Abstract
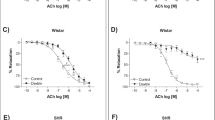
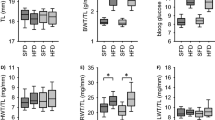
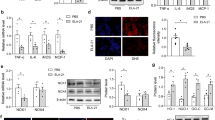
The matrix glycoprotein thrombospondin-1 (THBS1) modulates nitric oxide (NO) signaling in endothelial cells. A high-salt diet induces deficiencies of NO production and bioavailability, thereby leading to endothelial dysfunction. In this study we investigated the changes of THBS1 expression and its pathological role in the dysfunction of mesenteric artery endothelial cells (MAECs) induced by a high-salt diet. Wild-type rats, and wild-type and Thbs1−/− mice were fed chow containing 8% w/w NaCl for 4 weeks. We showed that a high salt diet significantly increased THBS1 expression and secretion in plasma and MAECs, and damaged endothelium-dependent vasodilation of mesenteric resistance arteries in wild-type animals, but not in Thbs1−/− mice. In rat MAECs, we demonstrated that a high salt environment (10–40 mM) dose-dependently increased THBS1 expression accompanied by suppressed endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and phospho-eNOS S1177 production as well as NO release. Blockade of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) activity by a TGF-β1 inhibitor SB 431542 reversed THBS1 up-regulation, rescued the eNOS decrease, enhanced phospho-eNOS S1177 expression, and inhibited Smad4 translocation to the nucleus. By conducting dual-luciferase reporter experiments in HEK293T cells, we demonstrated that Smad4, a transcription promoter, upregulated Thbs1 transcription. We conclude that THBS1 contributes to endothelial dysfunction in a high-salt environment and may be a potential target for treatment of high-salt-induced endothelium dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pilic L, Pedlar CR, Mavrommatis Y. Salt-sensitive hypertension: mechanisms and effects of dietary and other lifestyle factors. Nutr Rev. 2016;74:645–58.
Rust P, Ekmekcioglu C. Impact of salt intake on the pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:61–84.
Feng W, Dell’Italia LJ, Sanders PW. Novel paradigms of salt and hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:1362–9.
Kozina N, Mihaljevic Z, Loncar MB, Mihalj M, Misir M, Radmilovic MD, et al. Impact of high salt diet on cerebral vascular function and stroke in Tff3-/-/C57BL/6N knockout and WT (C57BL/6N) control mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1–25.
Cosic A, Jukic I, Stupin A, Mihalj M, Mihaljevic Z, Novak S, et al. Attenuated flow-induced dilatation of middle cerebral arteries is related to increased vascular oxidative stress in rats on a short-term high salt diet. J Physiol. 2016;594:4917–31.
Raffai G, Durand MJ, Lombard JH. Acute and chronic angiotensin-(1-7) restores vasodilation and reduces oxidative stress in mesenteric arteries of salt-fed rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301:H1341–1352.
Rogers NM, Sharifi-Sanjani M, Yao M, Ghimire K, Bienes-Martinez R, Mutchler SM, et al. TSP1-CD47 signaling is upregulated in clinical pulmonary hypertension and contributes to pulmonary arterial vasculopathy and dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113:15–29.
Shimoda LA, Kuebler WM. ‘Hypoxio-spondin’: thrombospondin and its emerging role in pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;109:1–3.
Buda V, Andor M, Cristescu C, Tomescu MC, Muntean DM, Baibata DE, et al. Thrombospondin-1 serum levels in hypertensive patients with endothelial dysfunction after one year of treatment with perindopril. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3515–26.
Matsuo Y, Tanaka M, Yamakage H, Sasaki Y, Muranaka K, Hata H, et al. Thrombospondin 1 as a novel biological marker of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 2015;64:1490–9.
Rogers NM, Ghimire K, Calzada MJ, Isenberg JS. Matricellular protein thrombospondin-1 in pulmonary hypertension: multiple pathways to disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113:858–68.
