Abstract
Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles undergoing cycles of fusion and fission to modulate their morphology, distribution, and function, which are referred as ‘mitochondrial dynamics’. Dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) is known as the major pro-fission protein whose activity is tightly regulated to clear the damaged mitochondria via mitophagy, ensuring a strict control over the intricate process of cellular and organ dynamics in heart. Various posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of Drp1 have been identified including phosphorylation, SUMOylation, palmitoylation, ubiquitination, S-nitrosylation, and O-GlcNAcylation, which implicate a role in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. An intact mitochondrial homeostasis is critical for heart to fuel contractile function and cardiomyocyte metabolism, while defects in mitochondrial dynamics constitute an essential part of the pathophysiology underlying various cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). In this review, we summarize current knowledge on the critical role of Drp1 in the pathogenesis of CVDs including endothelial dysfunction, smooth muscle remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy, pulmonary arterial hypertension, myocardial ischemia–reperfusion, and myocardial infarction. We also highlight how the targeting of Drp1 could potentially contribute to CVDs treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Mitochondria are the “power houses” of cells, producing the energy necessary for a myriad of cellular processes [1, 2]. Intriguingly, they are highly dynamic organelles that undergo fusion and fission to regulate their morphology and control their number and size, a process called “mitochondrial dynamics” [3, 4]. Mitochondrial dynamics has attracted increasing attention over the past decade because of its close interconnection with mitochondrial function. Mitochondrial dynamics processes are regulated by specific proteins, known as mitochondria-shaping proteins, among which the cytosolic GTPase dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) is the main pro-fission protein with activity that is tightly controlled to ensure balanced mitochondrial dynamics according to cellular needs [5].
As a main energy-demanding organ, the heart relies heavily on mitochondrial ATP production to fuel contractile function and cardiomyocyte metabolism [6]. Emerging evidence suggests that disrupted mitochondrial dynamics play vital roles in the pathogenesis of many cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), mainly by influencing cellular energy, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, intracellular calcium levels, apoptogenic protein production and some other mechanisms in a cell- or tissue-specific manner [7]. However, all these findings indicate a close relationship between mitochondrial dynamics in CVDs and Drp1-induced mitochondrial fragmentation. Hence, we will review current knowledge on the critical role of Drp1 in the pathogenesis of CVDs, including pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), heart failure, cardiac hypertrophy, and myocardial infarction (MI). We will also highlight how the targeting of Drp1 may potentially contribute to CVD treatment.
Drp1 and mitochondrial dynamics
Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles capable of fusion, fission, and migration toward other organelles for communication and interaction, which ensure cell-specific mitochondrial morphology, function, and intracellular distribution and satisfy changing metabolic and energetic demands of cells in a timely manner. Moreover, fission and fusion are essential for many important cellular functions, including ATP production, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) distribution, mitochondrial respiratory activity, cell survival, apoptosis, and calcium signaling. However, imbalanced mitochondrial dynamics cause mitochondrial structural alterations and dysfunction. Insufficient mitochondrial fission can lead to the accumulation of damaged and inactive mitochondria, while inadequate mitochondrial fusion results in the fragmentation of mitochondria, as indicated by changes in tubular morphology that lead to debris [8].
The regulation of mitochondrial dynamics is a complicated process involving various dynamin-related GTPases, which maintain a balance between mitochondrial fission and fusion [9]. As a key regulator in the mitochondrial fission process, Drp1 exerts its pro-fission function in four distinct steps: it is trafficked from the cytosol to the outer membrane of mitochondria (OMM), incorporating into higher-order complexes that constrict the organelle in a GTP-dependent manner, ultimately bisecting the parent organelle into two daughters [10]. The two daughter mitochondria generally possess unequal and extreme membrane potential; however, damaged mitochondria that fail to stabilize their polarity tend to be completely depolarized and are ultimately targeted for mitophagy [11].
Drp1 structure and functions
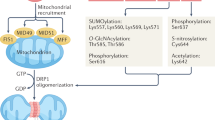
The Drp1 protein is known to have four domains, a C-terminal GTPase effector domain, variable domain (also known as insert B), helical middle domain, and highly conserved N-terminal GTPase domain (Fig. 1) [12]. Moreover, a crystal structural study revealed that the variable domain acts as a hinge by forming a T-shaped dimer or tetramer and binding the targeted membrane effectively [13]. In contrast to classical dynamins, Drp1 does not have a lipid-interacting pleckstrin homology domain; therefore, it can only anchor to the mitochondrial membrane by binding to its receptor to form a functional complex, and then a larger oligomer is assembled and transported to fission sites [14]. To date, four mitochondrial outer membrane (MOM) receptors and/or adapters that recruit Drp1 from the cytosol to the OMM for fission have been identified: mitochondrial dynamics protein 49 and 51 (MiD49 and MiD51), mitochondrial fission factor (Mff), and fission 1 (Fis1). Fis1 was the first MOM adapter identified as a recruiter of Drp1; it forms oligomers that serve as scaffolds on the OMM and interacts with Drp1 through its two tetratricopeptide repeat-like motifs [6]. However, excessive Drp1/Fis1 interaction is associated with some pathological conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease [15]. Fortunately, a specific inhibitor, P110, has been developed that selectively blocks the Drp1–Fis1 interaction under pathological conditions without disturbing the interaction between Drp1 and other mitochondrial adapters [16]. In contrast, inhibiting the Drp1–Mff interaction with peptide P259 results in elongated mitochondrial morphology and dysregulated mitochondrial motility and function, indicating a key role for the Mff–Drp1 interaction under physiological conditions [17]. Moreover, Mff can recruit Drp1 independently of Fis1 and is thought to be the major adapter protein for ubiquitously expressed Drp1 in all metazoans with involvement in the recruitment of Drp1 to both mitochondrial and peroxisomal membranes [18]. Another two receptors, MiD49 and MiD51, are chordate-specific mitochondrial elongation factor proteins, and both can recruit Drp1 to mitochondrial fission sites independent of Fis1 and Mff [18]. Intriguingly, in cells lacking Drp1, MiD51, and MiD49 are diffusely distributed on the MOM, while Mff remains at the constriction site [18]. In particular, MiD51/49 can also coordinate with Mff to regulate Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission. MiD51/49 can facilitate the binding of Mff to Drp1 by interacting with both Drp1 and Mff, thus serving as molecular adapters in a trimeric Drp1-MiD51/49-Mff complex at the MOM [19]. Hence, the relative levels of Mff and MiD51/49 and the balance between Mff and MiD51/49 during their interactions with Drp1 are both vital determinants of balanced mitochondrial dynamics in cells [19].
Notably, accumulating evidence has revealed the interdependent relationship between Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and mitophagy, the mitochondria-specific form of autophagy. Mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1 is a critical step to initiate mitophagy, and it is accompanied by the dephosphorylation of Ser-637 and the phosphorylation of Ser-616 [20]. Excessive levels of mitochondrial fragments during pathological conditions can be targeted by autophagosomes for sequestration and subsequent lysosomal degradation. Drp1 inhibition is relevant to repressed mitophagy in several cell types, including cardiomyocytes (CMs) [21]. Moreover, several studies regarding cardiac myocyte-specific ablation of Drp1 have described aberrant mitophagy and cardiomyopathy, indicating a crucial role for fission in mitophagy [22,23,24]. Understanding how mitophagy is regulated by Drp1 under pathologic status is critical. The process is complex, which may contribute to the development of specific therapeutic interventions in CVD patients.
