Abstract
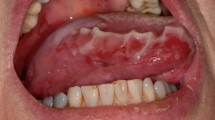
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare, immune-mediated, vesiculobullous disease that predominantly affects the oral cavity and conjunctiva. In MMP, autoantibodies are directed against hemidesmosomal proteins in the basement membrane zone, most commonly BP180. Clinical signs and symptoms include gingival desquamation, erosions, and ulcerations. Differential diagnoses include other immune-mediated blistering diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid. Definitive diagnosis is reached through history taking, physical examination, tissue biopsy and/or serology testing. MMP, although not curable, is typically managed with topical or systemic corticosteroids, in addition to immunosuppressive therapies and biologic agents in recalcitrant cases. Untreated MMP can lead to life-threatening complications, such as blindness. As a condition that affects the oral cavity, it is important that dentists understand how to recognise, diagnose and manage the disease.
Key points
-
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare, vesiculobullous disease that can manifest as ulcerations, erosions, blisters, or desquamation of tissue. Thorough clinical examination is key during appointments.
-
Patients with MMP may manifest with extra-oral signs, such as eye and skin involvement. A thorough review of systems in office can help differentiate MMP from other conditions.
-
In practice, general dentistry providers may recommend avoidance of trauma to the tissue in order to reduce the risk of ulceration or blister formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carey B, Setterfield J. Mucous membrane pemphigoid and oral blistering diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol 2019; 44: 732-739.
Daniel B S, Murrell D F. Review of autoimmune blistering diseases: The pemphigoid diseases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2019; 33: 1685-1694.
Alrashdan M S, Kamaguchi M. Management of mucous membrane pemphigoid: A literature review and update. Eur J Dermatol 2022; 32: 312-321.
Hong-Hui X, Werth V P, Parisi E, Sollecito T P. Mucous membrane pemphigoid. Dent Clin North Am 2013; 57: 611-630.
Du G, Patzelt S, van Beek N, Schmidt E. Mucous membrane pemphigoid. Autoimmun Rev 2022; 21: 103036.
Rashid H, Lamberts A, Diercks G F et al. Oral lesions in autoimmune bullous diseases: an overview of clinical characteristics and diagnostic algorithms. Am J Clin Dermatol 2019; 20: 847-861.
Van Beek N, Schneider S W, Kleinheinz R et al. Incidence of pemphigoid diseases in Northern Germany in 2016 - first data from the Schleswig-Holstein Registry of Autoimmune Bullous Diseases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021; 35: 1197-1202.
Bin Woo S, Setterfield J F, Greenberg M S. Ulcerative, Vesicular, and Bullous Lesions. In Glick M, Greenberg M, Lockhart P, Challacombe J (eds) Burket's Oral Medicine. 13th ed. pp 35-84. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2021.
Kamaguchi M, Iwata H. The Diagnosis and Blistering Mechanisms of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 34.
Finn D J, Graham C, Holt D J, Kelly R, Rajlawat B P, Yesudian P D. Management of mucous membrane pemphigoid in a joint oral medicine-dermatology clinic. Clin Exp Dermatol 2020; 45: 685-690.
Patel P M, Jones V A, Murray T N, Amber K T. A Review Comparing International Guidelines for the Management of Bullous Pemphigoid, Pemphigoid Gestationis, Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid, and Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. Am J Clin Dermatol 2020; 21: 557-565.
Rashid H, Lamberts A, Borradori L et al. European guidelines (S3) on diagnosis and management of mucous membrane pemphigoid, initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology - Part I. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021; 35: 1750-1764.
Schmidt E, Rashid H, Marzano A V et al. European Guidelines (S3) on diagnosis and management of mucous membrane pemphigoid, initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology - Part II. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021; 35: 1926-1948.
Buonavoglia A, Leone P, Dammacco R et al. Pemphigus and mucous membrane pemphigoid: an update from diagnosis to therapy. Autoimmue Rev 2019; 18: 349-358.
Wong V K, Della Croce C, Schonfeld S, Mastrangelo M, Lebwohl M. Use and abuse of topical corticosteroids in infections of the skin and related structures. J Drugs Dermatol 2003; 2: 268-276.
Al-Shehhi F, Balakirski G, Baratli J, Leverkus M, Megahed M. Localized oral mucous membrane pemphigoid: successful topical treatment with 1% tacrolimus solution as steroid-sparing therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2017; 31: 176-178.
Buonavoglia A, Leone P, Dammacco R et al. Pemphigus and mucous membrane pemphigoid: An update from diagnosis to therapy. Autoimmun Rev 2019; 18: 349-358.
Thornburn D N, Ferguson M M. Topical corticosteroids and lesions of the oral mucosa. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 1994; 13: 135-149.
Kridin K, Ahn C, Huang W C, Ansari A, Sami N. Treatment Update of Autoimmune Blistering Diseases. Dermatol Clin 2019; 37: 215-228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Roopali Kulkarni: writing and editing. Eric T. Stoopler: editing. Thomas P. Sollecito: editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulkarni, R., T. Stoopler, E. & P. Sollecito, T. Oral mucous membrane pemphigoid: updates in diagnosis and management. Br Dent J 236, 293–296 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-024-7064-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-024-7064-x