Abstract
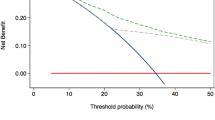
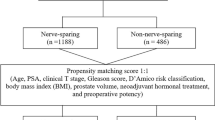
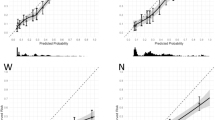
Limited evidence exists about preserving neurovascular bundles during radical prostatectomy (RP) for high-risk prostate cancer (HRPCa) patients. Hence, we validated an existing algorithm predicting contralateral extraprostatic extension (cEPE) risk in unilateral high-risk cases. This algorithm aims to assist in determining the suitability of unilateral nerve-sparing RP. Among 264 patients, 48 (18%) had cEPE. The risk of cECE varied: 8%, 17.2%, and 30.8% for the low, intermediate, and high-risk groups, respectively. Despite a higher risk of cECE among individuals classified as low-risk in the development group compared to the validation group, our algorithm’s superiority over always/never nerve-sparing RP was reaffirmed by decision curve analysis. Therefore, we conclude that bilateral excision may not always be justified in men with unilateral HRPCa. Instead, decisions can be based on our suggested nomogram.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mottet N, Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Eberli D, De Meerleer G, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTROESUR- ISUP-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Arnhem, The Netherlands: European Association of Urology; 2022.
Schaeffer EM, Srinivas S, Adra N, An Y, Barocas D, Bitting R, et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: prostate cancer, version 1.2023. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw JNCCN. 2022;20:1288–98.
Martini A, Soeterik TFW, Haverdings H, Rahota RG, Checcucci E, De Cillis S, et al. An algorithm to personalize nerve sparing in men with unilateral high-risk prostate cancer. J Urol. 2022;207:350–7.
Martini A, Wever L, Soeterik TFW, Rakauskas A, Fankhauser CD, Grogg JB, et al. Unilateral pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer patients diagnosed in the era of magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy: a study that challenges the dogma. J Urol. 2023;210:117–27.
Mossanen M, Nepple KG, Grubb RL, Androile GL, Kallogjeri D, Klein EA, et al. Heterogeneity in definitions of high-risk prostate cancer and varying impact on mortality rates after radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol Oncol. 2018;1:143–8.
Lombardo R, De Nunzio C. Nomograms in PCa: where do we stand. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023;26:447–8.
Diamand R, Roche JB, Lievore E, Lacetera V, Chiacchio G, Beatrici V, et al. External validation of models for prediction of side-specific extracapsular extension in prostate cancer patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol Focus. 2023;9:309–16.
Kováčik V, Maciak M, Baláž V, Babeľa J, Kubas V, Bujdák P, et al. Advanced Reconstruction of Vesicourethral Support (ARVUS) during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: first independent evaluation and review of other factors influencing 1 year continence outcomes. World J Urol. 2020;38:1933–41.
Kim M, Park M, Pak S, Choi SK, Shim M, Song C, et al. Integrity of the urethral sphincter complex, nerve-sparing, and long-term continence status after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol Focus. 2019;5:823–30.
Avulova S, Zhao Z, Lee D, Huang LC, Koyama T, Hoffman KE, et al. The effect of nerve sparing status on sexual and urinary function: 3-year results from the CEASAR study. J Urol. 2018;199:1202–9.
Nguyen LN, Head L, Witiuk K, Punjani N, Mallick R, Cnossen S, et al. The risks and benefits of cavernous neurovascular bundle sparing during radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol. 2017;198:760–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
LRS, AM, HG, SS, GG, MV, and GM were involved in the conception of research, interpretation of results, and manuscript approval. Data was collected by JZ, PR, QM, and LH. Statistical analysis was carried out by AM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The data utilized in this study were derived from preexisting records and databases, and no novel data were solicited from patients for the purpose of this research. To safeguard privacy, all patient data underwent de-identification procedures. Patient identities were anonymized, and any personal information was meticulously managed to uphold confidentiality.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Sanchez, L., Martini, A., Zhuang, J. et al. External validation of an algorithm to personalize nerve sparing approaches during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in men with unilateral high-risk prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00779-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00779-8