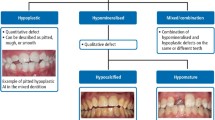
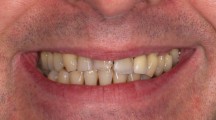
Abstract
Objective This clinical report aims to share with general practitioners a conservative approach to treat patients with amelogenesis imperfecta (AI).
Clinical considerations In relatively young patients, a conservative treatment approach is essential in order to maintain the vitality of the teeth and provide successful outcomes. In this clinical report, the diagnoses and treatment plan of an 18-year-old male patient diagnosed with AI is discussed. Composite rehabilitation followed by orthodontic treatment was considered the most conservative treatment approach for this patient.
Conclusion Bonding to well-mineralised enamel can be a predictable and successful treatment approach for young patients diagnosed with AI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gadhia K, McDonald S, Arkutu N, Malik K. Amelogenesis imperfecta: an introduction. Br Dent J 2012; 8: 377.
Lau E C, Mohandras T K, Shapiro L J, Slavkin H C, Snead M L. Human and mouse amelogenin gene loci are on the sex chromosomes. Genomics 1989; 4: 162-168.
Lau E C, Slavkin H C, Snead M L. Analysis of human enamel genes insights into genetic disorders of enamel. Cleft Palate J 1990; 27: 121-130.
Collins M A, Mauriello S M, Tyndall D A, Wright J T. Dental anomalies associated with amelogenesis imperfecta: a radiographic assessment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1999; 3: 358-364.
Wright J T. The molecular etiologies and associated phenotypes of Amelogenesis imperfecta. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 23: 2547-2555.
Sabandal M M, Schäfer E. Amelogenesis imperfecta: review of diagnostic findings and treatment concepts. Odontology 2016; 104: 245-256.
Weinmann J P, Svoboda J F, Woods R W. Hereditary disturbances of enamel formation and calcification. JADA 1945; 32: 397-418.
Witkop Jr C J. Amelogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia revisited: problems in classification. J Oral Pathol 1988; 17(9-10): 547-553.
Pavlič A, Battelino T, Trebušak Podkrajšek K, Ovsenik M. Craniofacial characteristics and genotypes of amelogenesis imperfecta patients. Eur J Orthod 2011; 33: 325-331.
Hunter L, Stone D. Supraoccluding cobalt-chrome onlays in the management of amelogenesis imperfecta in children: A 2year case report. Quintessence Int 1997; 28: 15-19.
Chan K H, Ho E H, Botelho M G, Pow E H. Rehabilitation of amelogenesis imperfecta using a reorganised approach: A case report. Quintessence Int 2011; 42: 385-391.
Seow W K. Developmental defects of enamel and dentine: challenges for basic science research and clinical management. Aust Dent J. 2014; 59: 143-154.
Horowitz R A, Gautam D K, Karol S, Kumari B. Periodontal management and restoration of an amelogenesis imperfecta patient: a case report. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2014; 35: e6-11.
Koruyucu M, Bayram M, Tuna E B, Gencay K, Seymen F. Clinical findings and long-term managements of patients with amelogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Dent 2014; 8: 546-552.
Nusier M, Yassin O, Hart T C, Samimi A, Wright J T. Phenotypic diversity and revision of the nomenclature for autosomal recessive amelogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2004; 97: 220-230.
Wright J T, Frazier-Bowers S, Simmons D et al. Phenotypic variation in FAM83H-associated amelogenesis imperfecta. J Dent Res 2009; 4: 356-360.
Bäckman B, Holm A K. Amelogenesis imperfecta: prevalence and incidence in a northern Swedish county. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1986; 1: 43-47.
Chosack A, Eidelman E, Wisotski I, Cohen T. Amelogenesis imperfecta among Israeli Jews and the description of a new type of local hypoplastic autosomal recessive amelogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1979; 2: 148-156.
Witkop Jr C J. Genetics and dentistry. Eugen Q 1958; 5: 15-21.
Witkop Jr C J. Genetic disease of the oral cavity. In Tiecke R W (ed) Oral Pathology. pp 801-805. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1965.
Coffield K D, Phillips C, Brady M, Roberts M W, Strauss R P, Wright J T. The psychosocial impact of developmental dental defects in people with hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. J Am Dent Assoc 2005; 5: 620-630.
Bouvier D, Duprez J P, Pirel C, Vincent B. Amelogenesis imperfecta - a prosthetic rehabilitation: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 1999; 2: 130-131.
Patel M, McDonnell S T, Iram S, Chan M F W-Y. Amelogenesis imperfecta - lifelong management. Restorative management of the adult patient. Br Dent J 2013; 9: 449-457.
Borges B C.D, de Vasconselos A A M, Cunha A G.G, Pinheiro F H S L, Machado, C T, dos Santos A J.S. Preliminary Clinical Reports of a Novel Night-Guard Tooth Bleaching Technique Modified by Casein Phosphopeptide-Amorphous Calcium Phosphate (CPP-ACP). Eur J Esthet Dent 2011; 6: 446-453.
Özgül B M, Saat S, Sönmez H, Öz F T. Clinical evaluation of desensitizing treatment for incisor teeth affected by molar-incisor hypomineralization. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2013; 38: 101-105.
Kwok-Tung L, King N. The restorative management of amelogenesis imperfecta in the mixed dentition. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2007; 31: 130-135.
Sapir S, Shapira J. Clinical solutions for developmental defects of enamel and dentin in children. Pediatr Dent 2007; 29: 330-336.
Chen C F, Hu J C, Bresciani E, Peters M C, Estrella M R. Treatment considerations for patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: a review. Braz Dent Sci 2013; 16: 7-18.
Seow W K, Amaratunge A. The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study. Pediatr Dent 1998; 20: 37-42.
Langeland K, Langeland L K. Pulp reactions to crown preparation, impression, temporary crown fixation, and permanent cementation. J Prosthet Dent 1965; 15: 129-143.
Strauch S, Hahnel S. Restorative treatment in patients with Amelogenesis imperfecta: a review. J Prosthodont 2018; 27: 618-623.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd Alraheam, I., Donovan, T. Management of amelogenesis imperfecta in an adult patient: a short review and clinical report. Br Dent J 229, 239–243 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-020-1990-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-020-1990-z