Abstract
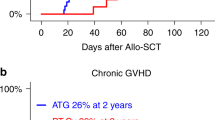
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) is effective for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis, but it may cause dose-dependent toxicities, particularly in frail patients. Therefore, we compared the outcomes with a reduced PT-Cy total dose (70 mg/kg) to those with the standard PT-Cy dose (100 mg/kg) in haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) patients aged ≥ 65 years and those with cardiac comorbidities. All consecutive patients with a hematological malignancy receiving peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) after a thiotepa-based conditioning with low-dose antithymocyte globulin were included. Thirty-three patients received PT-Cy at 70 mg/kg and 25 at 100 mg/kg. PT-Cy dose reduction did not increase the risk of GVHD and was associated with faster neutrophil and platelet recovery, and lower cumulative incidences of bacteremia (38% versus 72%, p = 0.004) and cardiac complications (12% versus 44%, p = 0.028). At 2 years, GVHD-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS) was higher with the reduced dose compared to the standard dose (60% versus 33%, p = 0.04). In conclusion, reducing PT-Cy total dose to 70 mg/kg is a safe and valid approach for elderly patients and those with cardiac comorbidities underdoing haploidentical HCT with PBSCs and low-dose antithymocyte globulin. The reduced PT-Cy dose was associated with improved hematological count recovery, lower incidence of toxicities, and higher GRFS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Malard F, Chevallier P, Guillaume T, Delaunay J, Rialland F, Harousseau JL, et al. Continuous reduced nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single-institution’s three decade experience. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1217–23.
Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Chabannon C, Basak GW, de la Cámara R, Corbacioglu S, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation and cellular therapy survey of the EBMT: monitoring of activities and trends over 30 years. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:1651–64.
Luznik L, O’Donnell PV, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Leffell MS, Zahurak M, et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14:641–50.
Raiola AM, Dominietto A, di Grazia C, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, Ibatici A, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical transplants compared with other alternative donors and matched sibling grafts. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1573–9.
Ciurea SO, Zhang MJ, Bacigalupo AA, Bashey A, Appelbaum FR, Aljitawi OS, et al. Haploidentical transplant with posttransplant cyclophosphamide vs matched unrelated donor transplant for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2015;126:1033–40.
Bashey A, Zhang X, Jackson K, Brown S, Ridgeway M, Solh M, et al. Comparison of outcomes of hematopoietic cell transplants from T-replete haploidentical donors using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide with 10 of 10 HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 allele-matched unrelated donors and HLA-identical sibling donors: a multivariable analysis including disease risk index. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:125–33.
Gauthier J, Poiré X, Gac AC, Leclerc M, Guillaume T, Chalandon Y, et al. Better outcome with haploidentical over HLA-matched related donors in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation-a study by the Francophone Society of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53:400–9.
Duléry R, Ménard AL, Chantepie S, El-Cheikh J, François S, Delage J, et al. Sequential conditioning with thiotepa in T Cell- replete hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of refractory hematologic malignancies: comparison with matched related, haplo-mismatched, and unrelated donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:1013–21.
Cytryn S, Abdul-Hay M. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation followed by ‘post-cyclophosphamide’: the future of allogeneic stem cell transplant. Clin Hematol Int. 2020;2:49–58.
Ruggeri A, Galimard JE, Labopin M, Rafii H, Blaise D, Ciceri F, et al. Comparison of outcomes after unrelated double-unit cord blood and haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in adults with acute myeloid leukemia, a study on behalf of Eurocord and ALWP-EBMT. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:710.e1–e10.
Luznik L, Pasquini MC, Logan B, Soiffer RJ, Wu J, Devine SM, et al. Randomized phase III BMT CTN trial of calcineurin inhibitor-free chronic graft-versus-host disease interventions in myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:356–68.
Nagler A, Labopin M, Dholaria B, Wu D, Choi G, Aljurf M, et al. Graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide versus cyclosporine A and methotrexate in matched sibling donor transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:86.e1–e8.
