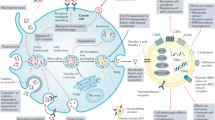
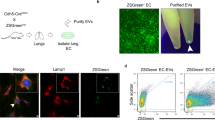
Abstract
We speculate ruptured circulating tumour cells (CTC) in capillaries could release a large number of small extracellular vesicle-like vesicles, namely mechanically extruded sEV (sEVme), which can encapsulate chromosomal DNA fragments. These sEVme have similar physicochemical properties compared to small extracellular vesicles spontaneously secreted by living cells (sEVss), and thus sEVme and sEVss cannot be effectively distinguished based on their size or membrane protein markers. Meanwhile, these sEVme derived from CTC inherit oncogenic payloads, deliver cargo through the bloodstream to recipient cells, and thus may promote cancer metastasis. The validation of this speculation could facilitate our understanding of EV biogenesis and cancer pathology. The potential finding will also provide a theoretical foundation for burgeoning liquid biopsy using DNA fragments derived from harvested sEV.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andaloussi SE, Mäger I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:347–57.
Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–79.
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750.
Imai T, Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Kato K, Morishita M, Yamashita T, et al. Macrophage-dependent clearance of systemically administered B16BL6-derived exosomes from the blood circulation in mice. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26238.
Czernek L, Chworos A, Duechler M. The uptake of extracellular vesicles is affected by the differentiation status of myeloid cells. Scand J Immunol. 2015;82:506–14.
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Abhange K, Makler A, Wen Y, Ramnauth N, Mao W, Asghar W, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in cancer. Bioact Mater. 2021;6:3705–43.
Guescini M, Genedani S, Stocchi V, Agnati LF. Astrocytes and glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J Neural Transm. 2010;117:1–4.
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Breakefield XO, et al. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat Commun. 2011;2:180.
Williams C, Rodriguez-Barrueco R, Silva JM, Zhang WJ, Hearn S, Elemento O, et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: a novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014;24:766–9.
Kahlert C, Melo SA, Protopopov A, Tang JB, Seth S, Koch M, et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:3869–75.
Takahashi A, Okada R, Nagao K, Kawamata Y, Hanyu A, Yoshimoto S, et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15287.
Yokoi A, Villar-Prados A, Oliphint PA, Zhang J, Song X, De Hoff P, et al. Mechanisms of nuclear content loading to exosomes. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaax8849.
Fischer S, Cornils K, Speiseder T, Badbaran A, Reimer R, Indenbirken D, et al. Indication of horizontal DNA gene transfer by extracellular vesicles. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0163665.
Wu S, Turner KM, Nguyen N, Raviram R, Erb M, Santini J, et al. Circular ecDNA promotes accessible chromatin and high oncogene expression. Nature. 2019;575:699–703.
Waldenström A, Gennebäck N, Hellman U, Ronquist G. Cardiomyocyte microvesicles contain DNA/RNA and convey biological messages to target cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e34653.
Kahlert C, Melo SA, Protopopov A, Tang J, Seth S, Koch M, et al. Identification of double stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:3869–75.
Thakur BK, Zhang H, Becker A, Matei I, Huang Y, Costa-Silva B, et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: a novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014;24:766–9.
Wan Y, Liu B, Lei H, Zhang B, Wang Y, Huang H, et al. Nanoscale extracellular vesicle-derived DNA is superior to circulating cell free DNA for mutation detection in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:2379–83.
Kowal J, Tkach M, Théry C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;29:116–25.
Shelke GV, Jang SC, Yin Y, Lässer C, Lötvall J. Human mast cells release extracellular vesicle-associated. DNA Matters. 2016;2:e201602000034.
Jeppesen DK, Fenix AM, Franklin JL, Higginbotham JN, Zhang Q, Zimmerman LJ, et al. Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell. 2019;177:428–45. e418
Malkin EZ, Bratman SV. Bioactive DNA from extracellular vesicles and particles. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:584.
Elzanowska J, Semira C, Costa-Silva B. DNA in extracellular vesicles: biological and clinical aspects. Mol Oncol. 2021;15:1701–14.
Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Sato TA, Ochiya T. Extracellular vesicles as trans-genomic agents: Emerging roles in disease and evolution. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:824–30.
Yang L, Yang D, Yang Q, Cheng F, Huang Y. Extracellular DNA in blood products and its potential effects on transfusion. Biosci Rep. 2020;40:BSR20192770.
Plaks V, Koopman CD, Werb Z. Circulating tumor cells. Science. 2013;341:1186–8.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563.
Xia YQ, Wan Y, Hao SJ, Nisic M, Harouaka RA, Chen YZ, et al. Nucleus of circulating tumor cell determines its translocation through biomimetic microconstrictions and its physical enrichment by microfiltration. Small. 2018;14:e1802899.
Weiss L, Orr FW, Honn KV. Interactions of cancer cells with the microvasculature during metastasis. FASEB J. 1988;2:12–21.
