Abstract
Background
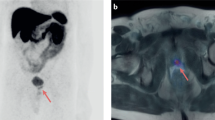
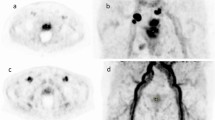
PSMA-PET is a novel imaging modality for the staging of prostate cancer (PCa). While there are several PSMA ligands available, F-18-PSMA-1007 is particularly of interest as it is not renally excreted and therefore does not impair the imaging of the pelvic area. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the F-18-PSMA-1007-PET for the primary staging of PCa and compared it to multi-parametric (mp) MRI and histopathology.
Methods
A retrospective study was performed of men with intermediate and high-risk PCa patients that underwent a F-18-PSMA-1007-PET after mpMRI with subsequent MR-guided target biopsy (MRGB). Suspicious mpMRI lesions and F-18-PSMA-1007-PET were simultaneously reviewed on both a per patient and per-lesion basis. Results were subsequently evaluated with histopathological outcome of MRGB, and if performed, the radical prostatectomy specimen.
Results
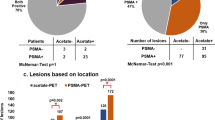
A total of 66 suspicious mpMRI lesions were identified in 53 patients and underwent MRGB. Two lesions had a maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) less than the mean SUVmax of healthy prostate tissue and were considered as non-PSMA-expressing. All PSMA avid tumors had higher SUVmax than the mean SUVmean of the bladder/urine, therefore all lesions were clearly distinguishable in the pelvic area. Twenty-three patients received a radical prostatectomy of which the histopathology specimens were evaluated. F-18-PSMA-1007-PET/CT correctly staged seminal vesicle invasion (i.e. pT3b) more often than mpMRI (90 vs. 76%), whereas mpMRI more accurately detected extracapsular extension (i.e. pT3a) compared to F-18-PSMA-1007-PET (90% vs 57%).
Conclusions
The present study of a selected cohort suggest that dual imaging with mpMRI and F-18-PSMA-1007-PET may improve staging of primary PCa. F-18-PSMA-1007-PET/CT had low renal clearance, which could assist the evaluation of tumors in proximity of the bladder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2017;71:618–29.
Mottet N, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Bourke L, Cornford P, De Santis M, et al. EAU– ESTRO–ESUR–SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer 2020. European Association of Urology Guidelines 2020 Edition. Arnhem: European Association of Urology Guidelines Office; 2020.
van der Leest M, Cornel E, Israel B, Hendriks R, Padhani AR, Hoogenboom M, et al. Head-to-head comparison of transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy versus multiparametric prostate resonance imaging with subsequent magnetic resonance-guided biopsy in biopsy-naive men with elevated prostate-specific antigen: a large prospective multicenter clinical study. Eur Urol. 2019;75:570–8.
Drost FH, Osses DF, Nieboer D, Steyerberg EW, Bangma CH, Roobol MJ, et al. Prostate MRI, with or without MRI-targeted biopsy, and systematic biopsy for detecting prostate cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;4:CD012663.
Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Haider MA, Macura KJ, et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging—reporting and data system: 2015, Version 2. Eur Urol. 2016;69:16–40.
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Huisman HJ, van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, et al. Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficients at 3.0-T MR imaging and Gleason grade in peripheral zone prostate cancer. Radiology. 2011;259:453–61.
de Rooij M, Hamoen EH, Witjes JA, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2016;70:233–45.
Ghosh A, Heston WD. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2004;91:528–39.
Fendler WP, Calais J, Eiber M, Flavell RR, Mishoe A, Feng FY, et al. Assessment of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET accuracy in localizing recurrent prostate cancer: a prospective single-arm clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:856–63.
van Kalmthout LWM, van Melick HHE, Lavalaye J, Meijer RP, Kooistra A, de Klerk JMH, et al. Prospective validation of gallium-68 prostate specific membrane antigen-positron emission tomography/computerized tomography for primary staging of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2020;203:537–45.
