Abstract
Objectives Causes of subcutaneous emphysema (SE) following dental treatment have changed with new operative techniques and equipment. This review demonstrates the frequency and aetiology of SE to inform prevention strategies for reducing SE occurrences.
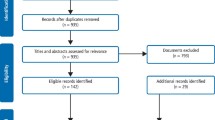
Methods A systematic search of Medline, Embase and PubMed databases identified 135 cases of SE which met inclusion criteria after independent review by two authors. Trends in frequency and causes of SE were displayed graphically and significant differences in frequency of SE by time period, site and hospital stay were analysed using t-tests.
Results Dental extractions often preceded development of SE (54% of cases), commonly surgical extractions. Treatment of posterior mandibular teeth most often resulted in development of SE. Most cases were iatrogenic, with 51% resulting from an air-driven handpiece and 9% from air syringes. Factors such as nose blowing accounted for 10%. There was a significant (p <0.05) increase in cases over time. Mandibular teeth had increased hospital stay time compared to maxillary teeth (p <0.01).
Conclusion Increased risks of SE were identified following use of air-driven handpieces during dental extractions and when treating lower molar teeth. Use of air-driven handpieces should be avoided during dental extractions to reduce risks and subsequent morbidity that results from SE.
Key points
-
This review provides insight into contemporary prevalence, risk factors and management of surgical emphysema following dental treatment.
-
Surgical emphysema is most often associated with use of an air rotor dental handpiece and most commonly results from treatment in the posterior mandible.
-
Dental professionals should be aware of surgical emphysema as a risk factor during some dental treatments to enable appropriate diagnosis and management where necessary.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turnbull A. A Remarkable Coincidence in Dental Surgery. Br Med J 1900; 5: 1131.
Heyman S N, Babayof I. Emphysematous complications in dentistry, 1960-1993: an illustrative case and review of the literature. Quintessence Int 1995; 26: 535-543.
Council on Dental Materials, Instruments and Equipment & American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. Air-driven handpieces and air emphysema. J Am Dent Assoc 1992; 123: 108-109.
McKenzie W S, Rosenberg M. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema of dental and surgical origin: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009; 67: 1265-1268.
Gulati A, Baldwin A, Intosh I M, Krishnan A. Pneumomediastinum, bilateral pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and surgical emphysema after routine apicectomy caused by vomiting. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008; 46: 136-137.
Ely E W, Stump T E, Hudspeth A S, Haponik E F. Thoracic complications of dental surgical procedures: Hazards of the dental drill. Am J Med 1993; 95: 456-465.
Goorhuis H, Rothrock S G. Cervicofacial and thoracic barotrauma following a minor dental procedure. Pediatr Emerg Care 1993; 9: 29-32.
Ouahes N, Petit A, Poirier F, Sigal-Nahum M. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum following dental extraction. Dermatology 1993; 186: 264-265.
Goodnight J W, Sercarz J A, Wang M B. Cervical and mediastinal emphysema secondary to third molar extraction. Head Neck 1994; 16: 287-290.
Bohnenkamp D M. Subcutaneous facial emphysema resulting from routine tooth preparation: A clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 1996; 76: 1-3.
Karras S C, Sexton J J. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema as the result of a dental procedure. J Emerg Med 1996; 14: 9-13.
Torres-Melero J, Arias-Diaz J, Balibrea J. Pneumomediastinum secondary to use of a high speed air turbine drill during a dental extraction. Thorax 1996; 51: 339-341.
Staines K, Felix D. Surgical emphysema: an unusual complication of punch biopsy. Oral Dis 1998; 4: 41-42.
Capes J O, Salon J M, Wells D L. Bilateral cervicofacial, axillary, and anterior mediastinal emphysema: a rare complication of third molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1999; 57: 996-999.
Chen S-C, Lin F-Y, Chang K-J. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum after dental extraction. Am J Emerg Med 1999; 17: 678-680.
Salib R, Valentine P, Akhtar S. Surgical emphysema following dental treatment. J Laryngol Otol1999; 113: 756-758.
Ali A, Cunliffe D, Watt-Smith S. Surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum complicating dental extraction. Br Dent J 2000; 188: 589-590.
Sekine J, Irie A, Dotsu H, Inokuchi T. Bilateral pneumothorax with extensive subcutaneous emphysema manifested during third molar surgery: A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2000; 29: 355-357.