Posttranslation modifications of Drp1 during mitochondrial fission
Drp1 is regulated by several posttranslational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation, SUMOylation, palmitoylation, ubiquitination, S-nitrosylation, and O-GlcNAcylation, mostly located in the B-insert region (Table 1 and Fig. 1). These PTMs play important roles in Drp1 activation, protein stability, protein–protein interactions, GTPase activity, and translocation between the cytosol and OMM [25]. Notably, the overexpression of Drp1 alone does not lead to fragmented mitochondria because the activation status of Drp1 depends on its MOM location, which is associated with PTMs [26].
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is one of the best characterized PTMs of Drp1, which can exert both activating and inhibitory effects depending on the specific site modified. Many phosphorylation sites have been characterized, namely, Ser-579, Ser-40, Ser-585, Ser-44, Ser-592, Ser-656, Ser-616, Ser-637, and Ser-693 [27]. Among these sites, two main sites, Ser-616 and Ser-637, have been extensively reported.
The phosphorylation of Ser-616 is an activating event contributing to the OMM localization of Drp1 and subsequent mitochondrial fission [6]. Phos-Ser-616 is known to be catalyzed by Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK), PKCδ, cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), ERK1/2, and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in various cell types tested in multiple laboratories [8, 28]. Specifically, a reciprocal effect of CDK-catalyzed phosphorylation on Drp1 oligomerization and mitochondrial translocation has been identified [7]. CDK5-catalyzed phosphorylation contributes to the trafficking of Drp1 to interphase microtubules, whereas CDK1-mediated phosphorylation leads to the translocation of Drp1 from microtubules to mitochondria [7]. Moreover, a recent study proposed a new pathway by which Ser-616 phosphorylation is regulated in a RhoA/ROCK-dependent manner in CMs to transmit environmental signals to mitochondria [29].
In contrast to the effects of Ser-616 phosphorylation, the functional consequences of Ser-637 phosphorylation, which is usually mediated by ROCK1, protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase D (PKD), Ca2+-dependent phosphatase calcineurin (CaN), etc. [8], are still highly controversial. Although in most cases, Ser-637 phosphorylation is linked to the diminished GTPase hydrolysis activity of Drp1, the specific role of Ser-637 phosphorylation is based on diverse internal and external parameters, such as cell type, Drp1 receptors, cellular context, and upstream molecules [6]. For example, the phosphorylation of Ser-637 by PKA inhibits the interaction between the GTP-binding domain and the GED domain and thus leads to decreased GTPase activity and attenuated mitochondrial fission [30]. The calcineurin-induced dephosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser-637 in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) contributes to the translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria [31]. In contrast, when phosphorylated by ROCK 1 and CAMK-1, Ser-637 activates Drp1 activity to promote mitochondrial fission in cultured hippocampal neurons [32, 33]. Similarly, another study involving cardiac mitochondrial signaling mechanisms showed that PKD-mediated phosphorylation at Ser-637 under pathophysiological conditions promotes mitochondrial fragmentation [34]. Notably, the same phosphorylation site is associated with different functions in mice and humans. In patients and animal models with diabetes, the phosphorylation of Drp1 at Ser-637 in humans and Ser-600 in mice was revealed under high-glucose conditions, with both leading to Drp1 translocation to the mitochondria [32].
The Ser-616/Ser-637 phosphorylation ratio was also associated with the pathogenesis of several diseases [35, 36]. Elevated phosphorylation of Ser-616 alone fails to induce mitochondrial fission. Considering the proximity of the Ser-616 and Ser-637 sites within the 3D structure, an elegant study showed that the phosphorylation level of Ser-637 participates in the regulation of Ser-616 phosphorylation in Drp1 [34]. However, the basal phosphorylation levels of the Ser-637 site are unaffected by the phosphorylation state of Ser-616 [37]. Indeed, it is interesting to speculate that the basal phosphorylation level of Ser-637 is necessary for maintaining the basal phosphorylation state of Ser-616 and that phosphorylation of Ser-637 primes Ser-616 phosphorylation [34].
SUMOylation
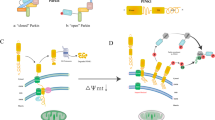
SUMOylation is another reversible and dynamic modification that usually alters the subcellular localization of proteins or protects them from ubiquitin-triggered destruction. Emerging evidence has demonstrated that small ubiquitin-like modifiers (i.e., SUMO proteins) are also involved in Drp1 activity regulation and stable binding of Drp1 to the MOM, leading to increased mitochondrial fission [38]. Drp1 SUMOylation is usually catalyzed by mitochondrial-anchored protein ligase (MAPL) and generally marks several nonconserved lysine residues within its B-insert (e.g., Lys-532, Lys-535, Lys-594, Lys-608, Lys-606, Lys-558, Lys-568, and Lys-597) [8]. MAPL-induced SUMOylation was found at ER/mitochondria contact sites during apoptosis, contributing to the stabilization of an ER/mitochondrial signaling platform involving cristae remodeling, calcium flux, and mitochondrial constriction [39]. The SUMOylated Drp1 plays a key role in zinc-induced cardioprotection against I/R injury. Mechanistically, mitophagy is activated in response to Drp1 SUMOylation, which represses ROS generation, removes damaged mitochondria, and controls mitochondrial quality, leading to improved myocardial function and decreased myocardial I/R damage [40]. Sentrin/SUMO-specific protease 5 (SENP5) is critical for the deSUMOylation of Drp1 and the repression of mitochondrial fission via its interaction with Drp1. In particular, SENP5 is the only SENP that is upregulated in human heart failure. In CM-specific SENP5-overexpressing mice, decreased SUMOylation of Drp1 leads to swollen mitochondria and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, culminating in cardiomyopathy and heart failure [41]. Moreover, the removal of Drp1 SUMO1 by SENP2 and SUMO2/3 by SENP3 has also been reported [40, 42]. However, Drp1 SUMOylation catalyzed by distinct SUMO isoforms leads to distinct functional consequences. SUMO1-modified Drp1 is preferentially localized to mitochondria, while the SUMO2/3 modification represses Drp1 recruitment to mitochondria [43]. The specific roles of different SUMO isoforms in the process of Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission needs further study (Fig. 2).