Eiber M, Weirich G, Holzapfel K, Souvatzoglou M, Haller B, Rauscher I, et al. Simultaneous (68)Ga-PSMA HBED-CC PET/MRI Improves the Localization of Primary Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;70:829–36.
Djavan B, Moul JW, Zlotta A, Remzi M, Ravery V. PSA progression following radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy: new standards in the new Millennium. Eur Urol. 2003;43:12–27.
Donato P, Roberts MJ, Morton A, Kyle S, Coughlin G, Esler R, et al. Improved specificity with (68)Ga PSMA PET/CT to detect clinically significant lesions “invisible” on multiparametric MRI of the prostate: a single institution comparative analysis with radical prostatectomy histology. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:20–30.
Koerber SA, Utzinger MT, Kratochwil C, Kesch C, Haefner MF, Katayama S, et al. (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in newly diagnosed carcinoma of the prostate: correlation of intraprostatic PSMA uptake with several clinical parameters. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1943–8.
Grubmuller B, Baltzer P, Hartenbach S, D’Andrea D, Helbich TH, Haug AR, et al. PSMA Ligand PET/MRI for primary prostate cancer: staging performance and clinical impact. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:6300–7.
Maurer T, Eiber M, Schwaiger M, Gschwend JE. Current use of PSMA-PET in prostate cancer management. Nat Rev Urol. 2016;13:226–35.
Freitag MT, Kesch C, Cardinale J, Flechsig P, Floca R, Eiber M, et al. Simultaneous whole-body (18)F-PSMA-1007-PET/MRI with integrated high-resolution multiparametric imaging of the prostatic fossa for comprehensive oncological staging of patients with prostate cancer: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:340–7.
Kuten J, Fahoum I, Savin Z, Shamni O, Gitstein G, Hershkovitz D, et al. Head- to head comparison of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 with (18)F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT in staging prostate cancer using histopathology and immunohistochemical analysis as reference-standard. J Nucl Med. 2020; 61:527–32.
Kesch C, Vinsensia M, Radtke JP, Schlemmer HP, Heller M, Ellert E, et al. Intraindividual comparison of (18)F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT, multiparametric MRI, and radical prostatectomy specimens in patients with primary prostate cancer: a retrospective, proof-of-concept study. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1805–10.
D’Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Blank K, Broderick GA, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA. 1998;280:969–74.
Cardinale J, Schafer M, Benesova M, Bauder-Wust U, Leotta K, Eder M, et al. Preclinical evaluation of (18)F-PSMA-1007, a new prostate-specific membrane antigen ligand for prostate cancer imaging. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:425–31.
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B, Srigley JR, Humphrey PA, et al. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: definition of grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:244–52.
Giesel FL, Will L, Lawal I, Lengana T, Kratochwil C, Vorster M, et al. Intraindividual comparison of (18)F-PSMA-1007 and (18)F-DCFPyL PET/CT in the prospective evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed prostate carcinoma: a pilot study. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1076–80.
Ferreira G, Iravani A, Hofman MS, Hicks RJ. Intra-individual comparison of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 and (18)F-DCFPyL normal-organ biodistribution. Cancer Imaging. 2019;19:23.
Piron S, De Man K, Van Laeken N, D’Asseler Y, Bacher K, Kersemans K, et al. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution of (18)F-PSMA-11 for PET imaging of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:1736–42.
Martini A, Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Scuderi S, Bravi CA, Mazzone E, et al. Defining clinically meaningful positive surgical margins in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for localised prostate cancer. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019;S2588-9311:30039–2.
Hicks RM, Simko JP, Westphalen AC, Nguyen HG, Greene KL, Zhang L, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI compared with multiparametric MRI in the detection of prostate cancer. Radiology. 2018;289:730–7.
Turkbey B, Mena E, Lindenberg L, Adler S, Bednarova S, Berman R, et al. 18F-DCFBC prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted PET/CT imaging in localized prostate cancer: correlation with multiparametric MRI and histopathology. Clin Nucl Med. 2017;42:735–40.
