. et al. TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 849–860 (2008).
Cambiaghi, V. et al. TRIM proteins in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 770, 77–91 (2012).
Pizon, V. et al. Transient association of titin and myosin with microtubules in nascent myofibrils directed by the MURF2 RING-finger protein. J. Cell. Sci. 115, 4469–4482 (2002).
McElhinny, A. S. et al. Muscle-specific RING finger-2 (MURF-2) is important for microtubule, intermediate filament and sarcomeric M-line maintenance in striated muscle development. J. Cell. Sci. 117, 3175–3188 (2004).
Gralinski, L. E. et al. Genome wide identification of SARS-CoV susceptibility loci using the collaborative cross. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005504 (2015).
Lu, Y. et al. Bioinformatics analysis of proteomic profiles during the process of anti-Thy1 nephritis. Mol. & Cell. Proteom. 11(M111), 008755 (2012).
Li, Z. et al. Expression and significance of integrin-linked kinase in cultured cells, normal tissue, and diseased tissue of aging rat kidneys. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 59, 984–996 (2004).
Soleimani, V. D. et al. Chromatin tandem affinity purification sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 8, 1525–1534 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81330019) and the National Basic Research Program of China (Nos. 2014CBA02005 and 2015CB553605).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Mei, Y., Chen, L. et al. The role of transcriptional factor D-site-binding protein in circadian CCL2 gene expression in anti-Thy1 nephritis. Cell Mol Immunol 16, 735–745 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-018-0020-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-018-0020-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SOCS1 Peptidomimetic Alleviates Glomerular Inflammation in MsPGN by Inhibiting Macrophage M1 Polarization
Inflammation (2023)
-
Sublytic C5b-9 induces glomerular mesangial cell proliferation via ERK1/2-dependent SOX9 phosphorylation and acetylation by enhancing Cyclin D1 in rat Thy-1 nephritis
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)