Broers AEC, de Jong CN, Bakunina K, Hazenberg MD, van Marwijk Kooy M, de Groot MR, et al. Posttransplant cyclophosphamide for prevention of graft-versus-host disease: results of the prospective randomized HOVON-96 trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6:3378–85.
Stocker N, Gaugler B, Labopin M, Farge A, Ye Y, Ricard L, et al. High-dose post-transplant cyclophosphamide impairs γδ T-cell reconstitution after haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation using low-dose antithymocyte globulin and peripheral blood stem cell graft. Clin Transl Immunol. 2020;9:e1171.
Rambaldi B, Kim HT, Reynolds C, Chamling Rai S, Arihara Y, Kubo T, et al. Impaired T- and NK-cell reconstitution after haploidentical HCT with posttransplant cyclophosphamide. Blood Adv. 2021;5:352–64.
Duléry R, Mohty R, Labopin M, Sestili S, Malard F, Brissot E, et al. Early cardiac toxicity associated with post-transplant cyclophosphamide in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021;3:250–9.
Solomon SR, Sizemore CA, Sanacore M, Zhang X, Brown S, Holland HK, et al. Haploidentical transplantation using T cell replete peripheral blood stem cells and myeloablative conditioning in patients with high-risk hematologic malignancies who lack conventional donors is well tolerated and produces excellent relapse-free survival: results of a prospective phase II trial. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:1859–66.
Ruggeri A, Roth-Guepin G, Battipaglia G, Mamez AC, Malard F, Gomez A, et al. Incidence and risk factors for hemorrhagic cystitis in unmanipulated haploidentical transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2015;17:822–30.
Mohty R, Brissot E, Battipaglia G, Ruggeri A, Dulery R, Bonnin A, et al. Infectious complications after post-transplantation cyclophosphamide and anti-thymocyte globulin-based haploidentical stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2019;187:e64–8.
Ishida S, Doki N, Shingai N, Yoshioka K, Kakihana K, Sakamaki H, et al. The clinical features of fatal cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity in a conditioning regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Ann Hematol. 2016;95:1145–50.
Winkelstein A. Mechanisms of immunosuppression: effects of cyclophosphamide on cellular immunity. Blood. 1973;41:273–84.
Mayumi H, Himeno K, Tanaka K, Tokuda N, Fan JL, Nomoto K. Drug-induced tolerance to allografts in mice. IX. Establishment of complete chimerism by allogeneic spleen cell transplantation from donors made tolerant to H-2-identical recipients. Transplantation. 1986;42:417–22.
Colson YL, Wren SM, Schuchert MJ, Patrene KD, Johnson PC, Boggs SS, et al. A nonlethal conditioning approach to achieve durable multilineage mixed chimerism and tolerance across major, minor, and hematopoietic histocompatibility barriers. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950. 1995;155:4179–88.
Wachsmuth LP, Patterson MT, Eckhaus MA, Venzon DJ, Kanakry CG. Optimized timing of post-transplantation cyclophosphamide in MHC-haploidentical murine hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:230–41.
O’Donnell PV, Luznik L, Jones RJ, Vogelsang GB, Leffell MS, Phelps M, et al. Nonmyeloablative bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched related donors using posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8:377–86.
Duléry R, Bastos J, Paviglianiti A, Malard F, Brissot E, Battipaglia G, et al. Thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine conditioning regimen in T cell-replete HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1407–15.
El-Cheikh J, Devillier R, Dulery R, Massoud R, Al Chami F, Ghaoui N, et al. Impact of adding antithymocyte globulin to posttransplantation cyclophosphamide in haploidentical stem-cell transplantation. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20:617–23.
Battipaglia G, Labopin M, Blaise D, Diez-Martin JL, Bazarbachi A, Vitek A, et al. Impact of the addition of antithymocyte globulin to post-transplantation cyclophosphamide in haploidentical transplantation with peripheral blood compared to post-transplantation cyclophosphamide alone in acute myelogenous leukemia: a retrospective study on behalf of the acute leukemia working party of the European society for blood and marrow transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022;28:587.e1–e7.