Drp1 can be SUMOylated by both SUMO1 and SUMO2/3, which leads to distinct functional consequences. MAPL-dependent SUMO1-ylation as well as SENP-dependent de-SUMO2/3-ylation of Drp1 promotes its association with the MOM, which stabilizes a mitochondrial/ER platform, facilitating mitochondrial fission, calcium uptake, cytochrome c release, and activates mitophagy. In contrast, SUMO2/3 modification and de-SUMO1-ylation of Drp1 leads to the destabilized ER-mitochondria sites, accumulation of defective mitochondria, reduced ATP production, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
S-Palmitoylation
S-Palmitoylation is a posttranslational modification in which fatty acyl chains, typically palmitates (C16:0), are attached to cysteine residues of proteins via a reversible thioester bond [44]. Emerging evidence has shown that palmitoylation is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial fission–fusion via related signaling pathways [45]. Importantly, S-palmitoylation of Drp1 is a crucial event for its proper subcellular localization and normal function [46]. ZDHHC13-deficient mice display reduced Drp1 palmitoylation levels, which impair its translocation to mitochondria and disrupt mitochondrial dynamics, leading to abnormal mitophagy and failure of mitochondria division into daughter cells [46]. As a consequence, the accumulation of defective mitochondria leads to reduced ATP production and even causes some metabolic-related diseases, such as neurological disorders with energy deficits, tumorigenesis, and arrhythmia generation [46]. However, there are only a few reports proposing significant roles for Drp1 palmitoylation and depalmitoylation, and the relative contributions of Drp1 palmitoylation to regulating mitochondrial morphology and function under physiological and pathological conditions remains a topic to explore in the future.
Ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is an evolutionarily conserved 76 amino acid peptide that posttranslationally marks proteins for proteasomal degradation or modulates their biological function by changing their functional interactions [47]. Drp1 was found to be ubiquitinated by Parkin, which targets Drp1 for proteasomal degradation and thus affects the mitochondrial fission–fusion process [27]. Knockdown or pathogenic mutation of Parkin is associated with decreased degradation of Drp1, which leads to increased Drp1 activity and excessive mitochondrial division, ultimately leading to the occurrence of some diseases [27]. OMM-anchored membrane-associated ring finger 5 (MARCH5) is another ubiquitin ligase involved in mitochondrial dynamics. It has been demonstrated that MARCH5 participates in the modulation of mitochondrial morphology through the polyubiquitination of Drp1, culminating in Drp1 proteasomal degradation [48]. Further, Drp1 accumulation was observed in embryonic fibroblasts and tissues of MARCH5-knockout mice, accompanied by uncontrollable mitochondrial division and a significant increase in ROS [48]. In addition to the MARCH5-Drp1-UPS (ubiquitin-proteasome system) pathway, MARCH5 can also affect the homeostasis of mitochondria in the MARCH5-mediated mitophagy pathway. The re-expression of MARCH5 in MARCH5-knockout cells reversed the inhibition of stress-induced apoptosis [49]. Intriguingly, in addition to a substrate, Drp1 is also a regulator of MARCH5 activity [50]. New studies are expected to shed light on the role of MARCH5 in Drp1 activity and mitochondrial functions.
S-Nitrosylation
The signal messenger nitric oxide (NO) is known to covalently conjugate to the Cys residues of target proteins, in a process called S-nitrosylation [27]. Notably, S-nitrosylated Drp1 has been found in neuronal cells and is associated with an increase in the number of Drp1 oligomers, upregulated GTPase activity and altered protein conformation [27]. For instance, NO-mediated S-nitrosylation of Drp1 at Cys-644 within the GED domain, through a redox-based mechanism, can lead to mitochondrial fragmentation, synaptic injury, and bioenergetic failure, thus contributing to the pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease [51]. Consistently, S-nitrosylated Drp1 was found to be a key player in the excessive mitochondrial fission induced by mutant huntingtin and consequential dendritic spine loss in both animal models and humans with Huntington’s disease. However, these findings remain controversial because some other groups have shown that Drp1 S-nitrosylation has no direct effect on Drp1 activity but that NO or S-nitrosylation of Drp1 promotes Ser-616 phosphorylation, which leads to increased fission [52, 53]. These findings demonstrate a connection between aberrant NO production and mitochondrial and synaptic dysfunction, although the S-nitrosylation of Drp1 may not be the uniquely critical precursor. Considering the limited number of publications to date, further studies are needed to confirm the functional relevance of Drp1 S-nitrosylation.
O-GlcNAcylation
O-GlcNAcylation is a dynamic process that posttranslationally modifies proteins on serine and threonine residues and is generally modulated by the interplay between O-GlcNAcase and O-GlcNAc transferase. O-GlcNAcylation plays an important role in numerous biological processes. Notably, the effects between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation on Drp1 function are reciprocal because their sites overlap [54]. For example, O-GlcNAcylation of Drp1 at threonine 585 and 586 leads to the dephosphorylation at Ser-637 in CMs [55]. The O-GlcNAcylation modification also results in augmented GTP-bound active form of DRP1 and OMM translocation of DRP1, culminating in excessive mitochondrial fission, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, and loss of mitochondrial content. These defects would subsequently lead to a compensatory increase in oxidative phosphorylation per mitochondrion.
Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission and CVDs
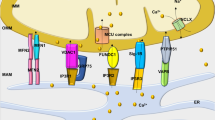
As the main energy-demanding organ in the body, the heart relies heavily on mitochondria to meet its tremendous energy requirements and fulfill the demands of cardiac excitation–contraction coupling. Cardiac mitochondria can be classified into three groups according to their subcellular location: perinuclear mitochondria, subsarcolemmal mitochondria and intermyofibrillar mitochondria [56]. They occupy over 30% of the cell volume and synthesize 6–7 kg ATP each day via oxidative phosphorylation [57]. Notably, Drp1-mediated mitochondrial dynamics play crucial roles in mitochondrial quality control in the heart. Repressed expression of Drp1 leads to significantly increased mitochondrial depolarization in the heart under basal and stressed conditions [23]. Disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis is known to be a relevant contributor to a great number of vascular disorders, such as endothelial dysfunction (ED), smooth muscle remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, IR injury, MI, and PAH [57] (Fig. 3). Maintaining balanced mitochondrial dynamics can protect the heart from energy stress and is of paramount importance for cardiac homeostasis [23].
The translocation of Drp1 to the MOM is induced by Drp1 adapters (e.g., Fis1, Mff, MiD49 and MiD51) under cardiac stress, accompanied by the phosphorylation of Ser-616 and the dephosphorylation of Ser-637. The interaction of Drp1 and Drp1 adapters is a hallmark of activated mitochondrial fission and leads to increased mitochondrial fragmentation and subsequent increased mitochondrial ROS, mPTP opening, cytochrome c release, MOM permeability, and cardiac cell death, which accelerate CVD progression. However, Drp1-dependent mitophagy is triggered secondary to mitochondrial dysfunction to remove damaged mitochondria. The depolarized mitochondria can be marked by Parkin and fragments segregated into autophagosomes for subsequent lysosomal degradation, which has been identified as an important means of self-regulation for cardiac cell function and survival. Notably, the detrimental effects of excessive mitochondrial fission can be reversed by drugs targeting Drp1, including mdivi-1, P110, metformin, and melatonin.
