Abstract
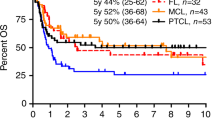
We performed a retrospective multicenter study including 140 patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) from March 1995 to November 2018. Our objective was to analyze long term outcomes. Seventy-four percent had received a previous auto-SCT (ASCT) and the median number of lines pre-allo-SCT was 3 (range 1–9). Three year-event free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were 38% and 44%, respectively. Non-relapse mortality (NRM) at day 100 was 19%. Cumulative incidence of grade III–IV acute graft versus host disease (GVHD) at day 100 was 16% and moderate/severe chronic GVHD at 3 years 34%. Active disease at allo-SCT (HR 1.95, p = 0.039) (HR 2.19, p = 0.019), HCT-CI ≥ 2 (2.45, p = 0.002) (HR 2.33, p = 0.006) and donor age >37 years (HR 2.75, p = 0.014) (HR 1.98, p = 0.043) were the only independent variables both for PFS and OS, respectively. NRM was significantly modified by HCT-CI ≥ 2 (HR 4.8, p = 0.008), previous ASCT (HR 4.4, p = 0.048) and grade III–IV acute GVHD on day 100 (HR 6.13, p = 0.016). Our data confirmed that allo-SCT is a curative option for patients with R/R DLBCL, displaying adequate results for fit patients with chemosensitive disease receiving an allo-SCT from a young donor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van der Lelie H, Bron D, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1540–5.
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130:1800–8.
van Kampen RJW, Canals C, Schouten HC, Nagler A, Thomson KJ, Vernant J-P, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation as salvage therapy for patients with diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma relapsing after an autologous stem-cell transplantation: an analysis of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1342–8.
Bacher U, Klyuchnikov E, Le-Rademacher J, Carreras J, Armand P, Bishop MR, et al. Conditioning regimens for allotransplants for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: myeloablative or reduced intensity? Blood. 2012;120:4256–62.
Fenske TS, Ahn KW, Graff TM, DiGilio A, Bashir Q, Kamble RT, et al. Allogeneic transplantation provides durable remission in a subset of DLBCL patients relapsing after autologous transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2016;174:235–48.
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45–56.
Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531–44.
Dreger P, Fenske TS, Montoto S, Pasquini MC, Sureda A, Hamadani M et al. Cellular Immunotherapy for Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma in the Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered T Cell Era: Still a Role for Allogeneic Transplantation? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.12.771.
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:579–86.
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059–68.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:1628–33.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation. 1974;18:295–304.
Harris AC, Young R, Devine S, Hogan WJ, Ayuk F, Bunworasate U, et al. International, Multicenter Standardization of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease Clinical Data Collection: A Report from the Mount Sinai Acute GVHD International Consortium. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:4–10.
Terwey TH, Vega-Ruiz A, Hemmati PG, Martus P, Dietz E, le Coutre P, et al. NIH-defined graft-versus-host disease after reduced intensity or myeloablative conditioning in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:536–42.
Sorror ML, Logan BR, Zhu X, Rizzo JD, Cooke KR, McCarthy PL, et al. Prospective Validation of the Predictive Power of the Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index: a Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research Study. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015;21:1479–87.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106:2912–9.
Armand P, Gibson CJ, Cutler C, Ho VT, Koreth J, Alyea EP, et al. A disease risk index for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120:905–13.
Holtan SG, DeFor TE, Lazaryan A, Bejanyan N, Arora M, Brunstein CG, et al. Composite end point of graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2015;125:1333–8.
Hamadani M, Saber W, Ahn KW, Carreras J, Cairo MS, Fenske TS, et al. Impact of Pretransplantation Conditioning Regimens on Outcomes of Allogeneic Transplantation for Chemotherapy-Unresponsive Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma and Grade III Follicular Lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:746–53.
Glass B, Hasenkamp J, Wulf G, Dreger P, Pfreundschuh M, Gramatzki M, et al. Rituximab after lymphoma-directed conditioning and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DSHNHL R3): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:757–66.
Avivi I, Canals C, Vernant J-P, Wulf G, Nagler A, Hermine O, et al. Matched unrelated donor allogeneic transplantation provides comparable long-term outcome to HLA-identical sibling transplantation in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014;49:671–8.