Wakoh M, Saitou C, Kitagawa H, Suga K, Ushioda T, Kuroyanagi K. Computed tomography of emphysema following tooth extraction. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2000; 29: 201-208.
Bumpous J M, Josephson G D, Wambach B A, Noordzji J P. Subcutaneous cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema after dental instrumentation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001; 124: 170-171.
Davies D. Pneumomediastinum after dental surgery. Anaesth Intensive Care 2001; 29: 638-641.
Hata T, Hosoda M. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema after oral laser surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2001; 39: 161.
Penna K J, Neshat K. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema after lower root canal therapy. N Y State Dent J 2001; 67: 28.
Sood T, Pullinger R. Pneumomediastinum secondary to dental extraction. Emerg Med J 2001; 18: 517-518.
Oliver R, Coulthard P. Post-operative surgical emphysema following the use of a peak flow meter. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002; 40: 452-453.
Barkdull T J. Pneumothorax during dental care. J Am Board Fam Pract 2003; 16: 165-169.
Aquilina P, McKellar G. Extensive surgical emphysema following restorative dental treatment. Emerg Med 2004; 16: 244-246.
Smatt Y, Browaeys H, Genay A, Raoul G, Ferri J. Iatrogenic pneumomediastinum and facial emphysema after endodontic treatment. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2004; 42: 160-162.
Frühauf J, Weinke R, Pilger U, Kerl H, Müllegger R R. Soft tissue cervicofacial emphysema after dental treatment: report of 2 cases with emphasis on the differential diagnosis of angioooedema. Arch Dermatol 2005; 141: 1437-1440.
Iqbal M, Ikram M, Raza F, Banday N. Surgical emphysema in the neck as a result of a dental procedure. Ear Nose Throat J 2005; 84: 723-724.
Schneider L, Weber L, Maetzke J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. A swollen face after dental surgery Akute Gesichtsschwellung nach Zahnarztbehandlung. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2005; 3: 987-989.
Chung I-H, Moon H-J, Suh J-D, Han K-D. Interesting case: cervicofacial emphysema and mediastinitis following restorative dental treatment - a case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2006; 44: 376.
Desai H. Odontogenic pneumomediastinumafter routine dental extraction. J Respir Dis 2006; 27: 536.
Karki A J, Stokes M M, Fraser J S, Adlam D M. Surgical emphysema following a restorative procedure: A case report. Dent Update 2006; 33: 171-174.
Mather A J, Stoykewych A A, Curran J B. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema complicating a dental procedure. J Can Dent Assoc 2006; 72: 565-568.
Satilmis A, Dursun O, VElipasaoglu S, Guven A G. Severe subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and pneumopericardium after central incisor extraction in a child. Pediatr Emerg Care 2006; 22: 771-772.
Torgay A, Aydin E, Cilasun U, Durmaz L, Arslan G. Subcutaneous emphysema after dental treatment: a case report. Paediatr Anaesth 2006; 16: 314-317.
Yang S-C, Chiu T-H, Lin T-J, Chan H-M. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum secondary to dental extraction: a case report and literature review. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2006; 22: 641-645.
Chan D C, Myers T, Sharawy M. A case for rubber dam application - Subcutaneous emphysema after Class V procedure. Oper Dent 2007; 32: 193-196.
Gamboa Vidal C A, Vega Pizarro C A, Almeida Arriagada A. Subcutaneous emphysema secondary to dental treatment: case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2007; 12: 76-78.
Kumar D, Farrell T, Tierney E. A frightening complication of general anaesthesia for paediatric dental extractions. Pediatr Surg Int 2007; 23: 613-616.
Steelman R J, Johannes P W. Subcutaneous emphysema during restorative dentistry. Int J Paediatr Dent 2007; 17: 228-229.
Sujeet K, Shankar S. Prevertebral emphysema after a dental procedure. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 173.
Uehara M, Okumura T, Asahina I. Subcutaneous cervical emphysema induced by a dental air syringe: a case report. Int Dent J 2007; 57: 286-288.
Gulati A, Baldwin A, Intosh I M, Krishnan A. Pneumomediastinum, bilateral pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and surgical emphysema after routine apicectomy caused by vomiting. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008; 46: 136-137.
Magni G, Imperiale C, Rosa G, Favaro R. Nonfatal cerebral air embolism after dental surgery. Anesth Analg 2008; 106: 249-251.
