Abstract
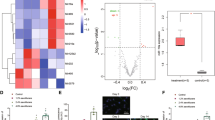
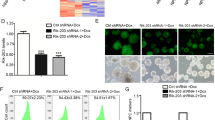
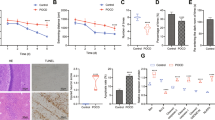
Sevoflurane exposure during rapid brain development induces neuronal apoptosis and causes memory and cognitive deficits in neonatal mice. Exosomes that transfer genetic materials including long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) between cells play a critical role in intercellular communication. However, the lncRNAs found in exosomes derived from neurons treated with sevoflurane and their potential role in promoting neurotoxicity remain unknown. In this study, we investigated the role of cross-talk of newborn mouse neurons with microglial cells in sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. Mouse hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells were exposed to sevoflurane, and then co-cultured with BV2 microglial cells. We showed that sevoflurane treatment markedly increased the expression of the lncRNA growth arrest-specific 5 (Gas5) in neuron-derived extracellular vesicles, which inhibited neuronal proliferation and induced neuronal apoptosis by promoting M1 polarization of microglia and the release of inflammatory cytokines. We further revealed that the exosomal lncRNA Gas5 significantly upregulated Foxo3 as a competitive endogenous RNA of miR-212-3p in BV2 cells, and activated the NF-κB pathway to promote M1 microglial polarization and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, thereby exacerbating neuronal damage. In neonatal mice, intracranial injection of the exosomes derived from sevoflurane-treated neurons into the bilateral hippocampi significantly increased the proportion of M1 microglia, inhibited neuronal proliferation and promoted apoptosis, ultimately leading to neurotoxicity. Similar results were observed in vitro in BV2 cells treated with the CM from HT22 cells after sevoflurane exposure. We conclude that sevoflurane induces the transfer of lncRNA Gas5-containing exosomes from neurons, which in turn regulates the M1 polarization of microglia and contributes to neurotoxicity. Thus, modulating the expression of lncRNA Gas5 or the secretion of exosomes could be a strategy for addressing sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin EP, Lee J-R, Lee CS, Deng M, Loepke AW. Do anesthetics harm the developing human brain? An integrative analysis of animal and human studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017;60:117–28.
Vutskits L, Davidson A. Update on developmental anesthesia neurotoxicity. Curr Opin Anesthesiol. 2017;30:337–42.
Walters JL, Paule MG. Review of preclinical studies on pediatric general anesthesia-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017;60:2–23.
Xu L, Xu Q, Xu F, Zhang W, Chen Q, Wu H, et al. MicroRNA-325-3p prevents sevoflurane-induced learning and memory impairment by inhibiting Nupr1 and C/EBPβ/IGFBP5 signaling in rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:5209.
Xu L, Xu Q, Dai S, Jiao C, Tang Y, Xie J, et al. lncRNA Xist regulates sevoflurane-induced social and emotional impairment by modulating miR-98-5p/EDEM1 signaling axis in neonatal mice. Mol Ther-Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:939–50.
Bell JD, Stary CM. Anesthetic neurotoxicity: an emerging role for glia in neuroprotection. J Mol Med. 2017;95:349–51.
Baud O, Saint-Faust M. Neuroinflammation in the developing brain: risk factors, involvement of microglial cells, and implication for early anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2019;128:718–25.
Tay TL, Savage JC, Hui CW, Bisht K, Tremblay MÈ. Microglia across the lifespan: from origin to function in brain development, plasticity and cognition. J Physiol. 2017;595:1929–45.
Mosser C-A, Baptista S, Arnoux I, Audinat E. Microglia in CNS development: Shaping the brain for the future. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;149:1–20.
Frost JL, Schafer DP. Microglia: architects of the developing nervous system. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26:587–97.
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Yang Q-W, Wang J. Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13:420–33.
Blandford SN, Galloway DA, Moore CS. T he roles of extracellular vesicle micro RNA s in the central nervous system. Glia. 2018;66:2267–78.
Rajendran L, Bali J, Barr MM, Krämer-Albers E-M, Picou F, Raposo G, et al. Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in the nervous system. J Neurosci. 2014;34:15482–9.
Sharma P, Mesci P, Carromeu C, McClatchy DR, Schiapparelli L, Yates IIIJR, et al. Exosomes regulate neurogenesis and circuit assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:16086–94.
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF. Long non-coding RNAs: novel targets for nervous system disease diagnosis and therapy. Neurotherapeutics. 2013;10:632–46.
Shaimardanova AA, Solovyeva VV, Chulpanova DS, James V, Kitaeva KV, Rizvanov AA. Extracellular vesicles in the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15:586.
Simeoli R, Montague K, Jones HR, Castaldi L, Chambers D, Kelleher JH, et al. Exosomal cargo including microRNA regulates sensory neuron to macrophage communication after nerve trauma. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1778.
Sun D, Yu Z, Fang X, Liu M, Pu Y, Shao Q, et al. Lnc RNA GAS 5 inhibits microglial M2 polarization and exacerbates demyelination. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:1801–16.
Chi X, Ding B, Zhang L, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang W. lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization via miR‐455‐5p/SOCS3 pathway in childhood pneumonia. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:13242–51.