Endothelial dysfunction
ED is the earliest response to vascular injury and the key factor that creates a vulnerable environment in arteries [58]. Notably, disrupted mitochondrial fission is associated with the impairment of angiogenesis [59], induction of apoptosis [32], production of mitochondrial ROS and reduction in eNOS-derived NO bioavailability [60] in endothelial cells. Altered mitochondrial morphology, loss of mitochondrial networks, and increased expression of fission proteins in endothelial cells under diabetic conditions have been found in an increasing number of studies [61,62,63]. However, these functional consequences can be abrogated when Drp1 expression is inhibited, indicating mitochondrial fragmentation as a major cause of ED in the setting of hyperglycemia, likely via increased mitochondrial ROS. Increased ROS production is a key contributor to ED because the ROS react with NO to form peroxynitrite, which causes the oxidation of cofactors, eNOS uncoupling, and oxidative modification of target enzymes [9]. However, further studies are needed to determine whether Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission triggers other ROS-generating enzymes, including NADPH oxidase, Nox1, Nox2, and Nox4.
The proinflammatory state is also a contributor to ED and the vascular diseases associate with it, such as atherosclerosis. Intriguingly, an increasing number of investigations have demonstrated that Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission plays a fundamental role in modulating inflammation. For example, the levels of IL-1β, IFNγ, and TNFα mRNA transcripts were higher in Drp1-deficient mice and were associated with defective efferocytosis, which led to advanced atherosclerotic lesions in fat-fed Ldlr−/− mice [27]. Moreover, Drp1 was involved in the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β-dependent inflammation. Mechanistically, Drp1-mediated mitophagy removes damaged mitochondria that release oxidized mtDNA, which is required for NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation [64]. NLRP3 formation leads to the conversion of pro-IL18 and pro-IL-1β to their mature forms, and they are then released from activated macrophages by nontraditional protein secretion [65].
Smooth muscle remodeling
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are known as relevant regulators of vessel tone and blood flow through the mechanism of contraction. However, VSMCs exhibit a highly proliferative and synthetic phenotype associated with the capacity to produce elevated levels of extracellular matrix in arterial diseases, including PAH and atherosclerosis, or after percutaneous coronary interventions. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the mitochondrial structure is a critical regulator of cell metabolism and hyperproliferative responses. Altered mitochondrial bioenergetics and morphology were associated with the hyperproliferative features of the synthetic VSMC phenotype but did not affect contractile proteins. The contractile-to-synthetic phenotype transition of VSMCs was accompanied by mitochondrial fragmentation, increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased glucose oxidation. These results are consistent with those of previous studies showing that the hyperproliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) is linked to excessive mitochondrial division [66], while the suppression of mitochondrial fission by mdivi-1 prevents both cell proliferation and cobalt-induced PAH in vivo [67]. These new findings establish the involvement of Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation in SMC synthetic phenotype remodeling, which may be a therapeutic target for hyperproliferative vascular disorders.
Cardiac hypertrophy
Myocardial hypertrophy is a compensatory process characterized by greater ventricular wall thickness, enhanced myocardial contractility, and increased myocardial cell volume under long-term pressure overload [68]. Mechanistically, the pathogenesis of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is related to diminished mitochondrial metabolism caused by changes in mitochondrial function and morphology, which is regulated by mitochondrial dynamics [69]. An analysis of the cardiac hypertrophy pathway demonstrated phosphorylation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1, which was subsequently confirmed in phenylephrine (PE)-treated rat neonatal CMs and transverse aortic banding (TAB)-treated mouse hearts, showing the culmination of an increased mitochondrial numbers, decreased mitochondrial volume and a loss of mitochondrial function [70]. Interestingly, reducing Drp1 levels with mitochondrial division inhibitor-1 (midiv-1) could inhibit TAB-induced hypertrophic responses and reduced PE-induced hypertrophic growth and oxygen consumption [70]. Midiv-1 was also found to be effective in treating hypertensive cardiac hypertrophy by repressing ROS production, which subsequently inhibited the activity of Ca2+/CaMKII and the Ca2+-activated protein phosphatase calcineurin [71]. Moreover, the hypertrophic agonist norepinephrine was found to act through the α1-adrenergic receptor–Ca2+–calcineurin–Drp1 signaling pathway to repress mitochondrial metabolism and function and thus trigger a hypertrophic response [72]. The balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission is a determinant in the onset and development of cardiac hypertrophy [72].
Notably, Drp1-mediated mitophagy plays an essential role during cardiac hypertrophy. Mitophagy is a critical biological process in degrading damaged mitochondria via asymmetrical mitochondrial fission and has been identified as a key player in the self-regulation of CM function and survival [73]. Intact mitophagy is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial network-related signaling, vascular endothelium protection, and mitochondria-associated cell death during cardiac hypertrophy. It is intriguing that mitophagy was transiently activated in mouse hearts during cardiac hypertrophy, and it was accompanied by Ser-616 phosphorylation and mitochondrial translocation of Drp1 [74]. Moreover, reduced Drp1 levels were associated with the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and accelerated progression of cardiac hypertrophy after TAC [74]. Consistently, another study showed that the inhibition of Drp1 contributed to the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria in the heart by repressing Bnip3-induced mitophagy. Moreover, mitophagy was abrogated in cardiac-specific heterozygous Drp1-knockout mice [74]. All these findings indicate that Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission is a prerequisite for mitophagy during cardiac hypertrophy [75].
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
PAH is a pulmonary vascular remodeling disease characterized by elevated pulmonary artery pressure, obstructive vascular remodeling, and vasoconstriction of small pulmonary arteries, which result in fatal right ventricular (RV) failure [76]. The hyperproliferation of PASMCs plays an essential role in the pathophysiology underlying PAH, because balanced mitochondrial dynamics and distribution of mitochondria are crucial. Excessive mitochondrial fission was revealed in PASMCs [76], pulmonary artery adventitial fibroblasts [77], RV fibroblasts [78], and RV myocytes [79] in PAH. Posttranslational modification of Drp1 constitutes an essential part of the fissogenic phenotype of PAH PASMCs, in which DRP1 Ser-637 is dephosphorylated, and DRP1 Ser-616 is phosphorylated, leading to the activation of Drp1, hyperproliferative and apoptosis-resistant phenotype of PASMCs, and the bioenergetic impairment of RV myocytes [67]. Notably, the inhibition of mitotic fission by the Drp1 inhibitor mdivi-1 attenuates the fragmented mitochondrial morphology, slows cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis in PAH models [80]. Daily mdivi-1 treatment for 5 days decreased pulmonary arteriole muscularization and improved hemodynamics, RV function, and exercise capacity in animals with established PAH [80]. Enhanced Drp1-induced fission was attributed to the upregulation of MiD49 and MiD51, the two major Drp1-binding partners, in the pathogenesis of PAH realized through dual mechanisms. On the one hand, MiDs attract more Drp1 to the OMM to enhance fission; on the other hand, MiDs activate kinases that control Drp1 activity, such as ERK1/2 [76]. In addition to hyperproliferation and excessive mitochondrial fission, greater collagen production was also observed in RV fibroblasts, a finding consistent with the increased RV fibrosis observed in monocrotaline-induced PAH. Notably, excessive collagen production is also linked with Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission because the antifibrotic phenotype can be rescued by mdivi-1 [78].