Porteri E, Rizzardi N, Rizzoni D et al. A strange chest pain after dental surgery. Intern Emerg Med 2008; 3: 123.
Arai I, Aoki T, Yamazaki H, Ota Y, Kaneko A. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema after dental extraction detected incidentally by regular medical checkup: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009; DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.12.019.
Cicciù M, Grossi G B, Beretta M, Farronato D, Scalfaro C, Maiorana C. Cervicofacial emphysema secondary to facebow injury: a case report. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2009; 33: 333-336.
Eskander M G. Facial swelling after a dental procedure. CMAJ 2009; 180: 139.
Imai T, Michizawa M, Arimoto E, Kimoto M, Yura Y. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum after intraoral laser irradiation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009; 67: 428-430.
Kung J-C, Chuang F-H, Hsu K-J, Shih Y-L, Chen C-M, Huang I-Y. Extensive subcutaneous emphysema after extraction of a mandibular third molar: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2009; 25: 562-566.
Parkar A, Medhurst C, Irbash M, Philpott C. Periorbital oooedema and surgical emphysema, an unusual complication of a dental procedure: a case report. Cases J 2009; 2: 8108.
Samuels T. Rare complications of surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum occurring post dental extraction. Postgrad Med J 2009; 85: 404.
Kim Y, Kim M-R, Kim S-J. Iatrogenic pneumomediastinum with extensive subcutaneous emphysema after endodontic treatment: report of 2 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2010; DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.09.013.
Matsuzawa N, Kinoshita H, Shirozu T, Takamura M, Nagao T. Mediastinal emphysema caused by a dental laser. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010; 22: 216-219.
Pousios D, Panagiotopoulos N, Sioutis N, Piyis A, Gourgiotis S. Iatrogenic pneumomediastinum and facial emphysema after surgical tooth extraction. Ann Thorac Surg 2010; 89: 640.
Sainsbury D, Jaiganesh T. Dentist's drill allergy? Int J Emerg Med 2010; 3: 427-429.
Afzali N, Malek A, Attar A H H. Cervicofacial emphysema and pneumomediastinum following dental extraction: case report. Iran J Pediatr 2011; 21: 253.
Coulier J, Deprez F. Iatrogenic facial subcutaneous emphysema after endodontic treatment. JBR-BTR 2011; 94: 38.
Hsu H-L, Chang C-C, Liu K-L. Subcutaneous emphysema after dental procedure. QJM 2011; 104: 545.
Maxwell M G, Thompson K M, Hedges M S. Airway compromise after dental extraction. J Emerg Med 2011; DOI: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.04.036.
Romeo U, Galanakis A, Lerario F, Daniele G M, Tenore G, Palaia G. Subcutaneous emphysema during third molar surgery: a case report. Braz Dent J 2011; 22: 83-86.
Uyanık L O, Aydın M, Buhara O, Ayalı A, Kalender A. Periorbital emphysema during dental treatment: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2011; DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.05.036.
Bilecenoglu B, Onul M, Altay O T, Sakul B U. Cervicofacial emphysema after dental treatment with emphasis on the anatomy of the cervical fascia. J Craniofac Surg 2012; DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31825aef02.
Chen C-H, Chang H, Liu H-C, Hung T-T, Huang W-C. Pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum and pneumopericardium complications arising from a case of wisdom tooth extraction. Rev Port Pneumol 2012; 18: 194-197.
Döngel İ, Bayram M, Uysal I O, Sunam G S. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum complicating a dental procedure. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2012; 18: 361-363.
Durukan P, Salt O, Ozkan S, Durukan B, Kavalci C. Cervicofacial emphysema and pneumomediastinum after a high-speed air drill endodontic treatment procedure. Am J Emerg Med 2012; DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2012.01.006.
Guillén-Paredes P, Novoa-Juiz V, Carrasco-González L. Asymptomatic pneumomediastinum after wisdom tooth extraction. Arch Bronconeumol 2012; 6: 217-218.
Suzuki J, Takahashi S. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum due to carbon dioxide laser therapy. J Pediatr 2012; 161: 167.
Terzic A, Becker M, Masterson K, Scolozzi P. Severe subcutaneous and deep cervicofacial emphysema of unusual aetiology. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 269: 303-308.