Devillier R, Galimard JE, Labopin M, Blaise D, Raiola AM, Pavlu J, et al. Reduced intensity versus non-myeloablative conditioning regimen for haploidentical transplantation and post-transplantation cyclophosphamide in complete remission acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57:1421–7.
Duléry R, Brissot E, Mohty M. Combining post-transplant cyclophosphamide with antithymocyte globulin for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in hematological malignancies. Blood Rev. 2023;101080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2023.101080. Epub ahead of print.
Sugita J, Kamimura T, Ishikawa T, Ota S, Eto T, Kuroha T, et al. Reduced dose of posttransplant cyclophosphamide in HLA-haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:596–604.
Duléry R, Goudet C, Mannina D, Bianchessi A, Granata A, Harbi S, et al. Reduced post-transplant cyclophosphamide doses in haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation for elderly patients with hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023;58:386–92.
Memoli M, Paviglianiti A, Malard F, Battipaglia G, Brissot E, Médiavilla C, et al. Thiotepa-busulfan-fludarabine as a conditioning regimen for patients with myelofibrosis undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation: a single center experience. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021;62:419–27.
Peric Z, Mohty R, Bastos J, Brissot E, Battipaglia G, Belhocine R, et al. Thiotepa and antithymocyte globulin-based conditioning prior to haploidentical transplantation with posttransplant cyclophosphamide in high-risk hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:763–72.
Paccoud O, Guitard J, Labopin M, Surgers L, Malard F, Battipaglia G, et al. Features of Toxoplasma gondii reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in a high seroprevalence setting. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:93–9.
Kanate AS, Nagler A, Savani B. Summary of scientific and statistical methods, study endpoints and definitions for observational and registry-based studies in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin Hematol Int. 2019;2:2–4.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106:2912–9.
Armand P, Kim HT, Logan BR, Wang Z, Alyea EP, Kalaycio ME, et al. Validation and refinement of the Disease Risk Index for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2014;123:3664–71.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, Williams KM, Wolff D, Cowen EW, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:389–401.e1.
Kitko CL, Pidala J, Schoemans HM, Lawitschka A, Flowers ME, Cowen EW, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: IIa. The 2020 clinical implementation and early diagnosis working group report. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27:545–57.
Holtan SG, DeFor TE, Lazaryan A, Bejanyan N, Arora M, Brunstein CG, et al. Composite end point of graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2015;125:1333–8.
Braverman AC, Antin JH, Plappert MT, Cook EF, Lee RT. Cyclophosphamide cardiotoxicity in bone marrow transplantation: a prospective evaluation of new dosing regimens. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:1215–23.
Fujimaki K, Maruta A, Yoshida M, Sakai R, Tanabe J, Koharazawa H, et al. Severe cardiac toxicity in hematological stem cell transplantation: predictive value of reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;27:307–10.
Offner F, Schoch G, Fisher LD, Torok-Storb B, Martin PJ. Mortality hazard functions as related to neutropenia at different times after marrow transplantation. Blood. 1996;88:4058–62.
Jones RJ, Barber JP, Vala MS, Collector MI, Kaufmann SH, Ludeman SM, et al. Assessment of aldehyde dehydrogenase in viable cells. Blood. 1995;85:2742–6.
Kaphan E, Germi R, Bailly S, Bulabois CE, Carré M, Cahn JY, et al. Risk factors of BK viral hemorrhagic cystitis in allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021;23:e13601.
Dequirez PL, Magro L, Alsuliman T, Ceballos P, Desbrosses Y, Yakoub-Agha I, et al. La cystite hémorragique après allogreffe de cellules souches hématopoïétiques: prophylaxie, diagnostic, et traitement. Bull Cancer (Paris) [Internet]. 2022; Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0007455122000406
Cesaro S, Dalianis T, Hanssen Rinaldo C, Koskenvuo M, Pegoraro A, Einsele H, et al. ECIL guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of BK polyomavirus-associated haemorrhagic cystitis in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73:12–21.
