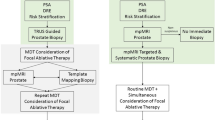
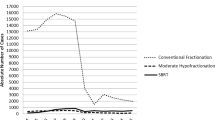
Abstract
External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is an important cornerstone in the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Current image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) techniques allow for more accurate and precise delivery of radiation treatment by the use of imaging before each fraction. Magnetic resonance guided radiotherapy (MRgRT) is the next step in IGRT with hybrid systems combining linear accelerators with MRI-scanners. With MRgRT, it is possible to visualize pelvic anatomy in great detail and subsequently perform replanning of the radiation dose distribution before each radiotherapy fraction. This technique has the potential to increase the therapeutic window of EBRT, by improved normal tissue sparing due to margin reduction and more accurate target dose delivery. This is particularly promising for prostate cancer, with its biology lending itself to ultra-hypofractionation, reducing radiotherapy treatment to as little as five fractions. Also, recent studies have shown that focal dose escalation to the intraprostatic tumor to high ablative doses can substantially increase disease-free survival. In this article, we discuss these unique opportunities as well as the potential future benefits of MRgRT in prostate cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zelefsky MJ, Kollmeier M, Cox B, Fidaleo A, Sperling D, Pei X, et al. Improved clinical outcomes with high-dose image guided radiotherapy compared with non-IGRT for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;84:125–9.
Raaymakers BW, Jurgenliemk-Schulz IM, Bol GH, Glitzner M, Kotte A, van Asselen B, et al. First patients treated with a 1.5 T MRI-Linac: clinical proof of concept of a high-precision, high-field MRI guided radiotherapy treatment. Phys Med Biol. 2017;62:L41–50.
Fischer-Valuck BW, Henke L, Green O, Kashani R, Acharya S, Bradley JD, et al. Two-and-a-half-year clinical experience with the world’s first magnetic resonance image guided radiation therapy system. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2017;2:485–93.
Kerkmeijer LGW, Groen VH, Pos FJ, Haustermans K, Monninkhof EM, Smeenk RJ, et al. Focal boost to the intraprostatic tumor in external beam radiotherapy for patients with localized prostate cancer: results from the FLAME randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:787–96.
Widmark A, Gunnlaugsson A, Beckman L, Thellenberg-Karlsson C, Hoyer M, Lagerlund M, et al. Ultra-hypofractionated versus conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the HYPO-RT-PC randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394:385–95.
Draulans C, van der Heide UA, Haustermans K, Pos FJ, van der Voort van Zyp J, Boer De H, et al. Primary endpoint analysis of the multicentre phase II hypo-FLAME trial for intermediate and high risk prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2020;147:92–8.
Kishan AU, Lamb J, Casado M, Wang X, Ma TM, Low D, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided versus computed tomography-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer (MIRAGE): interim analysis of a phase III randomized trial. Meeting Abstract|2022 ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium. 2022.
Ma TM, Neylon J, Casado M, Sharma S, Sheng K, Low D, et al. Dosimetric impact of interfraction prostate and seminal vesicle volume changes and rotation: a post-hoc analysis of a phase III randomized trial of MRI-guided versus CT-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2022;167:203–10.
van Schie MA, van Houdt PJ, Ghobadi G, Pos FJ, Walraven I, de Boer HCJ, et al. Quantitative MRI changes during weekly ultra-hypofractionated prostate cancer radiotherapy with integrated boost. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the manuscript. CR and LGWK contributed to the conceptualization. CR, EJLB and LGWK contributed to writing and revision of the manuscript, have read and have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Reijnen, C., Brunenberg, E.J.L. & Kerkmeijer, L.G.W. Advancing the treatment of localized prostate cancer with MR-guided radiotherapy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 26, 50–52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00632-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00632-4
This article is cited by
-
Functional outcomes and safety of focal therapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review on results and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs)
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2023)