Abrahams J M, Jakubowski J, Liang D, McClure S. Subcutaneous emphysema to the head and neck resulting from a dental crown preparation. J Mich Dent Assoc 2013; 95: 54-56.
Al-Qudah A, Amin F, Hassona Y. Periorbital emphysema during endodontic retreatment of an upper central incisor: a case report. Br Dent J 2013; 215: 459-461.
Bergen T. Unusual case of cervicofacial surgical emphysema. Emerg Med Australas 2013; 25: 473.
Elia F, Laface B, Pagnozzi F et al. Cervicofacial emphysema and pneumomediastinum complicating a dental procedure. J Emerg Med 2013; DOI: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.05.013.
Khandelwal V, Agrawal P, Agrawal D, Nayak P A. Subcutaneous emphysema of periorbital region after stainless steel crown preparation in a young child. BMJ Case Rep 2013; DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009952.
Mitsunaga S, Iwai T, Aoki N et al. Cervicofacial subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema caused by air cooling spray of dental laser. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2013; DOI: 10.1016/j.oooo.2011.10.037.
Olate S, Assis A, Freire S, de Moraes M, de Albergaria-Barbosa J R. Facial and cervical emphysema after oral surgery: a rare case. Int J Clin Exp Med 2013; 6: 840.
An G K, Zats B, Kunin M. Orbital, mediastinal, and cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema after endodontic retreatment of a mandibular premolar: a case report. J Endod 2014; 40: 880-883.
Baisi A, De Simone M, Cioffi U. Pneumomediastinum after a swimming race and dental extraction. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2014; 22: 367.
Fleischman D, Davis R M, Lee L B. Subcutaneous and periorbital emphysema following dental procedure. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2014; DOI: 10.1097/IOP.0b013e318295f982.
Haitz K A, Patel A J, Baughman R D. Periorbital subcutaneous emphysema mistaken for unilateral angioooedema during dental crown preparation. JAMA Dermatol 2014; 150: 907-909.
Johannesma P C, Noordegraaf A V. Pneumomediastinum and pneumopericardium due to high-speed air turbine drill used during a dental procedure. Ann Thorac Surg 2014; 98: 2232.
Lim J-L. Periorbital oooedema after dental extraction: a case study. Aust Fam Physician 2014; 43: 543.
Mishra L, Patnaik S, Patro S, Debnath N, Mishra S. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema of endodontic origin - case report with literature review. J Clin Diagn Res 2014; 8: 279.
Aslaner M A, Kasap G N, Demir C, Akkaş M, Aksu N M. Occurrence of pneumomediastinum due to dental procedures. Am J Emerg Med 2015; DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.05.055.
Fulton G. Carotid Sheath involvement and Pneumomediastinum following the use of high speed removal of a lower third molar. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015; DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2015.08.148.
Kim K, Cho J, Lee J, Kim C, Park J. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema after periodontal treatment using air-flow equipment: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015; 44: e246.
Lococo F, Trabucco L, Leuzzi G et al. Severe breathing and swallowing difficulties during routine restorative dentistry. Ann Ital Chir 2015; 86: S2239253X1502280X.
Nishimura T, Sawai T, Kadoi K et al. Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum following a high-speed air drill dental treatment procedure. Acute Med Surg 2015; DOI: 10.1002/ams2.109.
Önal Ö, Hasdıraz L, Oğuzkaya F. Iatrogenic Pneumomediastinum and Subcutaneous Emphysema after Mandibular Left First Molar Tooth Extraction. 2015.
Picard M, Dang N P, Mondie J M, Barthelemy I. Cervicothoracic subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum after third molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015; DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2015.07.030.
Sakakibara A, Suzuki H, Yamashita A et al. Facial emphysema after sinus lift. J Surg Case Rep 2015; DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjv067.
Shimi A, Benlamkaddem S, Tahse D, Derkaoui A, Khatouf M. Cervicofacial Emphysema and pneumomediastinum complicating a dental extraction. Case Rep Clin Med 2015; 4: 257.
Tomasetti P, Kuttenberger J, Bassetti R. Distinct subcutaneous emphysema following surgical wisdom tooth extraction in a patient suffering from 'Gilles de la Tourette syndrome'. J Surg Case Rep 2015; DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjv068.
Wong C, Collin J, Hughes C, Thomas S. Surgical emphysema and pneumomediastinum after coronectomy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015; 53: 763-764.
