Abstract
Background
The investigation of underlying mechanism and the exploitation of novel therapies for metastatic prostate cancer (PCa) are still urgently needed. miR-199b-5p has been suggested to function as tumour suppressor in various human cancers. However, the clinical significance and role of miR-199b-5p in PCa remain unclear.
Methods
The current study sought to investigate the expression status of miR-199b-5p in PCa and the involved molecular mechanisms in PCa metastasis by using bioinformatics analyses, loss-and gain-of-functions and rescue experiments in vitro and in vivo.
Results
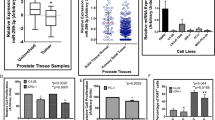
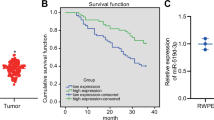
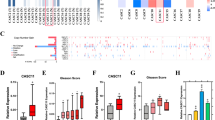
We demonstrated that miR-199b-5p was significantly downregulated in metastatic PCa tissues and cells when compared with the normal prostate tissue, the localised disease, the weakly metastatic and androgen-dependent PCa cell and the normal prostate epithelial cell. We also found that miR-199b-5p drastically suppressed PCa cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and inhibited xenografts tumour growth and metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, our results showed that miR-199b-5p could inhibit discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 (DDR1) expression by directly targeting its 3’-UTR, thereby hindering epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated traits, which were induced by DDR1 activating ERK signalling pathway. Moreover, PCa patients with low miR-199b-5p expression level had a remarkably shorter overall survival than those with high miR-199b-5p level, indicating an association of miR-199b-5p loss with poor prognosis in patients with PCa. Furthermore, DDR1 was upregulated in PCa, and significantly correlated with high Gleason score, advanced pathological stage, tumour metastasis and shorter overall survival.
Conclusions
Our study, for the first time, provide evidence of a tumour-suppressive function of miR-199b-5p in the invasion and metastasis of PCa, supporting the translational exploitation of miR-199b-5p-based therapeutic approaches for PCa metastases. Also, the miR-199b-5p-DDR1-ERK signalling axis identified in this study represents a novel mechanism of regulating EMT in PCa metastases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 January 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01258-w
References
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A. & Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424 (2018).
Chen, W., Zheng, R., Baade, P. D., Zhang, S., Zeng, H., Bray, F. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 115–132 (2016).
Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2014).
Calin, G. A. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 857–866 (2006).
Suer, I., Guzel, E., Karatas, O. F., Creighton, C. J., Ittmann, M. & Ozen, M. MicroRNAs as prognostic markers in prostate cancer. Prostate 79, 265–271 (2019).
Zhu, Z., Wen, Y., Xuan, C., Chen, Q., Xiang, Q., Wang, J. et al. Identifying the key genes and microRNAs in prostate cancer bone metastasis by bioinformatics analysis. FEBS Open Biol. 10, 674–688 (2020).
Chiu, L. Y., Kishnani, P. S., Chuang, T. P., Tang, C. Y., Liu, C. Y., Bali, D. et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in human hepatocellular adenoma associated with type I glycogen storage disease: a potential utility as biomarkers. J. Gastroenterol. 49, 1274–1284 (2014).
Lai, Y., Quan, J., Lin, C., Li, H., Hu, J., Chen, P. et al. miR-199b-5p serves as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 16, 436–444 (2018).
Lin, X., Qiu, W., Xiao, Y., Ma, J., Xu, F., Zhang, K. et al. MiR-199b-5p suppresses tumor angiogenesis mediated by vascular endothelial cells in breast cancer by targeting ALK1. Front. Genet. 10, 1397 (2020).
Favreau, A. J., Cross, E. L. & Sathyanarayana, P. miR-199b-5p directly targets PODXL and DDR1 and decreased levels of miR-199b-5p correlate with elevated expressions of PODXL and DDR1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 87, 442–446 (2012).
Zhou, S. J., Liu, F. Y., Zhang, A. H., Liang, H. F., Wang, Y., Ma, R. et al. MicroRNA-199b-5p attenuates TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 117, 233–244 (2017).
Kang, R., Zhao, S., Liu, L., Li, F., Li, E., Luo, L. et al. Knockdown of PSCA induces EMT and decreases metastatic potentials of the human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Cancer Cell Int. 16, 20 (2016).
Liu, L., Li, E., Luo, L., Zhao, S., Li, F., Wang, J. et al. PSCA regulates IL-6 expression through p38/NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer. Prostate 77, 1389–1400 (2017).
Li, E., Liu, L., Li, F., Luo, L., Zhao, S., Wang, J. et al. PSCA promotes prostate cancer proliferation and cell-cycle progression by up-regulating c-Myc. Prostate 77, 1563–1572 (2017).
Taylor, B. S., Schultz, N., Hieronymus, H., Gopalan, A., Xiao, Y., Carver, B. S. et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 18, 11–22 (2010).
Zhao, Z., Ma, W., Zeng, G., Qi, D., Ou, L. & Liang, Y. Small interference RNA-mediated silencing of prostate stem cell antigen attenuates growth, reduces migration and invasion of human prostate cancer PC-3M cells. Urol. Oncol. 31, 343–351 (2013).
Zhao, Z., He, J., Kang, R., Zhao, S., Liu, L. & Li, F. RNA interference targeting PSCA suppresses primary tumor growth and metastasis formation of human prostate cancer xenografts in SCID mice. Prostate 76, 184–198 (2016).
Zhao, Z., Li, E., Luo, L., Zhao, S., Liu, L., Wang, J. et al. A PSCA/PGRN-NF-κB- integrin-α4 axis promotes prostate cancer cell adhesion to bone marrow endothelium and enhances metastatic potential. Mol. Cancer Res. 18, 501–513 (2020).