Motegi K, Harada K, Ohe G, Jones SJ, Ellis IR, Crouch DH, et al. Differential involvement of TGF-beta1 in mediating the motogenic effects of TSP-1 on endothelial cells, fibroblasts and oral tumour cells. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314:2323–33.
Yafai Y, Eichler W, Iandiev I, Unterlauft JD, Jochmann C, Wiedemann P, et al. Thrombospondin-1 is produced by retinal glial cells and inhibits the growth of vascular endothelial cells. Ophthalmic Res. 2014;52:81–88.
Zak S, Treven J, Nash N, Gutierrez LS. Lack of thrombospondin-1 increases angiogenesis in a model of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008;23:297–304.
Venkatraman L, Tucker-Kellogg L. The CD47-binding peptide of thrombospondin-1 induces defenestration of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Liver Int. 2013;33:1386–97.
Bauer EM, Qin Y, Miller TW, Bandle RW, Csanyi G, Pagano PJ, et al. Thrombospondin-1 supports blood pressure by limiting eNOS activation and endothelial-dependent vasorelaxation. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;88:471–81.
Kim J, Lee KS, Kim JH, Lee DK, Park M, Choi S, et al. Aspirin prevents TNF-α-induced endothelial cell dysfunction by regulating the NF-κB-dependent miR-155/eNOS pathway: Role of a miR-155/eNOS axis in preeclampsia. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;104:185–98.
Sessa WC. eNOS at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2427–9.
Feletou M, Kohler R, Vanhoutte PM. Nitric oxide: orchestrator of endothelium-dependent responses. Ann Med. 2012;44:694–716.
Qian J, Fulton D. Post-translational regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelium. Front Physiol. 2013;4:1–11.
Chen Z, S DSO, Zimnicka AM, Jiang Y, Sharma T, Chen S, et al. Reciprocal regulation of eNOS and caveolin-1 functions in endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2018;29:1190–202.
Qin Y, Dong T, Jiang W, Ding W, Zhan T, Du J, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomics reveals serum protein changes in hypertensive rats induced by a high-salt diet. EXCLI J. 2020;19:1496–511.
Jiang W, Ye L, Yang Y, Wang P, Pan W, Du J, et al. TRPP2 associates with STIM1 to regulate cerebral vasoconstriction and enhance high salt intake-induced hypertensive cerebrovascular spasm. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1894–904.
Guo J, Zhao R, Zhou M, Li J, Yao X, Du J, et al. TRPP2 and STIM1 form a microdomain to regulate store-operated Ca2+ entry and blood vessel tone. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18:1–16.
Shen B, Cheng KT, Leung YK, Kwok YC, Kwan HY, Wong CO, et al. Epinephrine-induced Ca2+ influx in vascular endothelial cells is mediated by CNGA2 channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;45:437–45.
Suh SH, Vennekens R, Manolopoulos VG, Freichel M, Schweig U, Prenen J, et al. Characterisation of explanted endothelial cells from mouse aorta: electrophysiology and Ca2+ signalling. Pflug Arch. 1999;438:612–20.
Xin C, Ren S, Eberhardt W, Pfeilschifter J, Huwiler A. The immunomodulator FTY720 and its phosphorylated derivative activate the Smad signalling cascade and upregulate connective tissue growth factor and collagen type IV expression in renal mesangial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147:164–74.
Li W, Yong J, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ren H, et al. Glutathione depletion and dual-model oxygen balance disruption for photodynamic therapy enhancement. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2019;183:1–10.
Lee WK, Choi JK, Cha SH. Co-localization and interaction of human organic anion transporter 4 with caveolin-1 in primary cultured human placental trophoblasts. Exp Mol Med. 2008;40:505–13.
Tang EH, Feletou M, Huang Y, Man RY, Vanhoutte PM. Acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside cause long-term inhibition of EDCF-mediated contractions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H2434–2440.
Castiglione RC, Barros C, Boa BCS, De Souza M, Bouskela E. Effects of selenium in the microcirculation of fructose-fed hamsters. J Vasc Res. 2018;55:203–9.
