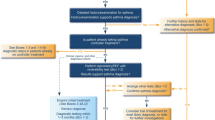
Abstract
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is a common and potentially devastating noninfectious pulmonary complication after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Currently, predictive tools for BOS are not available. We aimed to identify the clinical risk factors and establish a prognostic model for BOS in patients who undergo allo-HSCT. We retrospectively identified a cohort comprising 195 BOS patients from 6100 consecutive patients who were allografted between 2008 and 2022. The entire cohort was divided into a derivation cohort and a validation cohort based on the time of transplantation. Via multivariable Cox regression methods, declining forced expiratory volume at 1 s (FEV1) to <40%, pneumonia, cGVHD except lung, and respiratory failure were found to be independent risk factors for the 3-year mortality of BOS. A risk score called FACT was constructed based on the regression coefficients. The FACT model had an AUC of 0.863 (95% CI: 0.797–0.928) in internal validation and 0.749 (95% CI: 0.621–0.876) in external validation. The calibration curves showed good agreement between the FACT-predicted probabilities and actual observations. The FACT risk score will help to identify patients at high risk and facilitate future research on developing novel, effective interventions to personalize treatment.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barker AF, Bergeron A, Rom WN, Hertz MI. Obliterative bronchiolitis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1820–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1204664.
Williams KM. How I treat bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2017;129:448–55. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-693507.
Bergeron A, Cheng GS. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and other late pulmonary complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Chest Med. 2017;38:607–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2017.07.003.
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, Williams KM, Wolff D, Cowen EW, et al. National institutes of health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. The 2014 diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015;21:389–401.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.001.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:945–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.004.
Fujii N, Nakase K, Asakura S, Matsuo K, Nawa Y, Sunami K, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a 10-year experience of the Okayama BMT Group. Int J Hematol. 2014;99:644–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1556-4.
Au BK, Au MA, Chien JW. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome epidemiology after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2011;17:1072–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.11.018.
Gazourian L, Coronata AM, Rogers AJ, Weinhouse GL, Soiffer RJ, Antin JH, et al. Airway dilation in bronchiolitis obliterans after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Respir Med. 2013;107:276–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2012.11.002.
Bergeron A, Godet C, Chevret S, Lorillon G, Peffault de Latour R, de Revel T, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT: phenotypes and prognosis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:819–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.241.
Kuzmina Z, Krenn K, Petkov V, Kormoczi U, Weigl R, Rottal A, et al. CD19(+)CD21(low) B cells and patients at risk for NIH-defined chronic graft-versus-host disease with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Blood. 2013;121:1886–95. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-06-435008.
Chien JW, Duncan S, Williams KM, Pavletic SZ. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-an increasingly recognized manifestation of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2010;16:S106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.11.002.
Dudek AZ, Mahaseth H, DeFor TE, Weisdorf DJ. Bronchiolitis obliterans in chronic graft-versus-host disease: analysis of risk factors and treatment outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2003;9:657–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1083-8791(03)00242-8.
Hildebrandt GC, Fazekas T, Lawitschka A, Bertz H, Greinix H, Halter J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary chronic GVHD: report from the consensus conference on clinical practice in chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2011;46:1283–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.35.
Williams KM, Chien JW, Gladwin MT, Pavletic SZ. Bronchiolitis obliterans after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. JAMA. 2009;302:306–14. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1018.
Yan CH, Xu LP, Wang FR, Chen H, Han W, Wang Y, et al. Causes of mortality after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and the comparison with HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:391–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.306.
Lai YR, Chen YH, Hu DM, Jiang M, Liu QF, Liu L, et al. Multicenter phase II study of a combination of cyclosporine a, methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil for GVHD prophylaxis: results of the Chinese Bone Marrow Transplant Cooperative Group (CBMTCG). J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0059-3.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W, et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2006;38:291–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705445.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W, et al. Treatment of acute leukemia with unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:257–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.11.025.
Wu J, Fu HX, He Y, Mo XD, Liu X, Cai X, et al. Risk factors and outcomes of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:2097–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01293-y.
Cai X, Fu HX, Mo XD, Wang Y, Zhang YY, Wu J, et al. Comparison of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020;55:2087–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0903-8.
Sun X, Su Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, He Y, Han W, et al. Overt gastrointestinal bleeding following haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, outcomes and predictive models. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:1341–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-01187-5.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1995;15:825–8.
Revilla-Lopez E, Berastegui C, Saez-Gimenez B, Lopez-Meseguer M, Monforte V, Bravo C, et al. Lung retransplantation due to chronic lung allograph dysfunction: results from a spanish transplant unit. Arch Bronconeumol. 2019;55:134–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2018.07.025.
Soubani AO, Uberti JP. Bronchiolitis obliterans following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur Respir J. 2007;29:1007–19. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00052806.
Erard V, Chien JW, Kim HW, Nichols WG, Flowers ME, Martin PJ, et al. Airflow decline after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: the role of community respiratory viruses. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1619–25. https://doi.org/10.1086/504268.
Chien JW, Martin PJ, Gooley TA, Flowers ME, Heckbert SR, Nichols WG, et al. Airflow obstruction after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:208–14. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200212-1468OC.
Ahn JH, Jo KW, Song JW, Shim TS, Lee SW, Lee JS, et al. Prognostic role of FEV1 for survival in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Transpl. 2015;29:1133–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.12638.
Kemp R, Pustulka I, Boerner G, Smela B, Hofstetter E, Sabeva Y, et al. Relationship between FEV(1) decline and mortality in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome-a systematic literature review. Respir Med. 2021;188:106608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106608.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC2500304), Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82230004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81970113), Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82200136), and the Capital Health Research and Development of Special (No. 2022-1-4082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XHZ, QSH and TXH contributed to the concept and design. PZ, YJW, YH, XLZ, HXF, FRW, YYZ, XDM, WH, CHY, JZW, HC, YHC, TTH, ML, YC, QSH and TXH collected the data. QSH and XHZ contributed to data interpretation and data analysis. XHZ, QSH and TXH performed statistical analysis. YW, LPX, KYL, XJH and XHZ revised it critically. XHZ, QSH and TXH wrote the manuscript. XHZ designed, conceived and supervised the study, analyzed the data, and drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, QS., Han, TX., Chen, Q. et al. Clinical risk factors and prognostic model for patients with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 59, 239–246 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02151-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02151-9