Wan Y, Wang L, Zhu C, Zheng Q, Wang G, Tong J, et al. Aptamer-conjugated extracellular nanovesicles for targeted drug delivery. Cancer Res. 2017;78:798–808.
Denais CM, Gilbert RM, Isermann P, McGregor AL, te Lindert M, Weigelin B, et al. Nuclear envelope rupture and repair during cancer cell migration. Science. 2016;352:353–8.
Raab M, Gentili M, de Belly H, Thiam H-R, Vargas P, Jimenez AJ, et al. ESCRT III repairs nuclear envelope ruptures during cell migration to limit DNA damage and cell death. Science. 2016;352:359–62.
Jiang HY, Sun SX. Cellular pressure and volume regulation and implications for cell mechanics. Biophys J. 2013;104:479a–480a.
Apodaca G. Modulation of membrane traffic by mechanical stimuli. Am J Physiol-Ren. 2002;282:F179–F190.
van Meer G, Voelker DR, Feigenson GW. Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2008;9:112–24.
Ramasubramanian L, Kumar P, Wang A. Engineering extracellular vesicles as nanotherapeutics for regenerative medicine. Biomolecules. 2019;10:48.
Zhao QG, Hai B, Kelly J, Wu S, Liu F. Extracellular vesicle mimics made from iPS cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:29.
Ilahibaks NF, Lei Z, Mol EA, Deshantri AK, Jiang L, Schiffelers RM, et al. Biofabrication of cell-derived nanovesicles: a potential alternative to extracellular vesicles for regenerative medicine. Cells. 2019;8:1509.
Huang CC, Kang M, Lu Y, Shirazi S, Diaz JI, Cooper LF, et al. Functionally engineered extracellular vesicles improve bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;109:182–94.
Wang L, Abhange KK, Wen Y, Chen Y, Xue F, Wang G, et al. Preparation of engineered extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with ultrasonication for skin rejuvenation. ACS Omega. 2019;4:22638–45.
Han C, Jeong D, Kim B, Jo W, Kang H, Cho S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell engineered nanovesicles for accelerated skin wound closure. Acs Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5:1534–43.
Wang X, Hu S, Li J, Zhu D, Wang Z, Cores J, et al. Extruded mesenchymal stem cell nanovesicles are equally potent to natural extracellular vesicles in cardiac repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:55767–79.
Jo W, Jeong D, Kim J, Park J. Self-Renewal of bone marrow stem cells by nanovesicles engineered from embryonic stem cells. Adv Health Mater. 2016;5:3148–56.
Qi CX, Liu XS, Zhi DK, Tai YF, Liu YF, Sun QQ, et al. Exosome-mimicking nanovesicles derived from efficacy-potentiated stem cell membrane and secretome for regeneration of injured tissue. Nano Res. 2022;15:1680–90.
Fan JB, Lee CS, Kim S, Chen C, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Generation of small RNA-modulated exosome mimetics for bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2020;14:11973–84.
Kim HY, Bhang SH. Stem cell-engineered nanovesicles exert proangiogenic and neuroprotective effects. Materials. 2021;14:1078.
Xia Y-Q, Wan Y, Chen Y-Z, Zheng S-Y. Mechanical generated extracellular vesicles through capillary mimicking micro channels. Biomed Eng Annu Mtg (abstract 314) 2019.
Wen Y, Fu Q, Soliwoda A, Zhang S, Zheng M, Mao W, et al. Cell-derived nanovesicles prepared by membrane extrusion are good substitutes for natural extracellular vesicles. Extracell Vesicle. 2022;1:100004.
Lai CP, Kim EY, Badr CE, Weissleder R, Mempel TR, Tannous BA, et al. Visualization and tracking of tumour extracellular vesicle delivery and RNA translation using multiplexed reporters. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7029.
Verweij FJ, Revenu C, Arras G, Dingli F, Loew D, Pegtel DM, et al. Live tracking of inter-organ communication by endogenous exosomes in vivo. Dev Cell. 2019;48:573–89.
Hyenne V, Ghoroghi S, Collot M, Bons J, Follain G, Harlepp S, et al. Studying the fate of tumor extracellular vesicles at high spatiotemporal resolution using the zebrafish embryo. Dev Cell. 2019;48:554–72.
Plebanek MP, Angeloni NL, Vinokour E, Li J, Henkin A, Martinez-Marin D, et al. Pre-metastatic cancer exosomes induce immune surveillance by patrolling monocytes at the metastatic niche. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–12.
Kowal J, Arras G, Colombo M, Jouve M, Morath JP, Primdal-Bengtson B, et al. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016;113:E968–E977.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW and YX wrote the manuscript; YW and SZ edited the manuscript; all authors revised the manuscript critically; all authors approved the version to be published.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Y., Xia, YQ. & Zheng, SY. Extruded small extracellular vesicles: splinters of circulating tumour cells may promote cancer metastasis?. Br J Cancer 127, 1180–1183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-022-01934-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-022-01934-z
This article is cited by
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in circulating tumor cell-mediated distant metastasis
Molecular Cancer (2023)