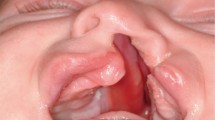
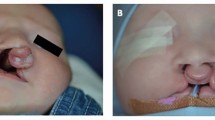
Abstract
This is the second of two papers outlining the orthodontic management of patients with cleft lip and palate. The first paper reviewed orthodontic input into children with cleft lip and palate from birth to the late mixed dentition before definitive orthodontics. In this second paper, I will discuss tooth management across the grafted cleft site and its impact on the bone graft itself. I will also discuss the some of the challenges of the adult patient returning to the service.
Key points
Appropriate alveolar bone graft timing and preparation leads to a reduction in orthodontic burden of care.
In orthodontic terms, children with a cleft involving their alveolus come with further additional dental/skeletal challenges compared to their peers.
Close liaison with the patient's general dental practitioner throughout the orthodontic management is critical to provide the optimal orthodontic outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Solis A, Figueroa A A, Cohen M, Polley J W, Evans C A. Maxillary dental development in complete unilateral alveolar clefts. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 1998; 35: 320-328.
Vandersluis Y R, Fisher D M, Stevens K, Tompson B D, Lou W, Suri S. Comparison of dental outcomes in patients with nonsyndromic complete unilateral cleft lip and palate who receive secondary alveolar bone grafting before or after emergence of the permanent maxillary canine. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2020; 157: 668-679.
Cash A C. Orthodontic treatment in the management of cleft lip and palate. Front Oral Biol 2012; 16: 111-123.
Greene L E, Wilson K, McIntyre G, Wilson J, Mehendale F V. A novel patient-controlled bidirectional palatal lift appliance. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2015; 52: 96-101.
Tortora C, Meazzini M C, Garattini G, Brusati R. Prevalence of abnormalities in dental structure, position, and eruption pattern in a population of unilateral and bilateral cleft lip and palate patients. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2008; 45: 154-162.
Russell K A, McLeod C E. Canine eruption in patients with complete cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2008; 45: 73-80.
Semb G. Alveolar bone grafting. Front Oral Biol 2012; 16: 124-136.
Jahanbin A, Kamyabnezhad E, Raisolsadat M A, Farzanegan F, Bardideh E J. Long-Term Stability of Alveolar Bone Graft in Cleft Lip and Palate Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Craniofac Surg 2022; DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000008254.
Stewart J A, Heo G, Glover K E, Williamson P C, Lam E W, Major P W. Factors that relate to treatment duration for patients with palatally impacted maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2001; 119: 216-225.
Becker A, Chaushu S. Success rate and duration of orthodontic treatment for adult patients with palatally impacted maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2003; 124: 509-514.
Long R E, Semb G, Shaw W C. Orthodontic Treatment of the Patient with Complete Clefts of Lip, Alveolus, and Palate: Lessons of the Past 60 Years. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2000; 37: 1-13.
Ribeiro L L, das Neves L T, Costa B, Gomide M R. Dental development of permanent lateral incisor in complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2002; 39: 193-196.
Maciel S P, Costa B, Gomide M R. Difference in the prevalence of enamel alterations affecting central incisors of children with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2005; 42: 392-395.
Feichtinger M, Mossböck R, Kärcher H. Assessment of bone resorption after secondary alveolar bone grafting using three-dimensional computed tomography: a three-year study. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2007; 44: 142-148.
Ozawa T, Omura S, Fukuyama E, Matsui Y, Torikai K, Fujita K. Factors influencing secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft lip and palate patients: prospective analysis using CT image analyser. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2007; 44: 286-291.
Bergland O, Semb G, Abyholm F E. Elimination of the residual alveolar cleft by secondary bone grafting and subsequent orthodontic treatment. Cleft Palate J 1986; 23: 175-205.
Enemark H, Sindet-Pedersen S, Bundgaard M. Long-term results after secondary bone grafting of alveolar clefts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1987; 45: 913-919.
Lee J C, Slack G C, Walker R et al. Maxillary hypoplasia in the cleft patient: contribution of orthodontic dental space closure to orthognathic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014; 133: 355-361.
Cassolato S F, Ross B, Daskalogiannakis J, Noble J, Tompson B, Paedo D. Treatment of dental anomalies in children with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate at SickKids hospital, Toronto. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2009; 46: 166-172.
Tereza G P, Santos M A, Winckler V P, Almeida A L, Dalben G D. The maxillary lateral incisor in the rehabilitation of cleft lip and palate. J Appl Oral Sci 2018; DOI: 10.1590/1678-7757-2017-0125.
Liao Y-F, Huang C-S. Presurgical and postsurgical orthodontics are associated with superior secondary alveolar bone grafting outcomes. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2015; 43: 717-723.
Jabbari F, Wiklander L, Reiser E, Thor A, Hakelius M, Nowinski D. Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Patients Born With Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate: A 20-Year Follow-up. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2018; 55: 173-179.
Ruppel J K, Long R E Jr, Oliver D R et al. The Americleft Project: A Comparison of Short- and Longer-Term Secondary Alveolar Bone Graft Outcomes in Two Centres Using the Standardized Way to Assess Grafts Scale. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2016; 53: 508-515.
Jabbari F, Skoog V, Reiser E, Hakelius M, Nowinski D. Optimization of dental status improves long-term outcome after alveolar bone grafting in unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2015; 52: 210-218.
Huynh-Ba G, Brägger U, Zwahlen M, Lang N P, Salvi G E. Periodontal disease progression in subjects with orofacial clefts over a 25-year follow-up period. J Clin Periodontol 2009; 36: 836-842.
Silveira G S, de Almeida N V, Pereira D M, Mattos C T, Mucha J N. Prosthetic replacement vs space closure for maxillary lateral incisor agenesis: A systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2016; 150: 228-237.
Freitas J A, Garib D G, Oliveira M et al. Rehabilitative treatment of cleft lip and palate: experience of the Hospital for Rehabilitation of Craniofacial Anomalies-USP (HRAC-USP) - part 2: paediatric dentistry and orthodontics. J Appl Oral Sci 2012; 20: 268-281.
Lopez-Gavito G, Wallen T R, Little R M, Joondeph D R. Anterior open-bite malocclusion: a longitudinal 10-year postretention evaluation of orthodontically treated patients. Am J Orthod 1985; 87: 175-186.
Zuroff J P, Chen S-H, Shapiro P A, Little R M, Joondeph D R, Huang G J. Orthodontic treatment of anterior open-bite malocclusion: stability 10 years postretention. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2010; 137: 302.
Khan R S, Horrocks E N. A study of adult orthodontic patients and their treatment. Br J Orthod 1991; 18: 183-194.
Lages E M, Marcos B, Pordeus I A. Oral health of individuals with cleft lip, cleft palate, or both. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2004; 41: 59-63.
Sales P H, Costa F W, Cetira Filho E L, Silva P G, Albuquerque A F, Leão J C. Effect of maxillary advancement on speech and velopharyngeal function of patients with cleft palate: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2021; 50: 64-74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Written consent to publish has been obtained for Figure 9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillgrass, T. The orthodontic management of patients with cleft lip and palate: from the permanent dentition and the adult returning to the service. Br Dent J 234, 892–898 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-023-5956-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-023-5956-9