Myocardial I/R
Myocardial IR injury is a central mechanism in many types of irreversible cardiac damage, including cardiomyocyte edema, arrhythmia, and MI, which can eventually lead to cardiomyocyte death [81]. A variety of studies on the role of mitochondrial homeostasis in myocardial IR injury have been conducted. IR can alter mitochondrial ultrastructure and morphology, causing mitochondrial swelling, cristae disintegration and loss of matrix density [79]. Accumulating evidence suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction during IR has a causative role in subsequent myocardial inefficiency, cardiac cell death and impaired ventricular function [82]. Indeed, Drp1-mediated mitochondrial division and ensuing fragmentation are triggers for apoptosis, which constitutes an essential part of the pathophysiology underlying IR injury [83]. Mechanistically, the excessive activation of Drp1 in response to I/R stimulation leads to a pathological cascade of elevated MOM permeability, mitochondrial dysfunction, increased ROS production, and calcium overload. Subsequently, mitochondrial depolarization, reduced ATP production, released cytochrome c, and, then, apoptosis occurred [83]. The protective role of the Notch1-Drp1/MFN1 axis in myocardial IR injury has also been revealed, by which Notch1 signaling reduces mitochondrial fission, inhibits ventricular remodeling, and reduces myocardial infarct size [84]. Fortunately, disrupting the Drp1–Fis1 interaction by P110 or inhibiting Drp1 GTPase activity by mdivi-1 are both effective strategies for attenuating IR injury because either enhances mitochondrial function and structure [79].
Myocardial infarction
MI is a high-mortality disease that involves the occlusion of a coronary artery, which destroys hemodynamic stability and leads to cardiac ischemia and subsequent rapid impairment of left ventricular function [85]. The essential function of mitochondria in MI has been revealed in numerous studies for more than a decade. A number of experimental studies have shown that Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission contributes to myocardial cell death during pressure overload and MI, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiomyocyte death [86]. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of Drp1 using mdivi-1 or P110 (a peptide inhibitor that selectively blocks the Drp1–Fis1 interaction under pathological conditions) was able to prevent the opening of the mitochondrial transition pore, reduce infarct size, and ameliorate cardiovascular dysfunction following pressure overload in rodent acute myocardial infarction (AMI) models, indicating potential clinical applicability of this therapeutic approach [86,87,88]. However, opposite results were reported in another clinically relevant pig AMI model, in which mdivi-1 did not exert any cardioprotective effects [89]. Drp1 inhibition by siRNA was also associated with increased cardiomyocyte contractility because it regulated cytosolic potassium and calcium levels [86]. Recycled calcium is a key regulator in cardiac relaxation, and aberrant calcium concentration can cause impaired cardiac function, which ultimately leads to cell death. Exacerbated mitochondrial fission caused the accumulation of cytosolic calcium by repressing Sarco endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (Serca) in mouse ventricular myocytes and was accompanied by increased cytochrome c leakage, which can be detrimental to CMs, and thus, MI progress was accelerated [86].
Drugs targeting Drp1 and their application to CVDs
Considering the multiple roles of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in the development and progression of CVDs, it is possible to manipulate its expression and activity pharmacologically or genetically to prevent and treat cardiac dysfunction [90]. Certain chemical compounds have been identified for this purpose. For example, mdivi-1 was found through chemical screening to inhibit Drp1 function by repressing its GTPase activity. Treating Drp1 with mdivi-1 can limit ischemic stress and protect the heart against IR injury by preserving mitochondrial morphology, improving mitochondrial function, preventing apoptosis, and inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening [87, 91]. Moreover, mdivi-1 treatment is capable of promoting ATP levels and mitochondrial complex I, IV, and V activity levels in diabetic hearts. In addition, mdivi-1 attenuated superoxide anion production, reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and improved cardiac dysfunction in diabetic mice. However, the effect of mdivi-1 appears to be time- and dose-dependent because complete or long-term inhibition of Drp1 induces harmful effects by promoting the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and impairing cardiac function in diabetic cardiomyopathy and cardiac hypertrophy [92].
Similar to the cardioprotective effects of mdivi-1, melatonin was recently found to have marked inhibitory effects on Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and to ameliorate cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice through the SIRT1-PGC1α pathway [93]. In addition, melatonin also mediates p-Drp1Ser-616 downregulation and p-Drp1S637 upregulation in an AMPKα-dependent manner, which leads to the recovery of mPTP opening, PINK1/Parkin upregulation, and the mitophagy-mediated death of cardiac microcirculation endothelial cells upon cardiac microvascular IR injury [94]. The beneficial role of melatonin in posttraumatic cardiac dysfunction has also been established in rats. Specifically, mechanical trauma-induced mitochondrial fission, cytochrome c release, ∆Ψm loss, and reduced mitochondrial complex I–IV activity levels are all alleviated in response to melatonin administration because Drp1 is inhibited [95]. These findings describe the significant pharmacological potential of melatonin in CVD treatment by preventing excessive mitochondrial fission.
Notably, the well-known antidiabetic drug metformin exerts cardiovascular protective effects in diabetic mellitus patients by targeting mitochondrial fission driven by Drp1. Using STZ-induced diabetic ApoE−/− mice, some researchers have demonstrated that metformin reduces hyperglycemia-enhanced Drp1 expression by activating AMPK, which subsequently contributes to attenuated mitochondrial fragmentation, enhanced endothelial-dependent vasodilation, suppressed mitochondria-derived superoxide release, inhibited vascular inflammation, and mitigated atherosclerotic lesions in STZ-induced diabetic ApoE−/− mice. These new findings suggest a mechanism through which metformin attenuates the development of diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis by reducing Drp1-mediated mitochondrial dynamics.
In recent years, short peptides functioning as effective inhibitors of Drp1 have also been isolated to modulate mitochondrial dynamics. For example, adapter-specific inhibitors of the Drp1/Fis1 interaction have been developed, named P11017. In contrast to mdivi-1, which cannot distinguish between pathological and physiological activities of Drp1, P110 rescues pathological fragmentation and subsequent mitochondrial dysfunction without interfering with basal fission in in vitro and in vivo models of septic cardiomyopathy [15]. In contrast, P259, a Drp1/Mff-specific inhibitor, is limited because of its inhibitory effect on physiological fission, which may not be as protective as was originally predicted and may, in fact, hastening disease progression [17]. These results indicate that physiological Drp1 activity constitutes an essential part of mitochondrial function [17]. Protecting physiological fission by inhibiting adapter-specific interactions with short peptides such as P110 is promising in the future.
Conclusions
This review summarizes recent progress in several significant aspects of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission, which plays a key role in the manifestation of cardiac pathology. Intriguingly, mitochondrial morphology is affected by numerous cellular biological factors. PTMs, complex assembly and disassembly, the hydrolysis of Drp1 and its interaction with specific receptors (Fis1, Mff, and MiD49/51) are all indispensable regulators of Drp1 activity, which in turn influences physiological and pathophysiological conditions within cells. Intact mitochondrial dynamics are critical for the maintenance of normal vascular function, and pharmacological modulation of mitochondrial dynamic proteins may emerge as novel therapeutic targets for a number of CVDs resulting from excessive fission. Inhibiting Drpl GTPase activity with mdivi-1 or disrupting the Drp1–Fis1 interaction with P110 can improve cardiac function by enhancing both mitochondrial structure and function, but the related toxicology and pharmacokinetics profiles still need further investigation because of its clinical usage.