Farina R, Zaetta A, Minenna L, Trombelli L. Orbital and periorbital emphysema following maxillary sinus floor elevation: a case report and literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016; DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.06.186.
Mañas V M, Lara R R, Sánchez G A. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema: A rare complication of dental extraction. Arch Bronconeumol 2016; 52: 104.
Soylu E, Asan C, Kilic E, Alkan A. An Unusual Complication After the Extraction of a Maxillary Third Molar: Extensive Subcutaneous Emphysema. A Case Report. J Clin Analyt Med 2016; DOI: 10.4328/JCAM.4573.
Vargo R J, Potluri A, Yeung A Y, Aldojain A, Bilodeau E A. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema: a clinical case and review of the literature. Gen Dent 2016; 64: 68.
Yepez-Ramos D, Dajer-Fadel W, Ramírez-Castañeda S, Flores-Calderón O, Latorre-Dávila C, Argüero-Sánchez R. Severe Subcutaneous Emphysema and Pneumomediastinum After a Molar Extraction: A Rare Case in Mexico. Chest 2016; 150: 61A.
Akra G A, Yousif K. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema complicating tooth extraction in an elderly patient: a preventable complication. BMJ Case Rep 2017; DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-219245.
Alonso V, García-Caballero L, Couto I, Diniz M, Diz P, Limeres J. Subcutaneous emphysema related to air-powder tooth polishing: a report of three cases. Aust Dent J 2017; 62: 510-515.
Boggess W J, Ronan J, Panchal N. Orbital, mediastinal and cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema after dental rehabilitation in a paediatric patient. Pediatr Dent 2017; 39: 465-467.
Gowans K, Patel M, Lewis K. Surgical emphysema: a rare complication of a simple surgical dental extraction without the use of an air-driven rotor. Dent Update 2017; 44: 217-220.
Ishikawa K, Omori K, Ohsaka H, Yanagawa Y. A pregnant woman with pneumomediastinum after tooth treatment. J Emerg Trauma Shock 2017; 10: 162-163.
Lee S-W, Huh Y-H, Cha M-S. Iatrogenic subcutaneous cervicofacial emphysema with pneumomediastinum after class V restoration. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2017; 43: 49-52.
Ramnarine M, Dubin Z. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema due to a dental procedure. J Emerg Trauma Shock 2017; 10: 34.
Sahoo N, Singh S, Roy I, Bhandari A. Early postoperative malignant subcutaneous emphysema: report and review. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2017; 16: 85-89.
Tan S, Nikolarakos D. Subcutaneous emphysema secondary to dental extraction: a case report. Aust Dent J 2017; 62: 95-97.
Thompson C, Gohil R. Pneumatic dental extractions: an unusual cause of extensive cervical surgical emphysema. BMJ Case Rep 2017; DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-218677.
Van Tubergen E, Tindle D, Fox G. Sudden onset of subcutaneous air emphysema after the application of air to a maxillary premolar located in a nonsurgical field. Oper Dent 2017; DOI: 10.2341/15-155-S.
Chang C-H, Lien W-C. Palpebral emphysema following a dental procedure. Am J Emerg Med 2018; DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.01.077.
Jeong C-H, Yoon S, Chung S-W, Kim J-Y, Park K-H, Huh J-K. Subcutaneous emphysema related to dental procedures. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2018; 44: 212-219.
Lee S-T, Subu M G, Kwon T-G. Emphysema following air-powder abrasive treatment for peri-implantitis. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2018; DOI: 10.1186/s40902-018-0151-7.
Liu C-C, Lin M-Y. Diffuse soft tissue emphysema after dental procedure. CJEM 2018; DOI: 10.1017/cem.2017.348.
Miller J, Lapinel N, Creek G, Kantrow S. Pneumomediastinum After Mandibular Molar Extraction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018; 197: A1800.
Tay Y, Loh W. Extensive subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and pneumorrhachis following third molar surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2018; 47: 1609-1612.
Zaheer S, Srinivasan S, Othman M I. Image challenge: acute chest pain after tooth extraction. Emerg Med J 2018; 35: 332.
Zaigham S, Doraiswamy M, Dy P, Patton C. Delayed Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneumothorax Post Dental Extraction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018; 197: A3244.
Chang J R, Rajaii F, McCulley T J. Delayed orbital emphysema mimicking orbital cellulitis: An uncommon complication of dental surgery. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 2019; 26: 175.