Dreger P, Sureda A, Ahn KW, Eapen M, Litovich C, Finel H, et al. PTCy-based haploidentical vs matched related or unrelated donor reduced-intensity conditioning transplant for DLBCL. Blood Adv. 2019;3:360–9.
Ulaner GA, Goldman DA, Sauter CS, Migliacci J, Lilienstein J, Gönen M, et al. Prognostic Value of FDG PET/CT before Allogeneic and Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for Aggressive Lymphoma. Radiology. 2015;277:518–26.
van Kampen RJW, Canals C, Schouten HC, Nagler A, Thomson KJ, Vernant J-P, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation as salvage therapy for patients with diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma relapsing after an autologous stem-cell transplantation: an analysis of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1342–8.
Rigacci L, Puccini B, Dodero A, Iacopino P, Castagna L, Bramanti S, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma relapsed after autologous stem cell transplantation: a GITMO study. Ann Hematol. 2012;91:931–9.
Fenske TS, Hamadani M, Cohen JB, Costa LJ, Kahl BS, Evens AM, et al. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation as Curative Therapy for Patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: increasingly Successful Application to Older Patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:1543–51.
Robinson SP, Goldstone AH, Mackinnon S, Carella A, Russell N, de Elvira CR, et al. Chemoresistant or aggressive lymphoma predicts for a poor outcome following reduced-intensity allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation: an analysis from the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2002;100:4310–6.
Farina L, Bruno B, Patriarca F, Spina F, Sorasio R, Morelli M, et al. The hematopoietic cell transplantation comorbidity index (HCT-CI) predicts clinical outcomes in lymphoma and myeloma patients after reduced-intensity or non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2009;23:1131–8.
Pollack SM, Steinberg SM, Odom J, Dean RM, Fowler DH, Bishop MR. Assessment of the hematopoietic cell transplantation comorbidity index in non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients receiving reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:223–30.
Kollman C, Spellman SR, Zhang M-J, Hassebroek A, Anasetti C, Antin JH, et al. The effect of donor characteristics on survival after unrelated donor transplantation for hematologic malignancy. Blood. 2016;127:260–7.
Karam E, Laporte J, Solomon SR, Morris LE, Zhang X, Holland HK, et al. Who Is a Better Donor for Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Young HLA-Mismatched Haploidentical Relative or an Older Fully HLA-Matched Sibling or Unrelated Donor? Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:2054–60.
Visram A, Aziz J, Bryant A, Zhang T, Cieniak C, Hamelin L, et al. Effect of Donor Age and Donor Relatedness on Time to Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Acute Leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018;24:2466–70.
Jain T, Bar M, Kansagra AJ, Chong EA, Hashmi SK, Neelapu SS, et al. Use of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Clinical Practice for Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: an Expert Panel Opinion from the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:2305–21.
Sehn LH, Herrera AF, Flowers CR, Kamdar MK, McMillan A, Hertzberg M, et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:155–65.
Goebeler M-E, Knop S, Viardot A, Kufer P, Topp MS, Einsele H, et al. Bispecific T-Cell Engager (BiTE) Antibody Construct Blinatumomab for the Treatment of Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results From a Phase I Study. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:1104–11.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ángel Cedillo for his contribution in obtaining the clinical data of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
LB and DC performed the research. LB, AG, SN, JM, JLP, LLC, MC, GG, MO, MB, ND, AP, RH, CF, ISO, IGC, PH, NR, GR, CM, LY, JZ, MRV, TZ, OLG, IH, IEM, CM, AS, JAPS, CS, AS, JS, AC and DC contributed to clinical data. LB, AG and DC contributed to the analysis and data interpretation. Statistical analysis was performed by AG. All authors contributed to review, provided their comments on this paper and approval the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bento, L., Gutiérrez, A., Novelli, S. et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation as a curative option in relapse/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Spanish multicenter GETH/GELTAMO study. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 1919–1928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01264-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01264-3
This article is cited by
-
Hypofractionated radiotherapy for refractory or relapsed aggressive B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era
BMC Cancer (2024)
-
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation and CAR-T in B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: a two-center experience and review of the literature
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation after bispecific antibodies in non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
The salvage role of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Evolving Role in the Era of CAR T-Cell Therapy
Current Oncology Reports (2023)