Kasamon YL, Bolaños-Meade J, Prince GT, Tsai HL, McCurdy SR, Kanakry JA, et al. Outcomes of nonmyeloablative HLA-haploidentical blood or marrow transplantation with high-dose post-transplantation cyclophosphamide in older adults. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3152–61.
Santoro N, Labopin M, Giannotti F, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, Brecht A, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical in comparison with matched unrelated donor stem cell transplantation in patients 60 years and older with acute myeloid leukemia: a comparative study on behalf of the ALWP of the EBMT. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:55.
Bashey ZA, Zhang X, Brown S, Jackson K, Morris LE, Holland HK, et al. Comparison of outcomes following transplantation with T-replete HLA-haploidentical donors using post-transplant cyclophosphamide to matched related and unrelated donors for patients with AML and MDS aged 60 years or older. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53:756–63.
Devillier R, Legrand F, Rey J, Castagna L, Fürst S, Granata A, et al. HLA-matched sibling versus unrelated versus haploidentical related donor allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients aged over 60 years with acute myeloid leukemia: a single-center donor comparison. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:1449–54.
Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Bacigalupo A, Gülbas Z, Koc Y, Blaise D, et al. Bone marrow versus mobilized peripheral blood stem cells in haploidentical transplants using posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Cancer. 2018;124:1428–37.
O’Donnell PV, Eapen M, Horowitz MM, Logan BR, DiGilio A, Brunstein C, et al. Comparable outcomes with marrow or peripheral blood as stem cell sources for hematopoietic cell transplantation from haploidentical donors after non-ablative conditioning: a matched-pair analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:1599–601.
Bashey A, Zhang MJ, McCurdy SR, St Martin A, Argall T, Anasetti C, et al. Mobilized peripheral blood stem cells versus unstimulated bone marrow as a graft source for T-cell-replete haploidentical donor transplantation using post-transplant cyclophosphamide. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3002–9.
Mehta RS, Saliba RM, Alsfeld LC, Jorgensen JL, Wang SA, Anderlini P, et al. Bone marrow versus peripheral blood grafts for haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27:1003.e1–e13.
Mariotti J, Devillier R, Bramanti S, Giordano L, Sarina B, Furst S, et al. Peripheral blood stem cells versus bone marrow for T cell-replete haploidentical transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide in Hodgkin lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1810–7.
Nagler A, Dholaria B, Labopin M, Savani BN, Angelucci E, Koc Y, et al. Bone marrow versus mobilized peripheral blood stem cell graft in T-cell-replete haploidentical transplantation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2020;34:2766–75.
Nagler A, Labopin M, Dholaria B, Angelucci E, Afanasyev B, Cornelissen JJ, et al. Comparison of haploidentical bone marrow versus matched unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with posttransplant cyclophosphamide in patients with acute leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:843–51.
Im A, Rashidi A, Wang T, Hemmer M, MacMillan ML, Pidala J, et al. Risk factors for graft-versus-host disease in haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation using post-transplant cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:1459–68.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the clinicians, the nursing staff, and all the supportive care team for providing excellent care for our patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RD designed the study, recruited patients, collected, assembled, and analyzed data, performed the statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. MM designed the study, supervised research, analyzed data, and commented on the manuscript. SE, AC, and EC helped design the study, performed cardiac evaluations of the patients, analyzed data, and commented on the manuscript. ML analyzed data, performed the statistical analysis, and commented on the manuscript. AB and TL contributed to patient care and commented on the manuscript. FM, EB, AB, SS, RB, MC, ZVW, and OL recruited patients and commented on the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved its submission for publication purposes.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duléry, R., Malard, F., Brissot, E. et al. Reduced post-transplant cyclophosphamide dose with antithymocyte globulin in peripheral blood stem cell haploidentical transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 58, 1215–1222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02085-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02085-2
This article is cited by
-
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide at 80 mg/kg with low dose post-engraftment anti-thymocyte globulin in haploidentical transplantation with myeloablative conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Dual T cell depletion for graft versus host disease prevention in peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with hematological malignancies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
ATG or post-transplant cyclophosphamide to prevent GVHD in matched unrelated stem cell transplantation?
Leukemia (2024)