Chien P H. Iatrogenic subcutaneous facial emphysema secondary to a class V dental restoration: a case report. Aust Dent J 2019; 64: 43-46.
Costa R, Oliveira J, Bassi A, Monnazzi M, Weber J, Gabrielli M. Subcutaneous emphysema envolving temporal, orbital, buccal, submandibular and cervical spaces after third molar surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2019; 48: 210-211.
Cuccia A M, Geraci A. Cervicofacial and mediastinal emphysema after dental extraction. Dent Med Probl 2019; 56: 203-207.
Fehrle C, Gillissen A. Mediastinal and Cutaneous Emphysema Following Dental Extraction. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2019; 116: 212.
Mascarenhas R J. Management of subcutaneous facial emphysema secondary to a class V dental restoration. Clin Case Rep 2019; 7: 1025.
North L, Sulman C. Subcutaneous emphysema and vocal fold paresis as a complication of a dental procedure. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019; 124: 76-78.
Paschos K A, Chatzigeorgiadis A. Cervicofacial Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum and Pneumothorax Caused by a Dental Procedure. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2019; 29: 191.
Rad M V, Chan E K Y, Ahmed I H. Cervicofacial subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum secondary to dental treatment in a young man. Respir Med Case Rep 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100918.
Kaliszewski K, Cendal I, Krassowska M, Szwed D, Wojtczak B, Rudnicki J. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema may follow dental extraction. Pol Arch Intern Med 2020; 130: 244-245.
Pan Y. Massive emphysema after tooth extraction. Am J Emerg Med 2020; DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.158412.
Shovelton D. Surgical emphysema as a complication of dental operations. Br Dent J 1957; 102: 125-129.
Oliver R, Coulthard P. Post-operative surgical emphysema following the use of a peak flow meter. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002; 40: 452-453.
Dasta J F, McLaughlin T P, Mody S H, Piech C T. Daily cost of an intensive care unit day: the contribution of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med 2005; 33: 1266-1271.
Briggs A D M, Scarborough P, Wolstenholme J. Estimating comparable English healthcare costs for multiple diseases and unrelated future costs for use in health and public health economic modelling. PLoS One 2018; DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197257.
Hohl C M, Small S S, Peddie D, Badke K, Bailey C, Balka E. Why Clinicians Don't Report Adverse Drug Events: Qualitative Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2018; DOI: 10.2196/publichealth.9282.
Cooper J, Edwards A, Williams H et al. Nature of Blame in Patient Safety Incident Reports: Mixed Methods Analysis of a National Database. Ann Fam Med 2017; 15: 455-461.
Kalenderian E, Obadan-Udoh E, Maramaldi P et al. Classifying Adverse Events in the Dental Office. J Patient Saf 2017; DOI: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000407.
Maunder R J, Pierson D J, Hudson L D. Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med 1984; 144: 1447-1453.
Alexandre A R, Marto N F, Raimundo P. Hamman's crunch: a forgotten clue to the diagnosis of spontaneous pneumomediastinum. Case Rep 2018; DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225099.
Konijn A J, Egbers P H, Kuiper M A. Pneumopericardium should be considered with electrocardiogram changes after blunt chest trauma: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2008; 2: 100.
Jevon P. Updated posters to help manage medical emergencies in the dental practice. BDJ Team 2016; 3: 16055.
Mettes T, Bruers J, van der Sanden W, Wensing M. Patient safety in dental care: A challenging quality issue? An exploratory cohort study. Acta Odontol Scand 2013; 71: 1588-1593.
Bailey E, Tickle M, Campbell S, O'Malley L. Systematic review of patient safety interventions in dentistry. BMC Oral Health 2015; 15: 152.
Bamford P, Smith G. LocSSIPs - The quest to improve patient safety. J Intensive Care Soc 2017; 182: 180-183.
Tagar H, Devine M, Obisesan O. How to create local safety standards for invasive procedures (LocSSIPs) by engaging the team in patient safety. Br Dent J 2019; DOI: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2019.51.
Ethics declaration
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, A., Stagnell, S., Renton, T. et al. Causes of subcutaneous emphysema following dental procedures: a systematic review of cases 1993-2020. Br Dent J 231, 493–500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-021-3564-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-021-3564-0
This article is cited by
-
Air of caution: sudden unilateral cervicofacial swelling amidst dental procedure? Think emphysema
Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine (2023)