Although promising, multiple questions related to treating CVDs by manipulating mitochondrial dynamics remain unsolved. Targeting mitochondrial fission is a double-edged sword because physiological fission is essential for mitochondrial function. Mitochondrial homeostasis, not fusion or fission processes, plays the most important role, and this balance should be maintained when targeting mitochondrial dynamics under pathological conditions. In addition, physiological mitochondrial fission under stress in the myocardium is necessary for the adaptation to increased energy demands, and repression of mitochondrial fission is not always beneficial. Moreover, although treating CVD with mdivi-1 is effective in the short term, chronic inhibition of mitochondrial fission can be detrimental, and the feasibility of targeting Drp1 warrants further clarification. How to finely modulate the activity of Drp1 while reducing any possible side effects at the same time is our primary challenge in the future. Finally, considering that the mitochondrial energy demands and the composition of the fission apparatus differ by cell type, especially between cardiac myocytes and others, selective Drp1 inhibitors to cardiac myocytes is also needed to avoid potential negative off-target effects. In addition, the complex regulatory mechanisms of Drp1 in different CVDs also need to be elucidated in future studies. The resolution of these issues will contribute to the development of novel therapeutic agents to reduce morbidity and mortality from CVDs.
References
Cogliati S, Enriquez JA, Scorrano L. Mitochondrial cristae: where beauty meets functionality. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:261–73.
Formosa LE, Ryan MT. Mitochondrial OXPHOS complex assembly lines. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:511–3.
Wai T, Langer T. Mitochondrial dynamics and metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016;27:105–17.
Eisner V, Picard M, Hajnóczky G. Mitochondrial dynamics in adaptive and maladaptive cellular stress responses. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:755–65.
Simula L, Campanella M, Campello S. Targeting Drp1 and mitochondrial fission for therapeutic immune modulation. Pharmacol Res. 2019;146:104317.
Serasinghe MN, Chipuk JE. Mitochondrial fission in human diseases. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;240:159–88.
Cho B, Choi SY, Cho HM, Kim HJ, Sun W. Physiological and pathological significance of dynamin-related protein 1 (drp1)-dependent mitochondrial fission in the nervous system. Exp Neurobiol. 2013;22:149–57.
Adaniya SM, O-Uchi J, Cypress MW, Kusakari Y, Jhun BS. Posttranslational modifications of mitochondrial fission and fusion proteins in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019;316:C583–604.
Rovira-Llopis S, Banuls C, Diaz-Morales N, Hernandez-Mijares A, Rocha M, Victor VM. Mitochondrial dynamics in type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological implications. Redox Biol. 2017;11:637–45.
Ong SB, Hausenloy DJ. Mitochondrial dynamics as a therapeutic target for treating cardiac diseases. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;240:251–79.
Breitzig MT, Alleyn MD, Lockey RF, Kolliputi N. A mitochondrial delicacy: dynamin-related protein 1 and mitochondrial dynamics. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018;315:C80–90.
Chang CR, Manlandro CM, Arnoult D, Stadler J, Posey AE, Hill RB, et al. A lethal de novo mutation in the middle domain of the dynamin-related GTPase Drp1 impairs higher order assembly and mitochondrial division. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:32494–503.
Frohlich C, Grabiger S, Schwefel D, Faelber K, Rosenbaum E, Mears J, et al. Structural insights into oligomerization and mitochondrial remodelling of dynamin 1-like protein. EMBO J. 2013;32:1280–92.
Macdonald PJ, Francy CA, Stepanyants N, Lehman L, Baglio A, Mears JA, et al. Distinct splice variants of dynamin-related protein 1 differentially utilize mitochondrial fission factor as an effector of cooperative GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:493–507.
Haileselassie B, Mukherjee R, Joshi AU, Napier BA, Massis LM, Ostberg NP, et al. Drp1/Fis1 interaction mediates mitochondrial dysfunction in septic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;130:160–9.
Qi X, Qvit N, Su Y-C, Mochly-Rosen D. A novel Drp1 inhibitor diminishes aberrant mitochondrial fission and neurotoxicity. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:789–802.
Kornfeld OS, Qvit N, Haileselassie B, Shamloo M, Bernardi P, Mochly-Rosen D. Interaction of mitochondrial fission factor with dynamin related protein 1 governs physiological mitochondrial function in vivo. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14034.
Kraus F, Ryan MT. The constriction and scission machineries involved in mitochondrial fission. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:2953–60.
Yu R, Liu T, Jin SB, Ning C, Lendahl U, Nister M, et al. MIEF1/2 function as adaptors to recruit Drp1 to mitochondria and regulate the association of Drp1 with Mff. Sci Rep. 2017;7:880.
Tong M, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J. The role of Drp1 in mitophagy and cell death in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;142:138–45.
Catanzaro MP, Weiner A, Kaminaris A, Li C, Cai F, Zhao F, et al. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated by unchecked mitochondrial fission and mitophagy. FASEB J. 2019;33:11096–108.
Kageyama Y, Hoshijima M, Seo K, Bedja D, Sysa-Shah P, Andrabi SA, et al. Parkin-independent mitophagy requires Drp1 and maintains the integrity of mammalian heart and brain. EMBO J. 2014;33:2798–813.
Ikeda Y, Shirakabe A, Maejima Y, Zhai P, Sciarretta S, Toli J, et al. Endogenous Drp1 mediates mitochondrial autophagy and protects the heart against energy stress. Circ Res. 2015;116:264–78.
Song M, Mihara K, Chen Y, Scorrano L, Dorn GW 2nd. Mitochondrial fission and fusion factors reciprocally orchestrate mitophagic culling in mouse hearts and cultured fibroblasts. Cell Metab. 2015;21:273–86.
Hu C, Huang Y, Li L. Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission plays critical roles in physiological and pathological progresses in mammals. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010144.
Rizza S, Cardaci S, Montagna C, Di Giacomo G, De Zio D, Bordi M, et al. S-nitrosylation drives cell senescence and aging in mammals by controlling mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E3388–97.
Qi Z, Huang Z, Xie F, Chen L. Dynamin-related protein 1: a critical protein in the pathogenesis of neural system dysfunctions and neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:10032–46.
Bo T, Yamamori T, Suzuki M, Sakai Y, Yamamoto K, Inanami O. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) mediates radiation-induced mitochondrial fission by regulating the phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) at serine 616. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495:1601–7.
Brand CS, Tan VP, Brown JH, Miyamoto S. RhoA regulates Drp1 mediated mitochondrial fission through ROCK to protect cardiomyocytes. Cell Signal. 2018;50:48–57.
Chang CR, Blackstone C. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates its GTPase activity and mitochondrial morphology. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:21583–7.
Yu X, Jia L, Yu W, Du H. Dephosphorylation by calcineurin regulates translocation of dynamin-related protein 1 to mitochondria in hepatic ischemia reperfusion induced hippocampus injury in young mice. Brain Res. 2019;1711:68–76.
