Abstract
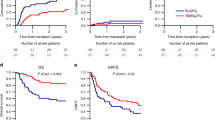
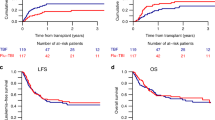
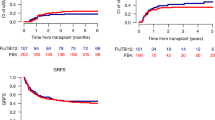
For acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients, total body irradiation (TBI)- based conditioning regimens are the first choice specially in young population. However, several studies have shown an equivalence in clinical outcomes with thiotepa-based conditioning regimen. We performed a retrospective study to evaluate the outcome of adult ALL patients who received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HCT) with a thiotepa-busulfan-fludarabine (TBF) myeloablative conditioning regimen with reduced toxicity. Fifty-five patients received a TBF regimen. The median age of the patients was 51 years (range, 17 to 72.4). Most patients had a diagnosis of B-ALL (93%) with 7% having T-ALL. Two - and 5-year overall survival was 73.2% and 64%, respectively. At 2 years, leukemia-free survival and GVHD-free, relapse-free survival were 59.5% and 57.6%, and at 5 years, 53.4% and 51.8%, respectively. The 5-year non-relapse mortality was 15%. The day 180 cumulative incidence (CI) of grade II–IV acute GVHD and grade III–IV acute GVHD were 38.2% and 5.5%, respectively. At 2 years, the CI of chronic GVHD and extensive chronic GVHD was 16.9% and 1.9%, respectively. Our study results do suggest that using TBF as the conditioning regimen in adult ALL patients is a promising option with acceptable toxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, AB, upon reasonable request.
References
Thomas X, Boiron JM, Huguet F, Dombret H, Bradstock K, Vey N, et al. Outcome of treatment in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of the LALA-94 trial. J Clin Oncol J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4075–86.
Hunault M, Harousseau JL, Delain M, Truchan-Graczyk M, Cahn JY, Witz F, et al. Better outcome of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia after early genoidentical allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) than after late high-dose therapy and autologous BMT: a GOELAMS trial. Blood. 2004;104:3028–37.
Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood. 2008;111:1827–33.
Giebel S, Labopin M, Socié G, Beelen D, Browne P, Volin L, et al. Improving results of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: an analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica. 2017;102:139–49.
Marks DI, Forman SJ, Blume KG, Pérez WS, Weisdorf DJ, Keating A, et al. A comparison of cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation with etoposide and total body irradiation as conditioning regimens for patients undergoing sibling allografting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first or second complete remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transpl. 2006;12:438–53.
Davies SM, Ramsay NK, Klein JP, Weisdorf DJ, Bolwell B, Cahn JY, et al. Comparison of preparative regimens in transplants for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2000;18:340–7.
Eroglu C, Pala C, Kaynar L, Yaray K, Aksozen MT, Bankir M, et al. Comparison of total body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimens in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:2474–9.
Cahu X, Labopin M, Giebel S, Aljurf M, Kyrcz-Krzemien S, Socié G, et al. Impact of conditioning with TBI in adult patients with T-cell ALL who receive a myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a report from the acute leukemia working party of EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:351–7.
Peters C, Dalle JH, Locatelli F, Poetschger U, Sedlacek P, Buechner J, et al. Total body irradiation or chemotherapy conditioning in childhood ALL: a multinational, randomized, noninferiority phase III study. J Clin Oncol J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2021;39:295–307.
Eder S, Canaani J, Beohou E, Labopin M, Sanz J, Arcese W, et al. Thiotepa-based conditioning versus total body irradiation as myeloablative conditioning prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A matched-pair analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2017;92:997–1003.
Swoboda R, Labopin M, Giebel S, Angelucci E, Arat M, Aljurf M, et al. Total body irradiation plus fludarabine versus thiotepa, busulfan plus fludarabine as a myeloablative conditioning for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation. A study by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57:399–406.
Baker KS, Leisenring WM, Goodman PJ, Ermoian RP, Flowers ME, Schoch G, et al. Total body irradiation dose and risk of subsequent neoplasms following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2019;133:2790–9.
Aristei C, Alessandro M, Santucci A, Aversa F, Tabillo A, Carotti A, et al. Cataracts in patients receiving stem cell transplantation after conditioning with total body irradiation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;29:503–7.
Savani BN, Montero A, Wu C, Nlonda N, Read E, Dunbar C, et al. Prediction and prevention of transplant-related mortality from pulmonary causes after total body irradiation and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:223–30.
Borras JM, Lievens Y, Barton M, Corral J, Ferlay J, Bray F, et al. How many new cancer patients in Europe will require radiotherapy by 2025? An ESTRO-HERO analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2016;119:5–11.
Paix A, Antoni D, Waissi W, Ledoux MP, Bilger K, Fornecker L, et al. Total body irradiation in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation conditioning regimens: a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018;123:138–48.
Wong JYC, Filippi AR, Scorsetti M, Hui S, Muren LP, Mancosu P. Total marrow and total lymphoid irradiation in bone marrow transplantation for acute leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:e477–87.