Liu C, Liu S, Xiong L, Zhang L, Li X, Cao X, et al. Genistein-3′-sodium sulfonate attenuates Neuroinflammation in stroke rats by Down-regulating microglial M1 polarization through α7nAChR-NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:1088.
Zhu X, Sun Y, Yu Q, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhao Y. Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization in allergic rhinitis via restraining mTORC1/ULK1/ATG13-mediated autophagy and subsequently activating NF-κB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121:110450.
Tsai M-C, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science. 2010;329:689–93.
Pazzaglia S, Tanno B, De Stefano I, Giardullo P, Leonardi S, Merla C, et al. Micro-RNA and proteomic profiles of plasma-derived exosomes from irradiated mice reveal molecular changes preventing apoptosis in neonatal cerebellum. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:2169.
Tie L, Xiao H, Wu D-l, Yang Y, Wang P. A brief guide to good practices in pharmacological experiments: Western blotting. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42:1015–7.
Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984;11:47–60.
Zhang Z, Wang M, Xie D, Huang Z, Zhang L, Yang Y, et al. METTL3-mediated N 6-methyladenosine mRNA modification enhances long-term memory consolidation. Cell Res. 2018;28:1050–61.
Huang X, Ying J, Yang D, Fang P, Wang X, Zhou B, et al. The mechanisms of sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:717745.
Zhang Y, Gao Y, Yang F, Wu X, Tang Z, Liu H. Neuroglobin alleviates the neurotoxicity of sevoflurane to fetal rats by inhibiting neuroinflammation and affecting microglial polarization. Brain Res Bull. 2022;183:142–52.
Pei Z, Wang S, Li Q. Sevoflurane suppresses microglial M2 polarization. Neurosci Lett. 2017;655:160–5.
Xu Y, Dong Y, Wang C, Jiang Q, Chu H, Tian Y. Lovastatin attenuates sevoflurane-induced cognitive disorder in aged rats via reducing Aβ accumulation. Neurochem Int. 2021;148:105078.
He J, Zhao H, Liu X, Wang D, Wang Y, Ai Y, et al. Sevoflurane suppresses cell viability and invasion and promotes cell apoptosis in colon cancer by modulating exosome‑mediated circ‑HMGCS1 via the miR‑34a‑5p/SGPP1 axis. Oncol Rep. 2020;44:2429–42.
Zhang Z, Li X, Chen F, Li Z, Wang D, Ren X, et al. Downregulation of LncRNA Gas5 inhibits apoptosis and inflammation after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2021;168:110–9.
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang H. Downregulation of lncRNA GAS5 prevents mitochondrial apoptosis and hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats through the microRNA-128-3p/Bax/Akt/GSK-3β axis. Neuroreport. 2021;32:1395–402.
Koldemir O, Özgür E, Gezer U. Accumulation of GAS5 in exosomes is a marker of apoptosis induction. Biomed Rep. 2017;6:358–62.
Patel RS, Impreso S, Lui A, Vidyarthi G, Albear P, Patel NA. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 contained in exosomes derived from human adipose stem cells promotes repair and modulates inflammation in a chronic dermal wound healing model. Biology. 2022;11:426.
Zhu X, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhao Y. Exosomal long non-coding RNA GAS5 suppresses Th1 differentiation and promotes Th2 differentiation via downregulating EZH2 and T-bet in allergic rhinitis. Mol Immunol. 2020;118:30–9.
Chen F, Zhang L, Wang E, Zhang C, Li X. LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496:184–90.
Cao Y, Jiang C, Lin H, Chen Z. Silencing of long noncoding RNA growth arrest–specific 5 alleviates neuronal cell apoptosis and inflammatory responses through sponging microRNA-93 to repress PTEN expression in spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:646788.
Hartwig J, Loebel M, Steiner S, Bauer S, Karadeniz Z, Roeger C, et al. Metformin attenuates ROS via FOXO3 activation in immune cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:581799.
Li X, Jiang X, Gao Q, Zhao P. FOXO3 regulates sevoflurane-induced neural stem cell differentiation in fetal rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022;42:1777–86.
Tan J, Luo J, Meng C, Jiang N, Cao J, Zhao J. Syringin exerts neuroprotective effects in a rat model of cerebral ischemia through the FOXO3a/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;90:107268.
Zhang X, Zhang F, Yao F, Wang P, Xiong Q, Neng P. Bergenin has neuroprotective effects in mice with ischemic stroke through antioxidative stress and anti-inflammation via regulating Sirt1/FOXO3a/NF-κB signaling. Neuroreport. 2022;33:549–60.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82271287), the Exploration Project of Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation (LY21H090006), the Zhejiang Health Science and Technology Planning Project (2021KY768), the Bureau of Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang, China (2018ZB065). This work was partly supported by grants from the Nanhu Brain-computer Interface Institute (010902001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LLX, MDY, and XZC conceived and designed the experiments. LLX and JQX performed the data analysis work and wrote the paper. JJS collected and processed the data; XZC revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Ll., Xie, Jq., Shen, Jj. et al. Neuron-derived exosomes mediate sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in neonatal mice via transferring lncRNA Gas5 and promoting M1 polarization of microglia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 45, 298–311 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01173-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-023-01173-9