Wang W, Wang Y, Long J, Wang J, Haudek SB, Overbeek P, et al. Mitochondrial fission triggered by hyperglycemia is mediated by ROCK1 activation in podocytes and endothelial cells. Cell Metab. 2012;15:186–200.
Han XJ, Lu YF, Li SA, Kaitsuka T, Sato Y, Tomizawa K, et al. CaM kinase I alpha-induced phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates mitochondrial morphology. J Cell Biol. 2008;182:573–85.
Jhun BS, O-Uchi J, Adaniya SM, Mancini TJ, Cao JL, King E, et al. Protein kinase D activation induces mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in cardiomyocytes. J Physiol. 2018;596:827–55.
DuBoff B, Gotz J, Feany MB. Tau promotes neurodegeneration via DRP1 mislocalization in vivo. Neuron. 2012;75:618–32.
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Kim MJ, Kang TC. LIM kinase-2 induces programmed necrotic neuronal death via dysfunction of DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:1036–49.
Xu S, Wang P, Zhang H, Gong G, Gutierrez Cortes N, Zhu W, et al. CaMKII induces permeability transition through Drp1 phosphorylation during chronic beta-AR stimulation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13189.
Santel A, Frank S. Shaping mitochondria: the complex posttranslational regulation of the mitochondrial fission protein DRP1. IUBMB Life. 2008;60:448–55.
Prudent J, Zunino R, Sugiura A, Mattie S, Shore GC, McBride HM. MAPL SUMOylation of Drp1 stabilizes an ER/mitochondrial platform required for cell death. Mol Cell. 2015;59:941–55.
Bian X, Xu J, Zhao H, Zheng Q, Xiao X, Ma X, et al. Zinc-induced SUMOylation of dynamin-related protein 1 protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1232146.
Kim EY, Zhang Y, Beketaev I, Segura AM, Yu W, Xi Y, et al. SENP5, a SUMO isopeptidase, induces apoptosis and cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;78:154–64.
Guo C, Wilkinson KA, Evans AJ, Rubin PP, Henley JM. SENP3-mediated deSUMOylation of Drp1 facilitates interaction with Mff to promote cell death. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43811.
Le NT, Martin JF, Fujiwara K, Abe JI. Sub-cellular localization specific SUMOylation in the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863:2041–55.
Yeste-Velasco M, Linder ME, Lu YJ. Protein S-palmitoylation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1856:107–20.
Tang M, Lu L, Huang Z, Chen L. Palmitoylation signaling: a novel mechanism of mitochondria dynamics and diverse pathologies. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2018;50:831–3.
Napoli E, Song G, Liu S, Espejo A, Perez CJ, Benavides F, et al. Zdhhc13-dependent Drp1 S-palmitoylation impacts brain bioenergetics, anxiety, coordination and motor skills. Sci Rep. 2017;7:12796.
Pagliuso A, Cossart P, Stavru F. The ever-growing complexity of the mitochondrial fission machinery. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75:355–74.
Nagashima S, Tokuyama T, Yonashiro R, Inatome R, Yanagi S. Roles of mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase MITOL/MARCH5 in mitochondrial dynamics and diseases. J Biochem. 2014;155:273–9.
Xu S, Cherok E, Das S, Li S, Roelofs BA, Ge SX, et al. Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH5 controls mitochondrial fission and cell sensitivity to stress-induced apoptosis through regulation of MiD49 protein. Mol Biol Cell. 2016;27:349–59.
Cherok E, Xu S, Li S, Das S, Meltzer WA, Zalzman M, et al. Novel regulatory roles of Mff and Drp1 in E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH5-dependent degradation of MiD49 and Mcl1 and control of mitochondrial dynamics. Mol Biol Cell. 2017;28:396–410.
Cho DH, Nakamura T, Fang J, Cieplak P, Godzik A, Gu Z, et al. S-nitrosylation of Drp1 mediates beta-amyloid-related mitochondrial fission and neuronal injury. Science. 2009;324:102–5.
Bossy B, Petrilli A, Klinglmayr E, Chen J, Lütz-Meindl U, Knott AB, et al. S-Nitrosylation of DRP1 does not affect enzymatic activity and is not specific to Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010;20:S513–26.
Lee DS, Kim JE. PDI-mediated S-nitrosylation of DRP1 facilitates DRP1-S616 phosphorylation and mitochondrial fission in CA1 neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:869.
Cheng X, Hart GW. Alternative O-glycosylation/O-phosphorylation of serine-16 in murine estrogen receptor beta: post-translational regulation of turnover and transactivation activity. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:10570–5.
Gawlowski T, Suarez J, Scott B, Torres-Gonzalez M, Wang H, Schwappacher R, et al. Modulation of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) function by increased O-linked-β-N-acetylglucosamine modification (O-GlcNAc) in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:30024–34.
Jhun BS, O-Uchi J, Adaniya SM, Cypress MW, Yoon Y. Adrenergic regulation of Drp1-driven mitochondrial fission in cardiac physio-pathology. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018;7:195. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7120195.
Morales PE, Arias-Duran C, Avalos-Guajardo Y, Aedo G, Verdejo HE, Parra V, et al. Emerging role of mitophagy in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Mol Asp Med. 2020;71:100822.
Jin J, Wang X, Zhi X, Meng D. Epigenetic regulation in diabetic vascular complications. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019;63:R103–15.
Lugus JJ, Ngoh GA, Bachschmid MM, Walsh K. Mitofusins are required for angiogenic function and modulate different signaling pathways in cultured endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51:885–93.
Shenouda SM, Widlansky ME, Chen K, Xu G, Holbrook M, Tabit CE, et al. Altered mitochondrial dynamics contributes to endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2011;124:444–53.
Göpel S, Zhang Q, Eliasson L, Ma XS, Galvanovskis J, Kanno T, et al. Capacitance measurements of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic alpha-, beta- and delta-cells within intact islets of Langerhans. J Physiol. 2004;556:711–26.
Trudeau K, Molina AJ, Guo W, Roy S. High glucose disrupts mitochondrial morphology in retinal endothelial cells: implications for diabetic retinopathy. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:447–55.
Makino A, Scott BT, Dillmann WH. Mitochondrial fragmentation and superoxide anion production in coronary endothelial cells from a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2010;53:1783–94.
Sanchez-Lopez E, Zhong Z, Stubelius A, Sweeney SR, Booshehri LM, Antonucci L, et al. Choline uptake and metabolism modulate macrophage IL-1β and IL-18 production. Cell Metab. 2019;29:1350–62.
Zhong Z, Liang S, Sanchez-Lopez E, He F, Shalapour S, Lin XJ, et al. New mitochondrial DNA synthesis enables NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2018;560:198–203.
Bonnet S, Michelakis ED, Porter CJ, Andrade-Navarro MA, Thébaud B, Bonnet S, et al. An Abnormal mitochondrial-hypoxia inducible factor-1α-Kv channel pathway disrupts oxygen sensing and triggers pulmonary arterial hypertension in fawn hooded rats: similarities to human pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2006;113:2630–41.
Marsboom G, Toth PT, Ryan JJ, Hong Z, Wu X, Fang YH, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 2012;110:1484–97.