Rowe SP, Gage KL, Faraj SF, Macura KJ, Cornish TC, Gonzalez-Roibon N, et al. 18F-DCFBC PET/CT for PSMA-based detection and characterization of primary prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1003–10.
Zamboglou C, Drendel V, Jilg CA, Rischke HC, Beck TI, Schultze-Seemann W, et al. Comparison of (68)Ga-HBED-CC PSMA-PET/CT and multiparametric MRI for gross tumour volume detection in patients with primary prostate cancer based on slice by slice comparison with histopathology. Theranostics. 2017;7:228–37.
Chen M, Zhang Q, Zhang C, Zhao X, Marra G, Gao J, et al. Combination of (68)Ga-PSMA PET/CT and multiparametric MRI improves the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer: a lesion-by-lesion analysis. J Nucl Med. 2019;60:944–9.
Giesel FL, Sterzing F, Schlemmer HP, Holland-Letz T, Mier W, Rius M, et al. Intra-individual comparison of (68)Ga-PSMA-11-PET/CT and multi-parametric MR for imaging of primary prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol imaging. 2016;43:1400–6.
von Klot CJ, Merseburger AS, Boker A, Schmuck S, Ross TL, Bengel FM. et al. (68)Ga-PSMA PET/CT imaging predicting intraprostatic tumor extent, extracapsular extension and seminal vesicle invasion prior to radical prostatectomy in patients with prostate cancer. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;51:314–22.
Silver DA, Pellicer I, Fair WR, Heston WD, Cordon-Cardo C. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:81–5.
Muehlematter UJ, Burger IA, Becker AS, Schawkat K, Hotker AM, Reiner CS, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric MRI versus (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI for extracapsular extension and seminal vesicle invasion in patients with prostate cancer. Radiology. 2019;293:350–8.
Briganti A, Larcher A, Abdollah F, Capitanio U, Gallina A, Suardi N, et al. Updated nomogram predicting lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer undergoing extended pelvic lymph node dissection: the essential importance of percentage of positive cores. Eur Urol. 2012;61:480–7.
Briganti A, Passoni N, Ferrari M, Capitanio U, Suardi N, Gallina A, et al. When to perform bone scan in patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer: external validation of the currently available guidelines and proposal of a novel risk stratification tool. Eur Urol. 2010;57:551–8.
Rauscher I, Kronke M, Konig M, Gafita A, Maurer T, Horn T, et al. Matched-pair comparison of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT and (18)F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT: frequency of pitfalls and detection efficacy in biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Nucl Med. 2020;61:51–7.
Amin A, Blazevski A, Thompson J, Scheltema MJ, Hofman MS, Murphy D, et al. Protocol for the PRIMARY clinical trial, a prospective, multicentre, cross-sectional study of the additive diagnostic value of gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen positron-emission tomography/computed tomography to multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnostic setting for men being investigated for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2020;125:515–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study received ethical approval from the Institutional Review Board (CMO 2016-3045; project: 19069).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Privé, B.M., Israël, B., Schilham, M.G.M. et al. Evaluating F-18-PSMA-1007-PET in primary prostate cancer and comparing it to multi-parametric MRI and histopathology. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 24, 423–430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-020-00292-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-020-00292-2
This article is cited by
-
Expanding the role of PSMA PET in active surveillance
BMC Urology (2023)
-
Evaluating the value of 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT in the detection and identification of prostate cancer using histopathology as the standard
Cancer Imaging (2023)
-
PET/CT imaging 2 h after injection of [18F]PSMA-1007 can lead to higher staging of prostate cancer than imaging after 1 h
European Journal of Hybrid Imaging (2023)
-
Status of 18F-PSMA-1007-PET/CT compared with multiparametric MRI in preoperative evaluation of prostate cancer
World Journal of Urology (2023)
-
Head-to-head comparison of prostate-specific membrane antigen PET and multiparametric MRI in the diagnosis of pretreatment patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis
European Radiology (2023)