Azizi, R., Salemi, Z., Fallahian, F. & Aghaei, M. Inhibition of didscoidin domain receptor 1 reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induce cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 19539–19552 (2019).
Wang, B., Gu, Y., Hui, K., Huang, J., Xu, S., Wu, S. et al. AKR1C3, a crucial androgenic enzyme in prostate cancer, promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through activating ERK signaling. Urol. Oncol. 36, 472.e11–472.e20 (2018).
Yin, B., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Liu, W., Yu, P. et al. RON and c-Met facilitate metastasis through the ERK signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 37, 3209–3218 (2017).
Wu, J., Ivanov, A. I., Fisher, P. B. & Fu, Z. Polo-like kinase 1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes epithelial cell motility by activating CRAF/ERK signaling. elife 5, e10734 (2016).
Fang, C., Wang, F. B., Li, Y. & Zeng, X. T. Down-regulation of miR-199b-5p is correlated with poor prognosis for breast cancer patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 84, 1189–1193 (2016).
Wu, A., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Lai, Y. & Liu, D. miR-199b-5p inhibits triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting DDR1. Oncol. Lett. 16, 4889–4896 (2018).
Dongre, A. & Weinberg, R. A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 69–84 (2018).
Valencia, K., Ormazábal, C., Zandueta, C., Luis-Ravelo, D., Antón, I., Pajares, M. J. et al. Inhibition of collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor-1 (DDR1) reduces cell survival, homing, and colonization in lung cancer bone metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 969–980 (2012).
Park, H. S., Kim, K. R., Lee, H. J., Choi, H. N., Kim, D. K., Kim, B. T. et al. Overexpression of discoidin domain receptor 1 increases the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in association with matrix metalloproteinase. Oncol. Rep. 18, 1435–1441 (2007).
Ram, R., Lorente, G., Nikolich, K., Urfer, R., Foehr, E. & Nagavarapu, U. Discoidin domain receptor-1a (DDR1a) promotes glioma cell invasion and adhesion in association with matrix metalloproteinase-2. J. Neurooncol. 76, 239–248 (2006).
Shen, Q., Cicinnati, V. R., Zhang, X., Iacob, S., Weber, F., Sotiropoulos, G. C. et al. Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol. Cancer 9, 227 (2010).
Shimada, K., Nakamura, M., Ishida, E., Higuchi, T., Yamamoto, H., Tsujikawa, K. et al. Prostate cancer antigen-1 contributes to cell survival and invasion through discoidin receptor 1 in human prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 99, 39–45 (2008).
Hao, M., Li, Y., Wang, J., Qin, J., Wang, Y., Ding, Y. et al. HIC1 loss promotes prostate cancer metastasis by triggering epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Pathol. 242, 409–420 (2017).
Wa, Q., Li, L., Lin, H., Peng, X., Ren, D., Huang, Y. et al. Downregulation of miR-19a-3p promotes invasion, migration and bone metastasis via activating TGF-β signaling in prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 39, 81–90 (2018).
Bonci, D., Coppola, V., Patrizii, M., Addario, A., Cannistraci, A., Francescangeli, F. et al. A microRNA code for prostate cancer metastasis. Oncogene 35, 1180–1192 (2016).
Huang, S., Wa, Q., Pan, J., Peng, X., Ren, D., Huang, Y. et al. Downregulation of miR-141-3p promotes bone metastasis via activating NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 36, 173 (2017).
Acknowledgements
NA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Z., L.L. and Q.X. conducted most of in vitro and in vivo experiments, generated site-directed mutagenesis clones and performed tumour studies in mice. J.W. performed the immunoblotting analysis and captured images of immunohistochemistry. S.Z. and Y.L. conducted in vivo imaging and necropsy of mice. Z. Zhu performed bioinformatics analyses using online tools. J.L. coordinated acquisition of human PCa patient tissues, pathologically reviewed these patient specimens and scored them based on the staining intensity. Z. Zhao conceived, designed and supervised the work. Z. Zhao and S.Z. critically analysed data, prepared figures and tables and wrote the paper. All of the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, and the written informed consent was obtained from all patients before participating in the study. Human specimens were handled and made anonymous in adherence to the ethical and legal standards. All procedures related to the animal experiments in this study were carried out in accordance with a mouse protocol, which was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Data availability
Data pertaining to this study are included in the manuscript. TargetScan, miRDB, miRWalk, miRTarBase, The Cancer Genome Atlas database (TCGA), Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA), and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets used and/or analysed in this work are publicly available from http://www.targetscan.org/, http://mirdb.org/, http://zmf.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/, http://mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu/, https://tcgadata.nci.nih.gov/tcga/, http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/ and http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, respectively. Other data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Funding information
This work was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572537 to Z. Zhao), The Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2015A030311007 to Z. Zhao), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (201607010376 to Z. Zhao) and The Major Program of Department of Guangdong Education (2017KZDXM067 to Z. Zhao).
Additional information
Note This work is published under the standard license to publish agreement. After 12 months the work will become freely available and the license terms will switch to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Zhao, S., Luo, L. et al. miR-199b-5p-DDR1-ERK signalling axis suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Br J Cancer 124, 982–994 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01187-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01187-8
This article is cited by
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4L inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing the β-catenin/HIF-1α positive feedback loop in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Exosomes Derived from hucMSCs Primed with IFN-γ Suppress the NF-κB Signal Pathway in LPS-Induced ALI by Modulating the miR-199b-5p/AFTPH Axis
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2024)
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
A network map of discoidin domain receptor 1(DDR1)-mediated signaling in pathological conditions
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Histone methyltransferase KMT2C plays an oncogenic role in prostate cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2022)