Zhang J, Yu J, Chen Y, Liu L, Xu M, Sun L, et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide supplement attenuates isoproterenol-induced myocardial hypertrophy in a sirtuin 3-dependent manner. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:9396089.
Sotomayor-Flores C, Rivera-Mejías P, Vásquez-Trincado C, López-Crisosto C, Morales PE, Pennanen C, et al. Angiotensin-(1-9) prevents cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by controlling mitochondrial dynamics via miR-129-3p/PKIA pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:2586–604.
Chang YW, Chang YT, Wang Q, Lin JJ, Chen YJ, Chen CC. Quantitative phosphoproteomic study of pressure-overloaded mouse heart reveals dynamin-related protein 1 as a modulator of cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell Proteom. 2013;12:3094–107.
Hasan P, Saotome M, Ikoma T, Iguchi K, Kawasaki H, Iwashita T, et al. Mitochondrial fission protein, dynamin-related protein 1, contributes to the promotion of hypertensive cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in Dahl-salt sensitive rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;121:103–6.
Pennanen C, Parra V, Lopez-Crisosto C, Morales PE, Del Campo A, Gutierrez T, et al. Mitochondrial fission is required for cardiomyocyte hypertrophy mediated by a Ca2+-calcineurin signaling pathway. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:2659–71.
Tong M, Saito T, Zhai P, Oka SI, Mizushima W, Nakamura M, et al. Mitophagy Is essential for maintaining cardiac function during high fat diet-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2019;124:1360–71.
Shirakabe A, Zhai P, Ikeda Y, Saito T, Maejima Y, Hsu CP, et al. Drp1-dependent mitochondrial autophagy plays a protective role against pressure overload-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and heart failure. Circulation. 2016;133:1249–63.
Lee Y, Lee HY, Hanna RA, Gustafsson ÅB. Mitochondrial autophagy by Bnip3 involves Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and recruitment of Parkin in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol-Heart Circulatory Physiol. 2011;301:H1924–31.
Chen KH, Dasgupta A, Lin J, Potus F, Bonnet S, Iremonger J, et al. Epigenetic dysregulation of the dynamin-related protein 1 binding partners MiD49 and MiD51 increases mitotic mitochondrial fission and promotes pulmonary arterial hypertension: mechanistic and therapeutic implications. Circulation. 2018;138:287–304.
Plecita-Hlavata L, Tauber J, Li M, Zhang H, Flockton AR, Pullamsetti SS, et al. Constitutive reprogramming of fibroblast mitochondrial metabolism in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55:47–57.
Tian L, Potus F, Wu D, Dasgupta A, Chen KH, Mewburn J, et al. Increased Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission promotes proliferation and collagen production by right ventricular fibroblasts in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension. Front Physiol. 2018;9:828. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00828.
Tian L, Neuber-Hess M, Mewburn J, Dasgupta A, Dunham-Snary K, Wu D, et al. Ischemia-induced Drp1 and Fis1-mediated mitochondrial fission and right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. J Mol Med. 2017;95:381–93.
Ryan J, Dasgupta A, Huston J, Chen KH, Archer SL. Mitochondrial dynamics in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Mol Med. 2015;93:229–42.
Hou H, Wang Y, Li Q, Li Z, Teng Y, Li J, et al. The role of RIP3 in cardiomyocyte necrosis induced by mitochondrial damage of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2018;50:1131–40.
Ghahremani R, Damirchi A, Salehi I, Komaki A, Esposito F. Mitochondrial dynamics as an underlying mechanism involved in aerobic exercise training-induced cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2018;213:102–8.
Zhang C, Huang J, An W. Hepatic stimulator substance resists hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating Drp1 translocation and activation. Hepatology. 2017;66:1989–2001.
Dai SH, Wu QC, Zhu RR, Wan XM, Zhou XL. Notch1 protects against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury via regulating mitochondrial fusion and function. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:3183–91.
Cooper HA, Eguchi S. Inhibition of mitochondrial fission as a novel therapeutic strategy to reduce mortality upon myocardial infarction. Clin Sci. 2018;132:2163–7.
Givvimani S, Pushpakumar SB, Metreveli N, Veeranki S, Kundu S, Tyagi SC. Role of mitochondrial fission and fusion in cardiomyocyte contractility. Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:325–33.
Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, Yellon DM, Davidson SM, Hausenloy DJ. Inhibiting mitochondrial fission protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2010;121:2012–22.
Disatnik MH, Ferreira JC, Campos JC, Gomes KS, Dourado PM, Qi X, et al. Acute inhibition of excessive mitochondrial fission after myocardial infarction prevents long-term cardiac dysfunction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000461.
Ong SB, Kwek XY, Katwadi K, Hernandez-Resendiz S, Crespo-Avilan GE, Ismail NI, et al. Targeting mitochondrial fission using Mdivi-1 in a clinically relevant large animal model of acute myocardial infarction: a pilot study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163972.
Xia Y, Chen Z, Chen A, Fu M, Dong Z, Hu K, et al. LCZ696 improves cardiac function via alleviating Drp1-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction in mice with doxorubicin-induced dilated cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017;108:138–48.
Disatnik MH, Ferreira JCB, Campos JC, Gomes KS, Dourado PMM, Qi X, et al. Acute Inhibition of excessive mitochondrial fission after myocardial infarction prevents long-term cardiac dysfunction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000461.
Nan J, Zhu W, Rahman MS, Liu M, Li D, Su S, et al. Molecular regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in cardiac disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017;1864:1260–73.
Ding M, Feng N, Tang D, Feng J, Li Z, Jia M, et al. Melatonin prevents Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in diabetic hearts through SIRT1-PGC1α pathway. J Pineal Res. 2018;65:e12491.
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Hu S, Shi C, Zhu P, Ma Q, et al. Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. 2017;63:e12413. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12413.
Ding M, Ning J, Feng N, Li Z, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial fission contributes to post-traumatic cardiac dysfunction in rats and the protective effect of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2018;64. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12447.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission of China (19JC1411300 to DM), Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader (20XD1400600 to DM), General Programs (81873469, 81670450 to DM, 81873536 to XHW, 81572713 to XLZ), and the Great Program (91639103 to DM) of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC2000202), the funding of Innovative Research Team of High-level Local Universities in Shanghai, a Key Laboratory Program of the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (ZDSYS14005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Jy., Wei, Xx., Zhi, Xl. et al. Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in cardiovascular disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42, 655–664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00518-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00518-y
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mechanistic insight of mitochondrial dysfunctions in cardiovascular diseases with potential biomarkers
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2024)
-
Rhein alleviates myocardial ischemic injury by inhibiting mitochondrial division, activating mitochondrial autophagy and suppressing myocardial cell apoptosis through the Drp1/Pink1/Parkin pathway
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Sepsis-induced Cardiomyopathy
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2024)
-
CD137 Signaling Mediates Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cell Proliferation Under Hypoxia By Regulating Mitochondrial Dynamics
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research (2024)
-
Multifaceted functions of Drp1 in hypoxia/ischemia-induced mitochondrial quality imbalance: from regulatory mechanism to targeted therapeutic strategy
Military Medical Research (2023)