Friedman DL, Rovo A, Leisenring W, Locasciulli A, Flowers MED, Tichelli A, et al. Increased risk of breast cancer among survivors of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the FHCRC and the EBMT-Late Effect Working Party. Blood. 2008;111:939–44.
Marks DI, Wang T, Pérez WS, Antin JH, Copelan E, Gale RP, et al. The outcome of full-intensity and reduced-intensity conditioning matched sibling or unrelated donor transplantation in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first and second complete remission. Blood. 2010;116:366–74.
Tanaka J, Kanamori H, Nishiwaki S, Ohashi K, Taniguchi S, Eto T, et al. Reduced-intensity vs myeloablative conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for patients aged over 45 years with ALL in remission: a study from the Adult ALL Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:1389–94.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, Gratwohl A, Socié G, Esteve J, et al. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2010;116:4439–43.
Mitsuhashi K, Kako S, Shigematsu A, Atsuta Y, Doki N, Fukuda T, et al. Comparison of cyclophosphamide combined with total body irradiation, oral Busulfan, or intravenous Busulfan for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:2194–200.
Kebriaei P, Anasetti C, Zhang MJ, Wang HL, Aldoss I, de Lima M, et al. Intravenous Busulfan compared with total body irradiation pretransplant conditioning for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018;24:726–33.
Patel B, Kirkwood AA, Dey A, Marks DI, McMillan AK, Menne TF, et al. Pegylated-asparaginase during induction therapy for adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: toxicity data from the UKALL14 trial. Leukemia. 2017;31:58–64.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980;69:204–17.
Socié G, Schmoor C, Bethge WA, Ottinger HD, Stelljes M, Zander AR, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease: long-term results from a randomized trial on graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with or without anti-T-cell globulin ATG-Fresenius. Blood. 2011;117:6375–82.
Speziali C, Daly A, Abuhaleeqa M, Nitta J, Abou Mourad Y, Seftel MD, et al. Fludarabine, busulfan, and low-dose TBI conditioning versus cyclophosphamide and TBI in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019;60:639–48.
Peric Z, Labopin M, Peczynski C, Polge E, Cornelissen J, Carpenter B, et al. Comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia >45 years undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation-a retrospective study by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:1560–9.
Czyz A, Labopin M, Giebel S, Socié G, Apperley J, Volin L, et al. Cyclophosphamide versus etoposide in combination with total body irradiation as conditioning regimen for adult patients with Ph-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplant: On behalf of the ALWP of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:778–85.
Greil C, Engelhardt M, Ihorst G, Duque-Afonso J, Shoumariyeh K, Bertz H, et al. Prognostic factors for survival after allogeneic transplantation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:841–52.
Gooley TA, Chien JW, Pergam SA, Hingorani S, Sorror ML, Boeckh M, et al. Reduced mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N. Engl J Med. 2010;363:2091–101.
Flowers MED, Inamoto Y, Carpenter PA, Lee SJ, Kiem HP, Petersdorf EW, et al. Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Blood. 2011;117:3214–9.
Jagasia M, Arora M, Flowers MED, Chao NJ, McCarthy PL, Cutler CS, et al. Risk factors for acute GVHD and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;119:296–307.
Tsirigotis PD, Resnick IB, Avni B, Grisariu S, Stepensky P, Or R, et al. Incidence and risk factors for moderate-to-severe veno-occlusive disease of the liver after allogeneic stem cell transplantation using a reduced intensity conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:1389–92.
Pavlů J, Labopin M, Zoellner AK, Sakellari I, Stelljes M, Finke J, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for primary refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Cancer. 2017;123:1965–70.
Campana D. Minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Semin Hematol. 2009;46:100–6.
Gökbuget N, Kneba M, Raff T, Trautmann H, Bartram CR, Arnold R, et al. Adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and molecular failure display a poor prognosis and are candidates for stem cell transplantation and targeted therapies. Blood. 2012;120:1868–76.
Bourlon C, Lacayo-Leñero D, Inclán-Alarcón SI, Demichelis-Gómez R. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the first complete remission in the era of minimal residual disease. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018;20:36.
Bazarbachi AH, Al Hamed R, Labopin M, Afanasyev B, Hamladji RM, Beelen D, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with sequential conditioning in adult patients with refractory or relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the EBMT Acute Leukemia Working Party. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:595–602.
de Labarthe A, Rousselot P, Huguet-Rigal F, Delabesse E, Witz F, Maury S, et al. Imatinib combined with induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the GRAAPH-2003 study. Blood. 2007;109:1408–13.
Brissot E, Labopin M, Beckers MM, Socié G, Rambaldi A, Volin L, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors improve long-term outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2015;100:392–9.
Pfeifer H, Wassmann B, Bethge W, Dengler J, Bornhäuser M, Stadler M, et al. Randomized comparison of prophylactic and minimal residual disease-triggered imatinib after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for BCR-ABL1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1254–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB and EB designed the study; ML performed the statistical analyses; AB wrote the manuscript; EB, AA and MM revised the manuscript, and all authors reviewed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Banet, A., Bazarbachi, A., Labopin, M. et al. Thiotepa, busulfan and fludarabine conditioning-regimen is a promising approach for older adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 58, 61–67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01841-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01841-0