Daubon T, Leon C, Clarke K, Andrique L, Salabert L, Darbo E, et al. Deciphering the complex role of thrombospondin-1 in glioblastoma development. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1–15.
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, ten Dijke P, Huet S, Gauthier JM. Direct binding of Smad3 and Smad4 to critical TGF β-inducible elements in the promoter of human plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 gene. EMBO J. 1998;17:3091–100.
Takekawa M, Tatebayashi K, Itoh F, Adachi M, Imai K, Saito H. Smad-dependent GADD45β expression mediates delayed activation of p38 MAP kinase by TGF-β. EMBO J. 2002;21:6473–82.
von Toerne C, Huth C, de Las Heras Gala T, Kronenberg F, Herder C, Koenig W, et al. MASP1, THBS1, GPLD1 and ApoA-IV are novel biomarkers associated with prediabetes: the KORA F4 study. Diabetologia. 2016;59:1882–92.
Kong P, Gonzalez-Quesada C, Li N, Cavalera M, Lee DW, Frangogiannis NG. Thrombospondin-1 regulates adiposity and metabolic dysfunction in diet-induced obesity enhancing adipose inflammation and stimulating adipocyte proliferation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013;305:E439–450.
Olerud J, Mokhtari D, Johansson M, Christoffersson G, Lawler J, Welsh N, et al. Thrombospondin-1: an islet endothelial cell signal of importance for β-cell function. Diabetes. 2011;60:1946–54.
Kong P, Cavalera M, Frangogiannis NG. The role of thrombospondin (TSP)-1 in obesity and diabetes. Adipocyte. 2014;3:81–84.
Nurkiewicz TR, Boegehold MA. High salt intake reduces endothelium-dependent dilation of mouse arterioles via superoxide anion generated from nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R1550–1556.
Maruhashi T, Kihara Y, Higashi Y. Assessment of endothelium-independent vasodilation: from methodology to clinical perspectives. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1460–7.
Yamamoto E, Kataoka K, Shintaku H, Yamashita T, Tokutomi Y, Dong YF, et al. Novel mechanism and role of angiotensin II induced vascular endothelial injury in hypertensive diastolic heart failure. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:2569–75.
Adejare A, Oloyo A, Anigbogu C, Jaja S. L-arginine supplementation increased only endothelium-dependent relaxation in Sprague-Dawley rats fed a high-salt diet by enhancing abdominal aorta endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene expression. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2020;14:1–9.
Bazzazi H, Zhang Y, Jafarnejad M, Isenberg JS, Annex BH, Popel AS. Computer simulation of TSP1 inhibition of VEGF-Akt-eNOS: an angiogenesis triple threat. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1–14.
Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Volpert OV, Bouck NP, Sipos B, Hahn SA, Klein-Scory S, et al. Smad4/DPC4-mediated tumor suppression through suppression of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:9624–9.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to Yun-xia Lu, Ph.D (and the technicians), in the Comprehensive Experiment Center of Basic Medical Sciences, Anhui Medical University, for the support of these facilities, and the Center for Scientific Research of Anhui Medical University for valuable assistance with this study. The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Regional Innovation and Development Joint Fund (grant No. U22A20272), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 82204381), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (grant No. 2108085MH260 and 2208085QH277), Anhui Province Key Research and Development Project (grant No. 201904a07020032), and Applied Medicine Research Project of Hefei Municipal Health Commission (grant No. 2019-172-2-15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FFX, FZ, CBZ and BS conceived and designed the study. FFX, FZ, YC and YW conducted major experiments and analyzed the data. SBM, WD, YC, LSZ and JZG performed primary cell culture, transfection and confocal experiments. BS drafted the manuscript. BS, YW and CBZ supervised the whole study and wrote the manuscript. All authors edited the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Ff., Zheng, F., Chen, Y. et al. Role of thrombospondin-1 in high-salt–induced mesenteric artery endothelial impairment in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 45, 545–557 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01181-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01181-9